About This Program
This program aims to develop anti-iNOS therapeutic monoclonal antibody for immuno-oncology.
Rationality when developing program:
-
(Nitric Oxide) NO is a small, impermanent gas molecule required by various physiological processes, including immune responses, neurotransmission, and vascular vasodilation.
-
The function of NO in cancer is complicated because it could promote but also inhibit the progression of tumors, depending on settings. High NO level may cause tumor cell apoptosis, and low levels will induce cell proliferation by stimulating angiogenesis.
-
Increased expression of (Inducible nitric oxide synthase) iNOS is significantly associated with angiogenesis, chemoresistance, metastasis and immune resistance in certain malignancies such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, gastric cancer, and melanoma.
-
Studies have reported iNOS expression is associated with poor prognosis in human cancers
In summary, iNOS may be a raising prognostic biomarker or therapeutic target to be studied.
iNOS
NO is a gas that does not exist in most cells under normal conditions. However, when cells are exposed to chronic inflammatory conditions, the enzyme, iNOS, will catalyze and synthesizes higher levels of NO. Multiple studies have shown that:
These data indicate endogenous roles of NO and iNOS activity in CSC biology.
-
Continuous exposure to moderate or high concentration NO promotes tumor transformation and initiation.
-
Downstream effects of NO production include DNA damage, enhanced angiogenesis and perfusion, chemotherapy resistance, escape from apoptosis, and increased inflammation and immune resistance.
-
Endothelial NO synthase, the enzyme controls NO synthesis in the vascular endothelium, localizes near tumor cells displaying stem cell markers and exogenous NO donors support stem cell signaling pathways in glioma cells.
-
NO produced by iNOS contributes to cancer stem cells (CSC) formation and has the ability to self-renew.
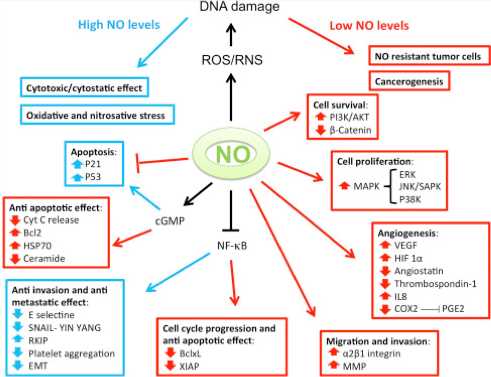 Fig.1 The dual role of iNOS in cancer.1
Fig.1 The dual role of iNOS in cancer.1
iNOS in Cancer Studies
Here are some published data about INOS working as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy.
-
Elevated iNOS expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with HCC (left) and liver cancer (right).
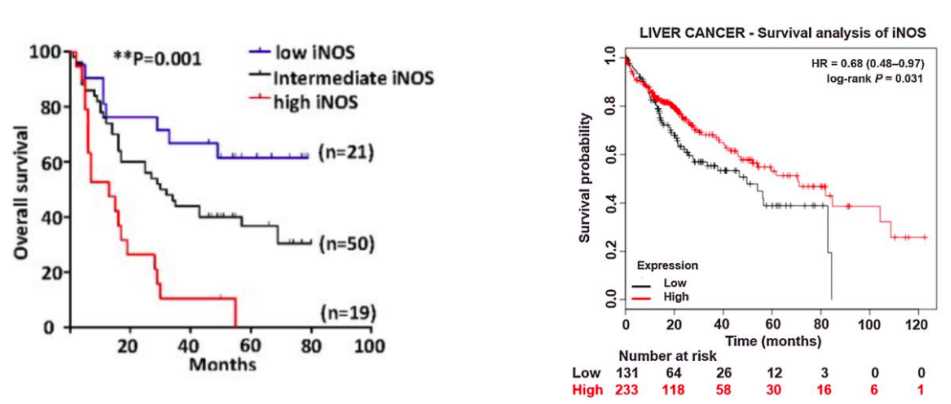 Fig.2 The Kaplan–Meier analysis (left) and the survival probability (right) showed that high iNOS expression was significantly associated with decreased survival of patients with HCC.2,3
Fig.2 The Kaplan–Meier analysis (left) and the survival probability (right) showed that high iNOS expression was significantly associated with decreased survival of patients with HCC.2,3
-
Oleanolic acid (OA) enhanced the anti-tumor effects of regorafenib in liver cancer treatment.
