Stem cells are non-specialized cells and they have the ability to become many different types of cells. Therefore, these cells play a key role in the body's healing process and the stem cell regenerative medicine which also as known as Stem Cell Therapy (SCT). Donor stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are known to permanently overcome various disorders at both preclinical and early clinical trials. Creative Biolabs have the ability to provide stem cell-based therapeutics development. Since stem cells are vital to the development, growth, maintenance, and repair of brains, bones, muscles, nerves, blood, skin, and other organs, we provided disease-specific stem cells therapy services, iPSC-derived cells therapy services. Also, to fit the rapid growth of stem cell therapy around the world, our scientists are using stem cells to develop customized disease modeling and to facilitated new drugs discovery for clients worldwide.
Stem cell therapy research and development focuses on harnessing the potential of stem cells to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries. Stem cells, characterized by their ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types, hold promise for regenerative medicine and personalized treatment. In the lab, researchers study how these cells can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues, regenerate organs, and develop new therapeutic strategies for conditions like neurodegenerative diseases, heart disease, diabetes, and even cancer.
Key areas of focus in stem cell therapy research include:
The development of stem cell therapies also involves overcoming challenges like ensuring the safety of stem cell use, preventing immune rejection, and scaling up production for widespread clinical use.
Generally, there are two categories of stem cells upon their sources. One is called early stem cells, also known as embryonic stem cells, which are derived from embryos at a developmental stage before the time of implantation which normally occurs in the uterus. These cells are self-replicating pluripotent cells that are potentially immortal. Another type of stem cells is mature stem cells. Unlike embryonic stem cells, these cells are undifferentiated totipotent or multipotent cells, which are found throughout the body after embryonic development, which multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues. For example, the sources of embryonic stem cells (ESC) are blastula and skin fibroblasts, these two types of cells can differentiation into cardiomyocytes. It treats cardiovascular disease via a direct contribution to contractility and remodeling of electrical properties. Also, the mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can be derived from bone marrow or fat cells. The mechanism of treatment is through paracrine effects, the endogenous stem cells activated. At Creative Biolabs, we provided disease-specific stem cells for various diseases.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell which has properties similar to embryonic stem cells. Forced expression of defined transcription factors, including Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc can manipulate somatic cells back to pluripotent state. iPSCs hold great promise in the field of regenerative medicine. They can not only propagate indefinitely, but also represent a single source of every other cell types in the body. Unlike embryonic stem cells, each individual could have their own iPSCs cell line, which means that the risk of immune rejection can be avoided. Also, without controversy surrounding their use and ethical issues, the iPSCs can be mass industrial product and legal commercial use. At Creative Biolabs, we provided iPSC derived immune cell therapy and iPSC derived stem cell therapy services. Please feel free to inquire to discuss your unique needs with us.
