- Cancer
Monoclonal antibodies against cancer therapy are now on the market to treat cancer by recognizing cancer-related antigens. However, it is difficult for monoclonal antibodies with large molecular size to penetrate the tumor and bind to the target. At the same time, the high cost caused by the complex structure makes it difficult to guarantee the accessibility of antibody drugs. Compared with monoclonal antibodies, single-domain antibodies can penetrate uniformly in tumor tissues. The absence of the Fc domain improves the safety and the effectiveness of single-domain antibodies as a pure immunomodulatory molecule.
In cancer therapy, single-domain antibodies can act as antagonists to prevent ligand binding, thus changing the conformation and leading to the activation of signal cascades. At the same time, single-domain antibodies can also be used as allosteric inhibitors to regulate the enzyme activity of their target proteins.

Fig 1. Cancer treatment strategy based on single-domain antibody
At present, a number of pharmaceutical companies have developed targeted anti-tumor single-domain antibodies against EGFR, HER2, VEGFR2, c-Met, CXCR7, and so on. ALX-0651, which targets two epitopes of chemokine CXCR4, developed by Ablynx, is the first clinical single-domain antibody against GPCR. The clinical trial has been discontinued because it did not show better efficacy than standard treatments. BI-836880, developed by Boehringer Ingelheim as a single-domain antibody to block VEGF/Ang-2, is currently under phase II clinical trial for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic tubular squamous cell carcinoma.
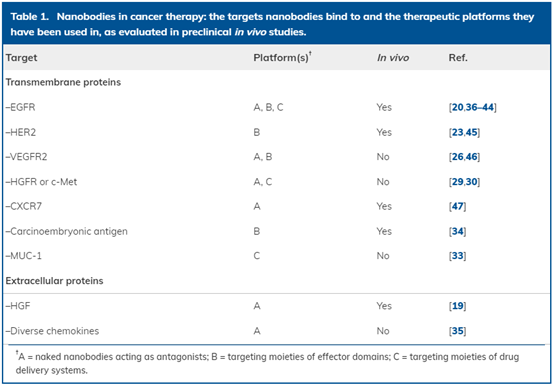
Table 1. Application of single-domain antibody in cancer treatment
- Blood Disease
Caplacizumab is a bivalent humanized single-domain antibody against the GPIb-IX-V binding site of the von Willebrand factor (vWF) A1 domain developed by Ablynx. By binding to vWF protein, it can prevent super-large vMF protein from binding to platelets, thus preventing clotting. It was first marketed in Germany in 2018 for the treatment of adult acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP). In the United States, the product was approved for the same indication in 2019. In 2020, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) adopted a positive opinion and recommended the product for adolescents with aTTP. The drug has been designated to treat orphans with aTTP in the United States, the European Union, and Japan, respectively.
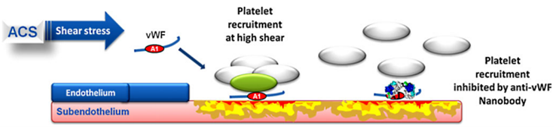
Fig 2. The mechanism of Caplacizumab
- Infection
Single-domain antibodies can be intervened at different stages of the virus replication cycle. For example, preventing virus attachment, just as single-domain antibodies against influenza virus and hepatitis C virus (HCV), can prevent virus shelling and virus uptake. Intracellular expressed single-domain antibodies (endosomes) or cell-penetrating single-domain antibodies (transplants) can help to interfere with viral nuclear translocation, such as endosomes targeting influenza virus nucleoprotein or HIV polymeric protein Rev, and transplants against HCV NS3/4A. The bivalent single-domain antibody expressed by modified lactic acid bacteria can prevent norovirus escape mutations. In addition, single-domain antibodies against rotavirus have also been developed. ALX-0171, an anti-RSV single-domain antibody, has been used in phase II clinical trials to treat respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in adult patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and RSV infection in infants, but the study stopped in 2018. XVR-011 is an anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody (VHH-Fc) developed by ExeVir for the treatment and prevention of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, and the treatment is currently being evaluated in phase I/II clinical trials.