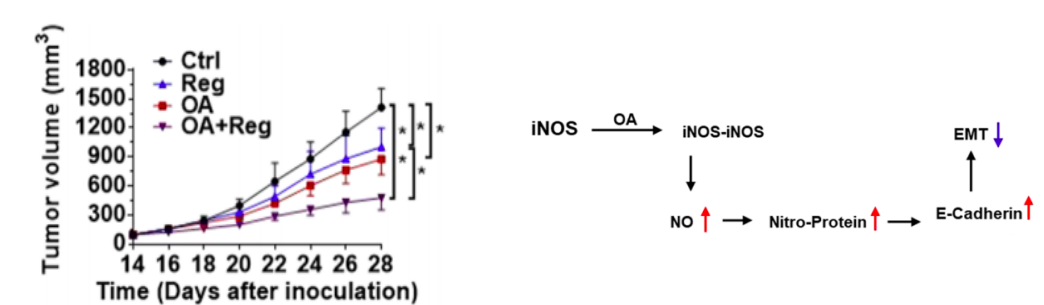 Fig.3 Tumor volumes of PLC-bearing BALB/c-null mice with indicated treatments.3
Fig.3 Tumor volumes of PLC-bearing BALB/c-null mice with indicated treatments.3
Ongoing Clinical Trials
-
Currently, several anti-iNOS antibodies are being evaluated in clinical trials after successful testings in animal models. However, further research is needed regarding safety, efficacy, and combination strategies.
-
Despite this, iNOS is still a compelling target for cancer immunotherapy. In an effort to optimally leverage iNOS-mediated immune response, our next generation of iNOS targeted treatment attempts to explore combination therapy trials with other immunomodulatory agents.
Program Planning and Management
We have extensive knowledge of end-to-end program development. For each program, we are committed to delivering the final complete program to our clients within 1.5 years before entering the IND stage.
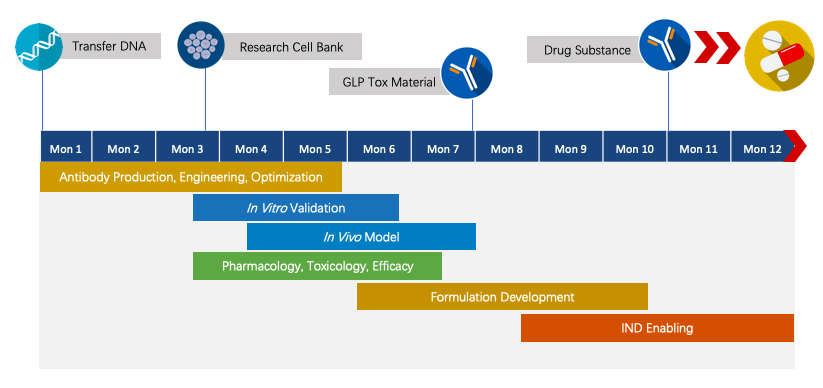 Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
Cooperation
Creative Biolabs is looking for potential partners (include but not limit to major pharma or biotech firms) to develop anti-INOS therapeutic monoclonal antibody program together. Our scientists are dedicated to bringing years of valuable experience to our partner and achieve a meaningful partnership. For any partners interest in our Next-IO™ programs, Creative Biolabs welcomes collaboration.
Here are two ways for your choice, and please contact us for more details.
1) Collaborate with us and co-develop the programs from the discovery phase to IND enabling. Costs will be shared.
2) Become a licensed candidate for our programs.
With our quality control protocol and knowledge of global regulatory requirements, we can help our partners advance their programs with more chance to succeed. Look forward to cooperating with you in the near future.


 Fig.1 The dual role of iNOS in cancer.1
Fig.1 The dual role of iNOS in cancer.1
 Fig.2 The Kaplan–Meier analysis (left) and the survival probability (right) showed that high iNOS expression was significantly associated with decreased survival of patients with HCC.2,3
Fig.2 The Kaplan–Meier analysis (left) and the survival probability (right) showed that high iNOS expression was significantly associated with decreased survival of patients with HCC.2,3
 Fig.3 Tumor volumes of PLC-bearing BALB/c-null mice with indicated treatments.3
Fig.3 Tumor volumes of PLC-bearing BALB/c-null mice with indicated treatments.3
 Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure