Next-IO™ Anti-Ang2 Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibody Program
About This Program
This program aims to develop anti-Ang2 therapeutic monoclonal antibody for immuno-oncology.
Angiogenesis, a process for the formation of new blood vessels, is heavily regulated by chemical signals in the body. Hence, angiogenesis is believed to play a significant role in tumor growth. Major regulators for tumor angiogenesis are VEGF, angiopoietin (Ang) 1, and Ang2. Among them, Angiotensin II (Ang-2) and its receptor Tie-2 plays the most important regulatory role in the system and works as a therapeutic target for angiogenesis in malignant tumors.
ANG2
Ang-2 is part of the Ang / Tie signaling pathway. To put it simply, with the presence of VEGF, binding of Ang2 to Tie2 results in endothelial cell migration and proliferation and produces angiogenic signals. When in the absence of VEGF, binding of such can destabilize the cell-matrix and induce endothelial cell apoptosis or vasospasm.
Highlighted Functions:
-
Ang-2 / Tie-2 signaling pathway interferes the instability of resting EC and could induce angiogenesis in the existence of VEGF.
-
Upregulation Ang2 cause poor prognosis for patients with cancer.
-
Inhibition of Ang2 in a mouse mammary tumor model confirms its role of tumor growth inhibition and vasculature regression.
-
Increased Ang-2 levels are associated with abnormal tumor angiogenesis in several malignancies, including hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic colorectal cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, prostate cancer, and ovarian cancer.
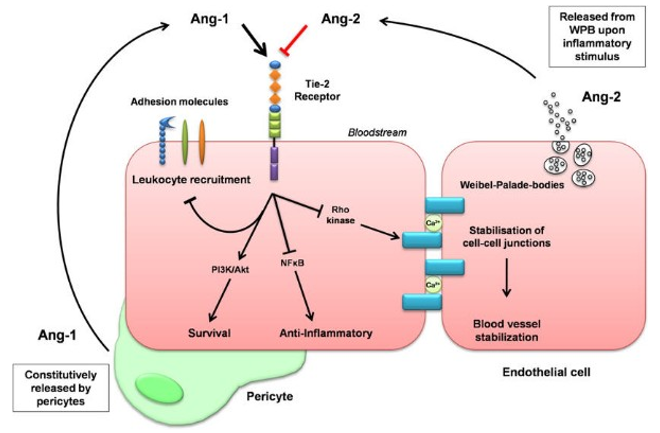 Fig.1 The Angiopoietin-Tie2 ligand-receptor system. (Van Meurs, 2009)
Fig.1 The Angiopoietin-Tie2 ligand-receptor system. (Van Meurs, 2009)
Ang2 in Cancer Studies
Multiple studies have shown that Ang2 antibody when using alone, show limited efficacy, however, it shows a robust efficacy when combining with other angiogenesis molecules. Here are some published data about Ang2 working as a potential target in cancer immunotherapy.
-
Anti-Ang-2-VEGF-A treatment reduces tumor growth in postsurgical metastases.