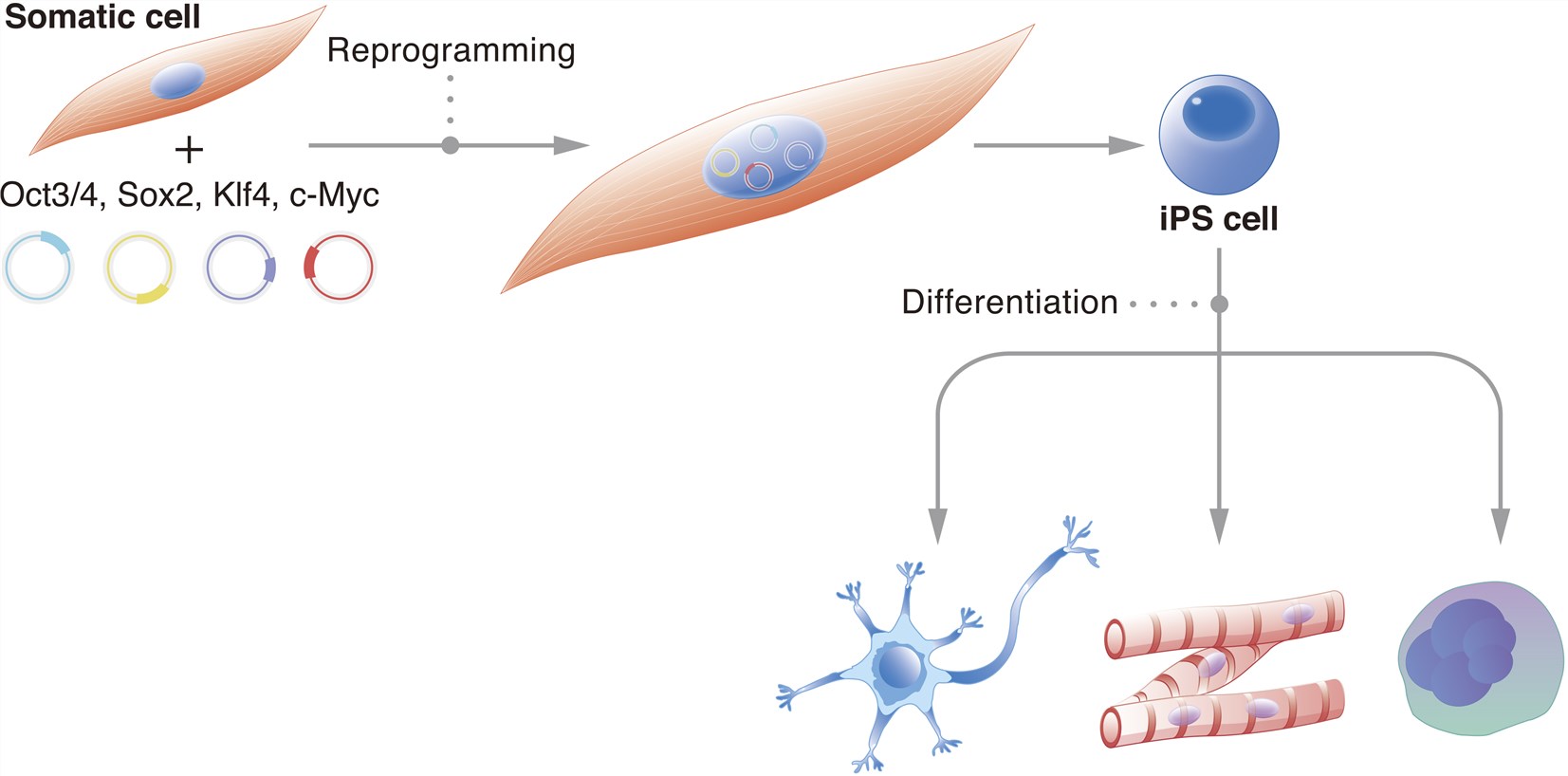 Fig.1 Exogenous TFs expression in somatic cells induces reprogramming.1
Fig.1 Exogenous TFs expression in somatic cells induces reprogramming.1
Based on gene variation, hereditary state, and even the telomere and telomerase status of individual patients, the stem cells technology provides a means to obtain the required research materials for disease modeling. For individual disease pathogenesis study, we provide stem cell-based disease modeling service which involves the nervous system, blood system, cardiovascular, diabetes, liver diseases, as well as various genetic diseases. To meet the need of drug screening, drug safety testing, and even the individualized treatment plan decision, our stem cell-based drug discovery services accommodate you with a customized solution.
Please feel free to contact us for more professional consultation.
We offer comprehensive and advanced services designed to accelerate your research and innovation in the field. Our R&D service features state-of-the-art technologies, specialized expertise, and customized solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of academic and pharmaceutical research teams. All our services are strictly for research use only, with the goal of driving scientific discovery and development in the area of regenerative medicine, disease modeling, and therapeutic interventions.
Key features of our service:
By choosing our stem cell therapy research and development services, you gain access to world-class expertise, innovative technologies, and custom-tailored solutions to advance your research in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine.
Reference
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.