HGF Assay Portfolio Service
Introduction What We Can Offer Workflow Why Creative Biolabs Customer Reviews FAQs Related Services Contact Us
Creative Biolabs' HGF assay portfolio service provides comprehensive solutions for understanding the intricate roles of HGF and its receptor c-Met in various biological and pathological processes. Creative Biolabs delivers precise quantification of HGF levels, detailed analysis of its biological activity, and in-depth insights into HGF/c-Met signaling pathways. Our service is designed to support your research from target identification and validation to preclinical drug development, ensuring you receive the actionable data needed to drive your projects forward.
The Biology of HGF
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is known as a paracrine cellular growth and motility, and morphogenic factor. It is secreted by mesenchymal cells and acts as a multi-functional cytokine on cells of mainly epithelial origin after binding to the protooncogenic c-MET receptor. HGF is secreted as a precursor polypeptide bound to heparin proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix. The HGF/c-Met signaling axis is a fundamental biological pathway critical for organ development, tissue regeneration, and cellular responses, including proliferation, motility, and angiogenesis. Its dysregulation is implicated in various pathologies, notably cancer, fibrosis, and inflammatory diseases.
Discover how we can help - Request a consultation.
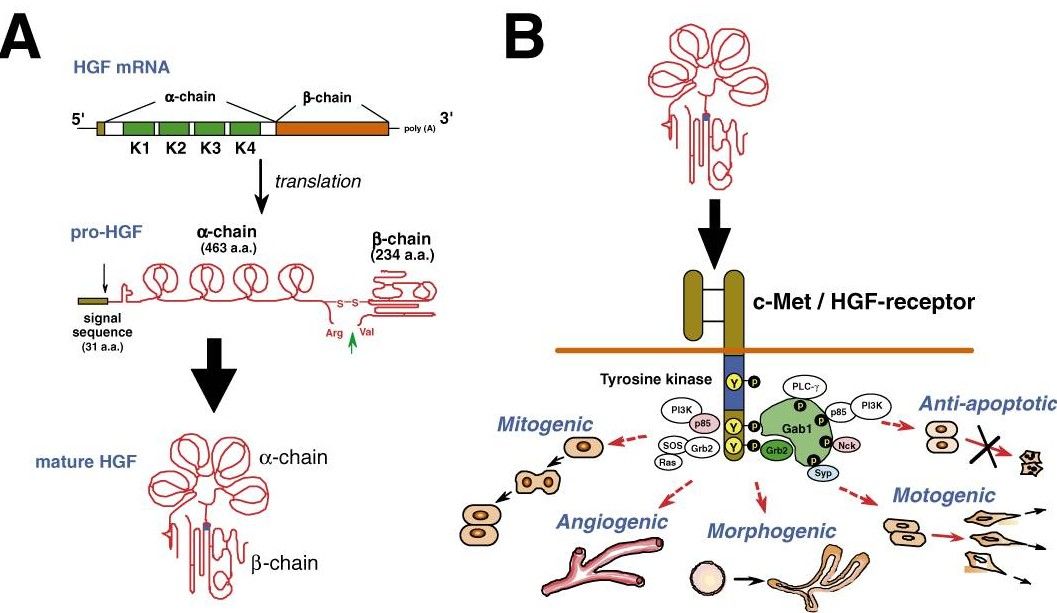 Fig.1 Structure and biological function of HGF.1
Fig.1 Structure and biological function of HGF.1
What We Can Offer
|
Quantitative and Functional Analysis
|
Advanced Immunological and Cell Biology Techniques
|
-
Angiogenesis Assays
-
Cell Adhesion Assays
-
Cell Apoptosis Assays
-
EMT Assays
|
-
Flow cytometry
-
Immunoblotting
-
ICC, IF, and IHC
|
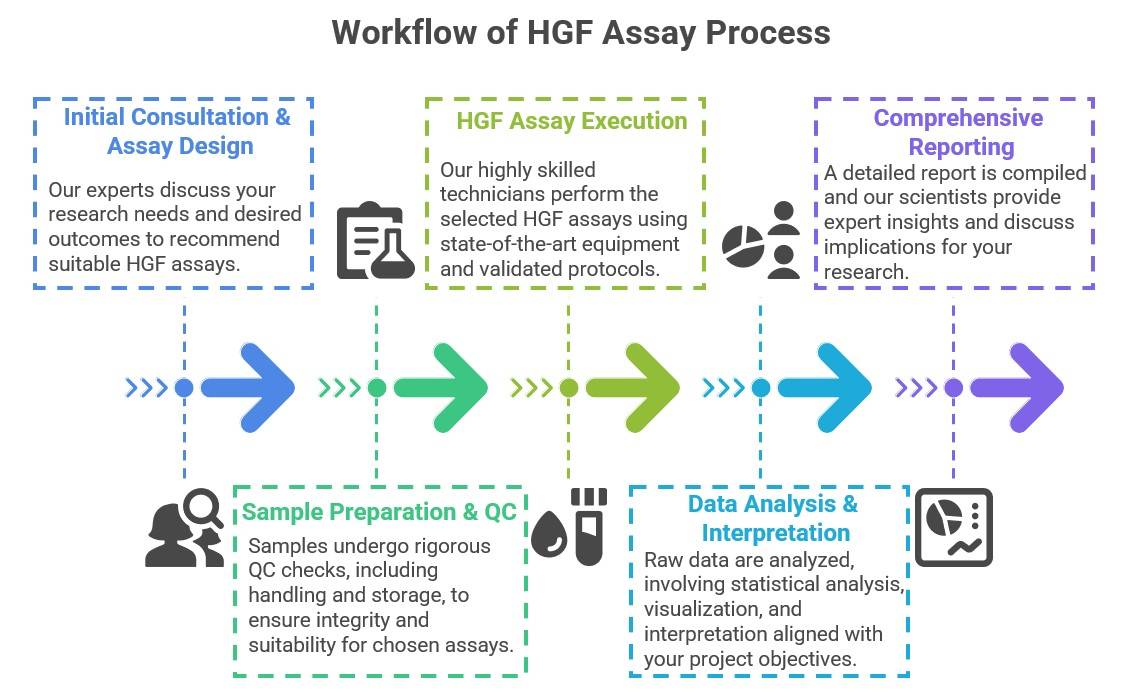
Workflow of HGF Assay Portfolio Service
Highlights
Unrivaled Expertise & Reliability
Creative Biolabs provides unparalleled scientific knowledge and understanding of its complex molecular challenges, ensuring the highest accuracy and reliability.
Accelerated Discovery & Cost Efficiency
Our clients experience an average 25% increase in HGF signaling pathway elucidation efficiency and a 30% reduction in assay development costs, avoiding significant investments in equipment, reagents, and specialized personnel.
Proven Success & High-Quality Data
Our methodologies and results have consistently contributed to numerous scientific publications, demonstrating the reliability and impact of our HGF assay services across diverse research areas.
Client-Centric Collaboration & Support
We offer expert consultation from assay design to data interpretation. Our flexible service model can be customized to your exact specifications, providing tailored solutions for high-throughput screening or in-depth mechanistic studies.
