Introduction to Antibody Epitope Binning
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are playing an increasingly important role in the biopharmaceutical market and human disease therapy, especially in the treatment of oncology and cancer. In the development and discovery of therapeutic mAbs, it is necessary to select the best candidate from a large number of leads, which is a critical step and determines the success of the project. Antibody epitope binning, or epitope binning assay, is a competitive immunoassay used to divide and characterize a group of mAbs into "bins" according to different antigen-binding domains (antigen epitopes).
Generally, the epitope of a mAb is related to its functional activity, so mAbs targeting similar epitopes usually have similar functions. In epitope binning assay, antibody leads specific to the same target are tested in a pairwise combinatorial manner by cross-competitive immunoassay. The two antibodies are considered to bind to similar or overlapping epitopes if the antigen binding of one antibody prevents the binding of another antibody. Conversely, if the binding of an antibody to an antigen does not interfere with the binding of another antibody, they are considered to bind to different, non-overlapping epitopes. After the characterization of each antibody lead, a competitive blocking profile will be obtained, and those antibodies with closely related binning profiles are grouped into "bins".
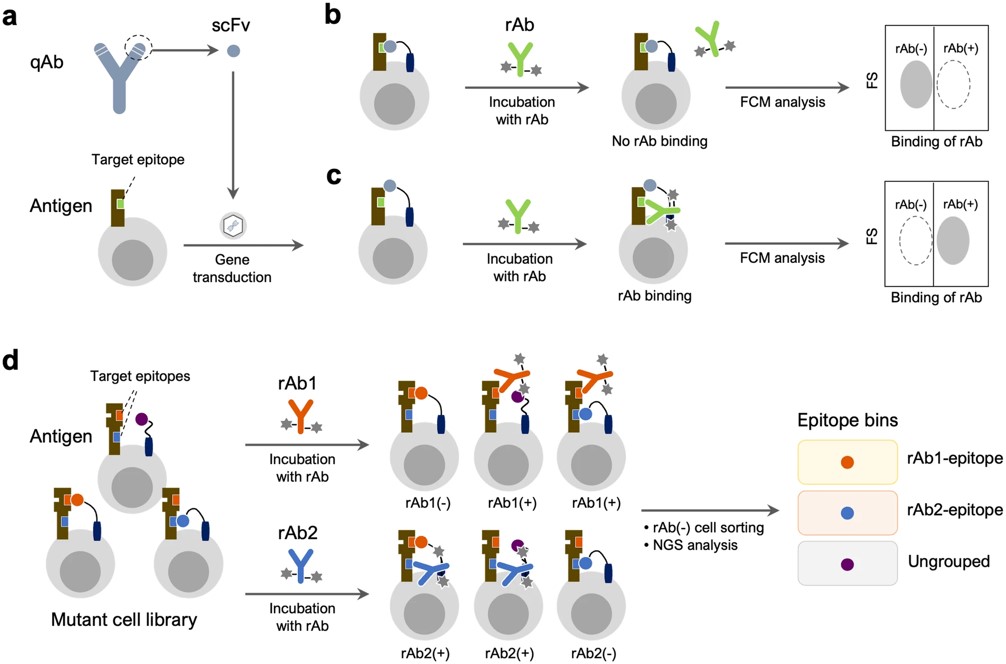 Fig.1 Overview of epitope similarity evaluation and epitope binning assay.1, 3
Fig.1 Overview of epitope similarity evaluation and epitope binning assay.1, 3
Native™ Antibody Discovery for Antibody Epitope Binning
Single B cell antibody technology is a novel technology for the rapid preparation of monoclonal antibodies. After being challenged by an antigen, each B cell of the host expressed only one specific antibody. The single antigen-specific antibody-secreting B cell can be isolated from tissues or peripheral blood of immunized individuals. Antigen-specific antibody heavy chain and light chain genes are sequenced and amplified by single-cell polymerase chain reaction (PCR). And the target mAb with biological activity can be obtained by expressing in different expression systems. Compared with other techniques, mAb produced by single B cell antibody technology retains the natural pairing of heavy chain and light chain variable regions and has advantages of matured affinity high efficiency, and all-natural origin. It has become an important strategy for the rapid development and discovery of Native™ antibodies.