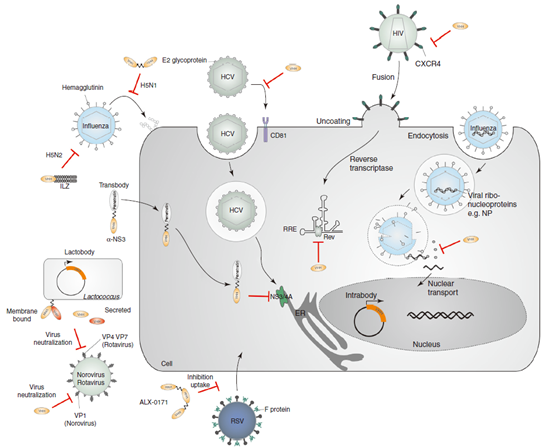
Fig 3. Application of single-domain antibody in anti-virus infection
The inhibition of single-domain antibodies on bacterial surface proteins can interfere with bacterial adhesion to host cells, such as preventive anti-F4 single-domain antibodies to enterotoxin-producing or Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli. The single-domain antibody was transplanted into porcine IgA Fc and expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana, which can be used for passive immunization of piglets with oral feed. Anti-adhesion single-domain antibody against buccal Streptococcus mutans linked non-specific antibacterial agent glucose oxidase to prevent dental caries. Single-domain antibodies can change the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Acinetobacter baumannii by targeting important biofilm forming media. Single-domain antibody antagonizes the type VI secretory system and prevents Gram-negative bacteria from secreting toxins. Secreted effector molecules, such as enzymes essential for adaptation to the bacterial environment, can also be neutralized by single-domain antibodies.
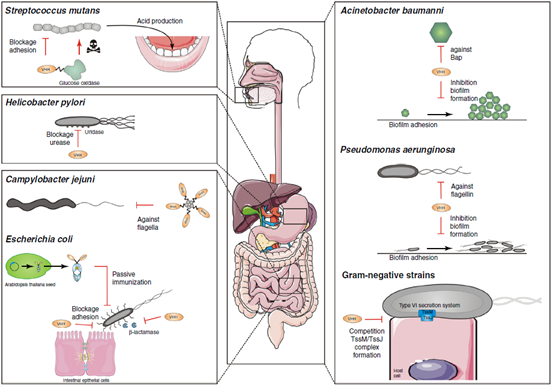
Fig 4. Application of single-domain antibody in anti-bacterial infection
In addition, single-domain antibodies have also been reported to be applied in anti-parasite infection and antidote.
Fig 5. Application of single-domain antibody in anti-parasite infection and antidote
- Autoimmune Disease
Systemic autoimmune disease is caused by the widespread deposition of the antigen-antibody complex in the blood vessel wall and other reasons. This is due to immune injury leading to cellulosic necrotizing inflammation of the vascular wall and stroma and subsequent proliferation of collagen fibers in multiple organs. Common autoimmune diseases include systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and so on.
Ozoralizumab is a humanized, trivalent bispecific anti-TNF- α single-domain antibody originally developed by Ablynx and is currently awaiting regulatory approval for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. Preclinical studies on the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease are underway, however, the latest progress of this study has not been reported. Pfizer has been evaluating the candidate for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn’s disease.
- Neurodegenerative Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. It is characterized by the accumulation and deposition of β-amyloid peptide plaques and the formation of nerve fiber tangles in the brain, leading to dementia and loss of cognitive function. Antibody plaques are formed by proteolysis of a large precursor protein, amyloid precursor protein (APP), by enzymes such as β site APP cleavage enzyme (BACE-1). Single-domain antibodies selective to different amyloid (precursor) peptides and antibodies that prevent the formation of mature antibody fibrils by stabilizing antibody fibrils have been produced. BI-1034020, a single-domain antibody against Alzheimer’s disease developed by Boehringer Ingelheim, has conducted a phase I clinical study to investigate the safety and tolerance of healthy male volunteers; however, the company decided to suspend the recruitment of participants.
Single-domain antibodies have also been reported in other neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease.