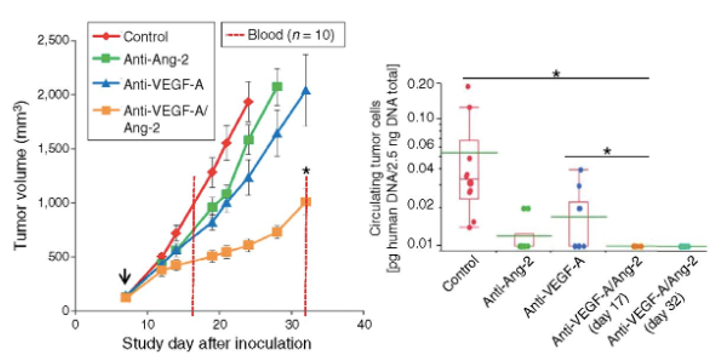
-
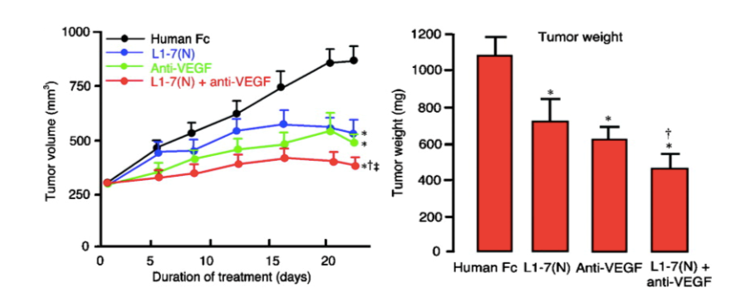
Inhibition of Ang2 by the peptide-Fc fusion protein L1-7(N) reduced the tumor growth by 62%.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
-
Currently, several anti-Ang2 monoclonal antibodies are evaluated in clinical trials. Cumulative clinical data has supported its role in cancer progression; however, safety, efficacy, and mechanism require further confirmation.
-
Despite this, Ang2 is still a compelling target to research in cancer immunotherapy. In an effort to optimally leverage Ang2-mediated immune response, our next generation Ang2 targeting treatment attempts to explore combination therapy by involving other immunomodulatory agents.
Program Planning and Management
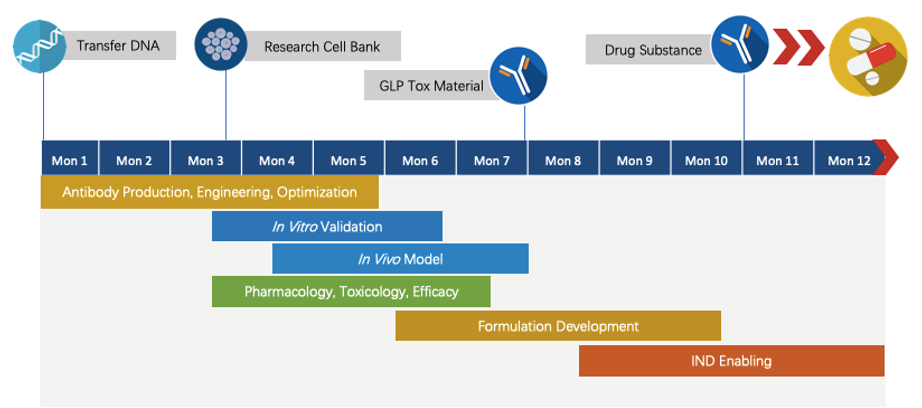
Creative Biolabs has extensive knowledge of end-to-end program development. For each program, we are committed to delivering the final complete program to our clients within 1.5 years before entering the IND stage.
Cooperation
Creative Biolabs is looking for potential partners (include but not limit to major pharma or biotech firms) to develop anti-ANG2 therapeutic monoclonal antibody program together. Our scientists are dedicated to bringing years of valuable experience to our partner and achieve a meaningful partnership together. We firmly believe that the power of collaboration will unleash the creative spirits from both parties and reach new heights in the field of immuno-oncology.
If you are interested, please feel free to contact us so that we can discuss the program and other opportunities for cooperation in detail. Look forward to working with you in the near future.
References
-
Van Meurs, M.; et al. Bench-to-bedside review: Angiopoietin signaling in critical illness–a future target?. Critical care. 2009, 13(2): 1-13.
-
Kienast, Y.; et al. Ang-2-VEGF-A CrossMab, a novel bispecific human IgG1 antibody blocking VEGF-A and Ang-2 functions simultaneously, mediates potent antitumor, antiangiogenic, and antimetastatic efficacy. Clinical Cancer Research. 2013, 19(24): 6730-6740.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 The Angiopoietin-Tie2 ligand-receptor system. (Van Meurs, 2009)
Fig.1 The Angiopoietin-Tie2 ligand-receptor system. (Van Meurs, 2009)



 Download our brochure
Download our brochure