The mAbs prepared by single human B cell sorting technology are usually obtained by immunization with homogeneous or identical antigens, thus these antibodies are natively paired human antibody repertoires sharing similar targeting and functions. Therapeutic mAbs developed from single B cell sorting can be directly screened by epitope binning assays to characterize their binding and targeting properties. And epitope binning also provides information for the discovery of therapeutic mAbs, enabling the rapid identification of leads or candidates with unique functional epitopes.
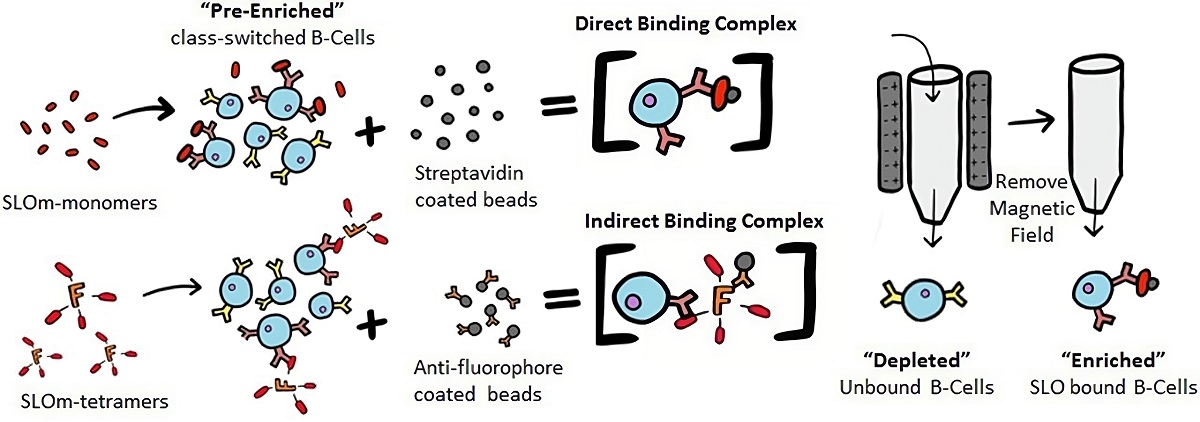 Fig.2 The direct and indirect methods of antigen-dependent single B lymphocyte isolation.2, 3
Fig.2 The direct and indirect methods of antigen-dependent single B lymphocyte isolation.2, 3
Let’s Work Together to Fulfil Your Rapid Antibody Development
Considering the need for rapid antibody discovery, Creative Biolabs has proudly pushed out comprehensive Native™ antibody discovery services to accelerate the development of therapeutic mAbs. More importantly, our featured Native™ antibody discovery services by single B cell technology can be combined with our monoclonal antibody epitope binning platforms, enabling global clients to rapidly find the most optimal antibody candidate. Please don’t hesitate to contact us.
References
-
Lin, Ning, et al. "Epitope binning for multiple antibodies simultaneously using mammalian cell display and DNA sequencing." Communications Biology 7.1 (2024): 652.
-
Lamb, Cheri L., et al. "Enrichment of Antigen-Specific Class-Switched B Cells from Individuals Naturally Immunized by Infection with Group A Streptococcus." Msphere 4.6 (2019): 10-1128.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Related Sections:
ONLINE INQUIRY

 Fig.1 Overview of epitope similarity evaluation and epitope binning assay.1, 3
Fig.1 Overview of epitope similarity evaluation and epitope binning assay.1, 3
 Fig.2 The direct and indirect methods of antigen-dependent single B lymphocyte isolation.2, 3
Fig.2 The direct and indirect methods of antigen-dependent single B lymphocyte isolation.2, 3

