The Critical Role of qPCR in iPSC Characterization
qPCR is a powerful and sensitive technique for measuring gene expression levels. It has become an indispensable tool for iPSC research due to its accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness. The principles of qPCR are relatively simple: the technique amplifies a specific DNA target and measures the amount of amplified product in real-time. This allows for the precise quantification of the amount of target DNA present in the original sample.
Ensuring the quality of iPSC lines is paramount for the success of any downstream application. qPCR plays a critical role in several key aspects of iPSC characterization:
- Confirmation of Pluripotency: qPCR is used to measure the expression of key pluripotency markers, such as OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG. High expression of these markers is a strong indicator of a pluripotent state.
- Monitoring of Differentiation: qPCR can be used to measure the expression of lineage-specific markers, providing a quantitative measure of differentiation efficiency. For example, when differentiating iPSCs into cardiomyocytes, we can monitor the expression of cardiac-specific markers such as TNNT2 and NKX2-5.
- Silencing of Reprogramming Transgenes: It is crucial to ensure that these transgenes are silenced after reprogramming is complete, as their continued expression can lead to tumorigenicity and other undesirable effects. qPCR is a sensitive method for detecting the expression of these transgenes, providing an important safety check for your iPSC lines.
- Quality Control and Safety: qPCR can also be used for a variety of other quality control and safety assays, such as detecting mycoplasma contamination and assessing the genomic integrity of your iPSC lines.
At Creative Biolabs, we have a state-of-the-art qPCR platform and a team of experienced scientists who can help you with all your gene expression analysis needs. We offer a comprehensive suite of qPCR services.
What We Measure
Creative Biolabs offers a multi-faceted suite of qPCR services. You can select individual assays or combine them into a comprehensive characterization package tailored to your specific research goals.
We curate markers to match your objectives. Below are typical panels, we tailor content to species, donor background, and protocol.
| Categories | Typical Panels |
|---|---|
| Pluripotency Core & Supportive Markers |
|
| Reprogramming Residuals & Safety Signals |
|
| Tri-Lineage Differentiation Readiness |
|
| Lineage-Specific Differentiation |
|
Our Workflow
At Creative Biolabs, we believe that reliable data comes from a meticulously controlled process. Our qPCR service is built on a foundation of quality assurance and technical excellence.
- Project Scoping & Experimental Design - We define your decision questions, confirm species/strain, reprogramming method, and intended panels. Power and replicate guidance included.
- Primer/Probe Design - Amplicons span exon–exon junctions where applicable, avoid SNPs, and are screened against off-targets. For vector residuals, we target unique backbone or SeV regions.
- RNA Extraction & DNase Treatment - Using SOP-controlled kits and instruments. RNA integrity is assessed.
- Reverse Transcription - Random hexamers/oligo(dT) mixed strategy by default; spike-ins optional. We include No-RT controls for genomic DNA exclusion checks.
- qPCR Runs - 96- or 384-well plates with inter-plate calibrators when needed. We include NTCs on every plate and run proper negative biological controls.
- Data Processing & Normalization - Baseline correction, automatic/manual Ct review, outlier handling rules, efficiency correction if required, and normalization to validated reference genes.
Technical Specifications and Sample Submission
We make the process straightforward and transparent, ensuring the highest quality starting material for your analysis.
Accepted Sample Types:
- Live cell cultures
- Cryopreserved cell vials
- Cell pellets (snap-frozen, shipped on dry ice)
- Purified total RNA (in an RNase-free buffer, shipped on dry ice)
- Pre-synthesized cDNA
Recommended Sample Amount:
- Cell Pellets: A minimum of 500,000 cells is recommended for standard analysis; 1-2 million cells is ideal.
- RNA: A minimum of 500 ng of total RNA with a RIN value ≥ 8.0.
- Shipping and Handling: Our project managers will provide detailed, step-by-step instructions for sample preparation and shipping to ensure your samples arrive in our facility with maximum integrity.
Published Data
In this study, the researchers determined whether the KI-1 and KI-2 gene-corrected cell lines remained pluripotent after gene targeting. Their qPCR results showed that gene-corrected cell lines expressed the pluripotent marker genes OCT4, SOX2, and LIN28 at levels similar to those of the parental hemophilia A patient-derived iPSC line. They also confirmed uniform expression of OCT4 and SSEA4 in iPSC colonies by immunocytochemistry analysis. In vitro three germ layer formation assays showed that these lines could be differentiated into three germ layers.
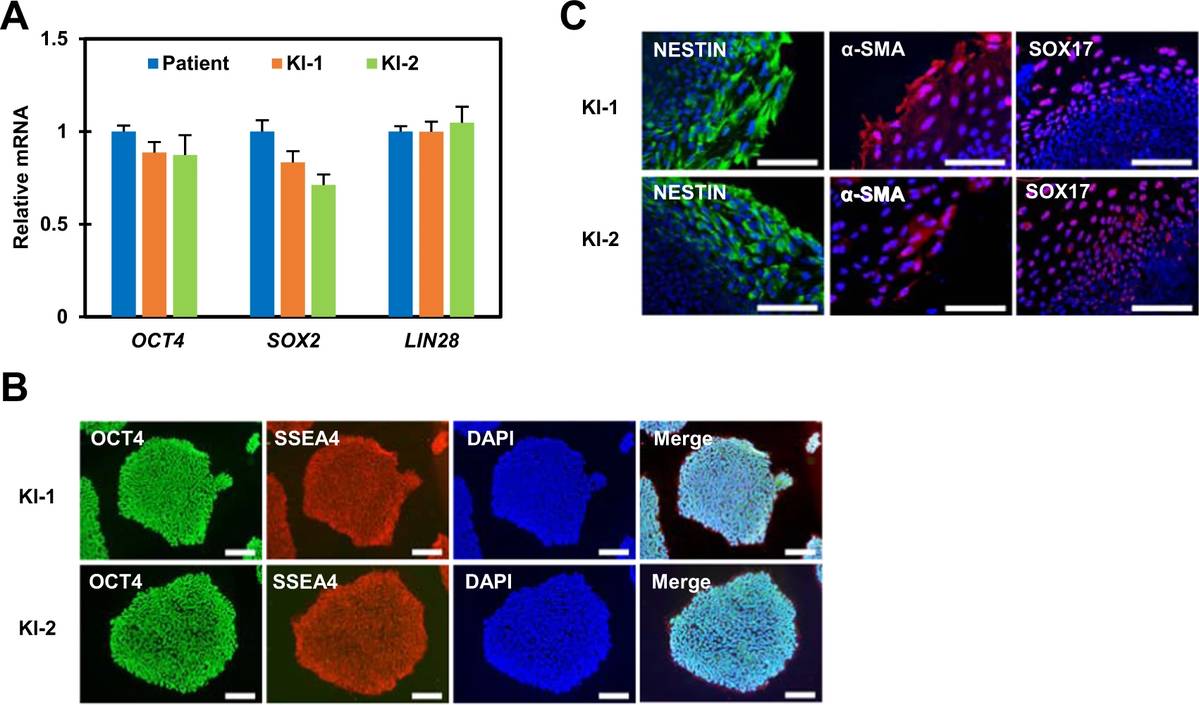 Fig. 1 Pluripotency analysis of gene-corrected iPSC lines.1,3
Fig. 1 Pluripotency analysis of gene-corrected iPSC lines.1,3
After reprogramming HFDK into iPSC, the researcher analyzed the resulting iPSC colonies for phenotypic characteristics by examining pluripotency and stem cell transcription markers. The qPCR analysis comparing the fold change in pluripotency gene expression of iPSC to the HFDK was conducted. The result showed that iPSC have upregulated SOX2, NANOG, POU5F1, DNMT3B, TERT, UTF1, DPPA5, IDO1, and KLF17 after reprogramming indicating the pluripotency characteristics of the cells, confirming the success of the reprogramming of HFDK to iPSC.
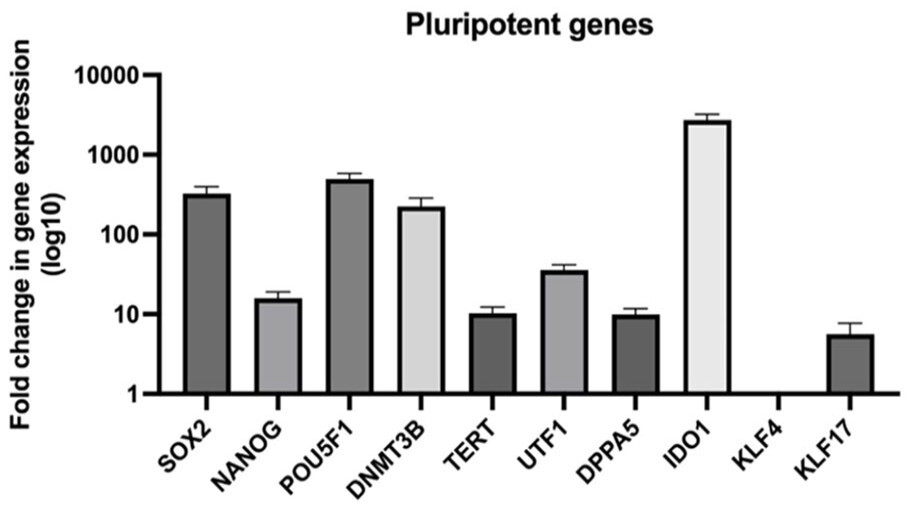 Fig. 2 qPCR analysis of pluripotency gene expression in iPSC relative to HFDK.2,3
Fig. 2 qPCR analysis of pluripotency gene expression in iPSC relative to HFDK.2,3
What Our Clients Say
"We sent Creative Biolabs a small batch of iPSC clones for basic pluripotency screening. The resulting report not only confirmed expression of OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG, but also highlighted subtle differences between clones that later correlated with differentiation efficiency. The inclusion of vector-residual testing and reference-gene validation saved us weeks of internal troubleshooting."
— Dr. Laura Peterson, Senior Scientist
"Our team needed a reliable partner to confirm Sendai clearance and pluripotency of patient-derived iPSCs before scale-up. Creative Biolabs designed a customized qPCR panel, handled RNA extraction, and returned clean, interpretable data within two weeks. The QC appendix and documentation were publication-ready."
— Dr. Michael Chen, Director of Stem Cell Core Facility
"We've now run three independent qPCR characterization projects with Creative Biolabs, each involving dozens of iPSC and differentiated samples. The reproducibility has been exceptional. A genuine long-term partner for stem cell analytics."
— Dr. Ethan Miller, Cell Therapy R&D Manager
FAQs
Q: What's the minimum number of samples or replicates required for a reliable analysis?
A: We recommend a minimum of three biological replicates per condition or clone and triplicate technical wells for each target. However, if you are in an early discovery phase with limited material, we can design a reduced test plan and include technical variance estimates to maintain interpretability.
Q: Can you design species-specific panels?
A: Yes. Our bioinformatics team designs and validates primers specific to the genome assembly of your species of interest. We ensure no cross-amplification with pseudogenes or closely related orthologs.
Q: Can qPCR replace flow cytometry or immunostaining for pluripotency confirmation?
A: qPCR provides quantitative transcript-level confirmation, while flow cytometry and ICC validate protein-level expression and cell-population uniformity. We recommend combining both methods for complete characterization. Creative Biolabs can coordinate these assays under the same project to generate fully correlated data sets.
Q: Can Creative Biolabs combine qPCR data with other omics analyses?
A: Yes. We can integrate qPCR results with RNA-Seq, individual cell sequencing, or proteomic datasets to validate expression patterns. This integrative approach provides deeper biological insight and supports cross-platform correlation for publication or product development.
Q: How can I start a new project with Creative Biolabs?
A: Simply send a brief inquiry through our contact form or email our stem cell service team with:
- Your project objective (e.g., clone validation, differentiation confirmation)
- Sample type and number
- Any preferred gene list or assay format
We'll respond within 24 hours with a tailored panel design, timeline, and quotation.
Propel Your Research with Data You Can Trust














1. Contact Us
via the Inquiry Form or Email
2. Define Your Needs
Cell Type, Function, Quantity, Modifications
3. Kickstart the Project
Our Expert Team Guiding Every Step
Let Creative Biolabs provide the quantitative certainty you need. Our expert-driven qPCR analysis services will equip you with the clear, actionable data required to validate your iPSCs and advance your project to the next stage.
Contact us today to speak with one of our iPSC characterization specialists. Let's discuss your project and design a qPCR analysis plan that provides the answers you need.
References
- Sung, Jin Jea, et al. "Restoration of FVIII expression by targeted gene insertion in the FVIII locus in hemophilia A patient-derived iPSCs." Experimental & molecular medicine 51.4 (2019): 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0243-1
- Matsuda, N., et al. "Raster plots machine learning to predict the seizure liability of drugs and to identify drugs." Scientific reports 12.1 (2022): 2281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05697-8
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Created October 2025