Experience the Creative Biolabs advantage - Get a quote today.
Customer Reviews
-
Unparalleled Precision
Creative Biolabs' service improved the precision of our HGF quantification, allowing us to confidently advance our therapeutic lead selection and reduce follow-up experiments. This enhanced accuracy saved time and resources, providing critical confidence for decision-making. - J. Do***.
-
Comprehensive Support
The comprehensive data analysis and expert consultation for our HGF binding studies were invaluable. Their team's nuanced insights into binding kinetics helped us characterize therapeutic antibodies and select candidates with optimal profiles, elevating the quality of our research. - A. K***mar.
FAQs
Is Creative Biolabs capable of developing custom HGF assays tailored to unique research questions?
Absolutely! Our core strength lies in our flexibility and scientific prowess in custom assay development. Our team of expert scientists excels at designing, optimizing, and validating bespoke HGF assays to precisely meet your unique research questions, specific sample types, or high-throughput screening requirements.
What are the distinct advantages of utilizing Creative Biolabs' HGF assay portfolio service compared to conducting assays in-house?
Partnering with Creative Biolabs offers significant advantages over in-house assays. Our optimized workflows accelerate project timelines and free up your internal resources. You also get access to state-of-the-art equipment and methodologies without the substantial investment. Our stringent quality control and validated protocols ensure the high-quality, reproducible data needed for publications.
Related Services
Cell Line Development
For researchers requiring specialized cellular models, our custom cell line development service creates stable cell lines expressing c-Met, HGF, or other HGF pathway components.
Learn More →
ADEPT Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis Service
Integrate HGF assay measurements into comprehensive PK/PD studies for your therapeutic candidates.
Learn More →
How to Contact Us
Creative Biolabs' HGF assay portfolio service offers an unparalleled combination of scientific expertise, advanced technology, and comprehensive solutions to accelerate your research and drug discovery efforts related to HGF. From precise quantification to in-depth functional and mechanistic studies, we are your trusted partner in unlocking the full potential of HGF pathways.
Contact us for more information and to discuss your project.
Reference
-
Nakamura, Toshikazu, and Shinya Mizuno. "The discovery of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell biology, life sciences and clinical medicine." Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B 86.6 (2010): 588-610. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.86.588
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Structure and biological function of HGF.1
Fig.1 Structure and biological function of HGF.1


