Cell Panel Screening Service for DDR Target Identification and Validation
Creative Biolabs is committed to advancing DDR research by providing cutting-edge cell panel screening services. Our DDR cell panel is an essential asset for researchers aiming to develop DDR-related therapeutics. Through a combination of robust assay formats, extensive cell line repositories, and advanced bioinformatic analyses, we provide comprehensive support for DDR research.
What is the DNA Damage Response (DDR)?
The DNA damage response (DDR) is a critical cellular mechanism that maintains genomic stability by detecting and repairing DNA damage. DDR consists of a series of complex signaling pathways and repair processes, making it a multifaceted yet crucial target for cancer therapeutics. Targeting DDR pathways is a promising strategy in oncology. By inhibiting key DDR proteins, cancer cells can be driven toward apoptosis.
There are five primary DDR mechanisms:
-
Mismatch Repair (MMR)
-
Base Excision Repair (BER)
-
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
-
Homologous recombination (HR)
-
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)
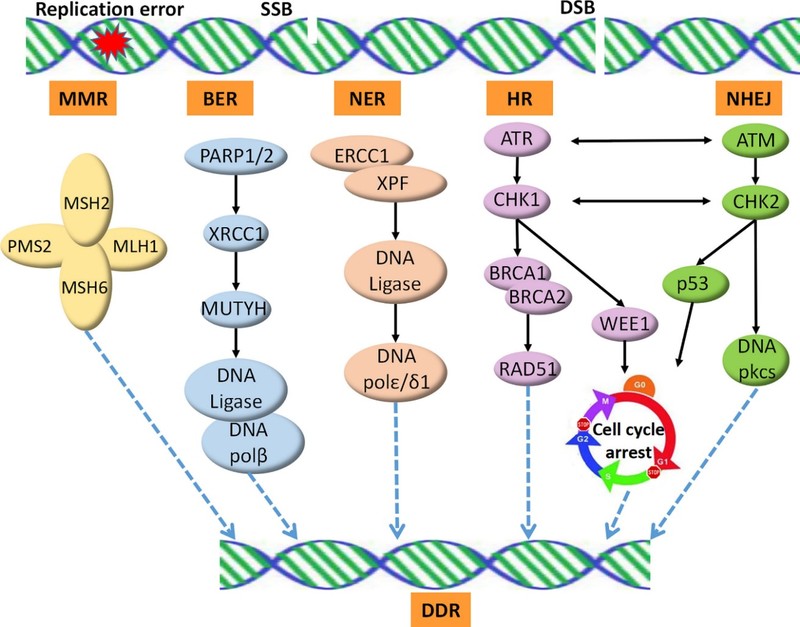 Fig.1 DDR pathway and targets.1
Fig.1 DDR pathway and targets.1
Our DDR Cell Panel
Creative Biolabs offers an advanced DDR cell panel aimed at screening the activity and selectivity of DDR-related inhibitors. Our cell panel includes 75 types of tumor cells, encompassing 12 tumor types and over 500 cancer cell lines. Our collection consists of wild-type cell lines, gene-edited cell lines, and drug-resistant cell lines. This diversity ensures that our screening processes can address the complexity and heterogeneity of cancer, providing a more comprehensive understanding of DDR inhibitor efficacy.
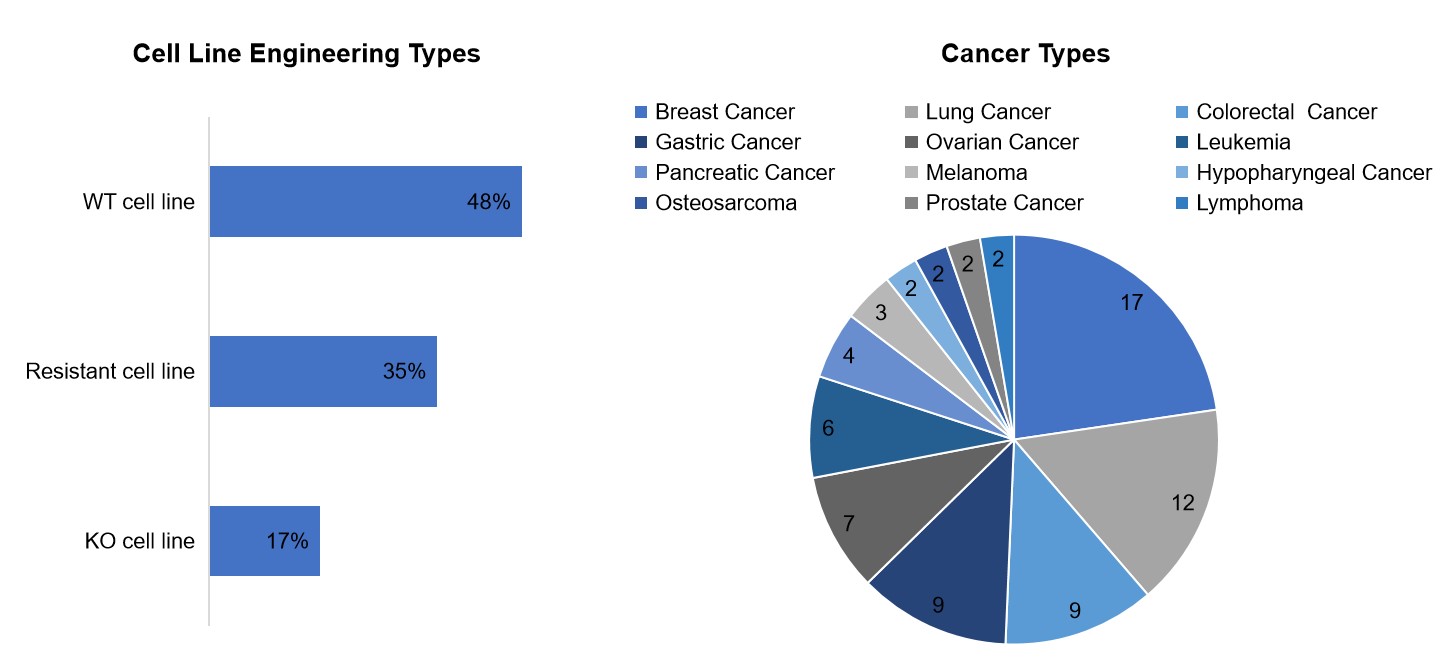
The functional assays we provide cover various formats, including 2D proliferation, 3D proliferation, colony formation, and apoptosis assays. These assays are designed with flexibility and no constraints on assay timelines, thereby accommodating the unique needs of each research project.
-
RNA-seq-Based Bioinformatic Analysis
Our services incorporate advanced RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) techniques to analyze drug-resistant cell lines. This approach provides detailed information on gene expression, enriched pathways, and featured gene profiles, enabling the identification of novel therapeutic targets and enhancing the understanding of DDR biology.
Panel Types
|
Panel Type
|
Description
|
|
DDR 30 Cell Panel
|
30 cell lines for detecting DDR-related targets.
|
|
DDR 65 Cell Pane
|
65 cell lines for detecting DDR-related targets.
|
|
DDR Customized Cell Pane
|
Offering flexible cell line selection.
|
Key Features
-
Our DDR cell panel includes a variety of cell lines with different DDR pathway deficiencies. This diversity is crucial for assessing the broad-spectrum efficacy and selectivity of potential inhibitors across different genetic backgrounds.
-
Our cell panel provides ready-to-use assays specifically designed for the screening and identification of DDR inhibitors. These assays cover essential pathways and targets such as WRN, PARP, BRCA1, CDK, ASAH, POLQ, PARG, and P53.
-
Ready-to-use screening services ensure fast and reliable results with the flexibility to adapt to the unique timelines and requirements of different research projects.
Applications
-
DDR Inhibitor Screening
Evaluate compound efficacy and selectivity across diverse DDR-deficient tumor models to accelerate the identification of potent DDR-targeted therapeutics.
-
Mechanism-of-Action Studies
Use RNA-seq analysis and functional assays to explore molecular mechanisms, signaling pathways, and gene expression changes triggered by DDR inhibition.
-
Combination Therapy Validation
Test DDR inhibitors in combination with other agents using various tumor cell models to identify synergistic effects and optimize treatment strategies.
-
Drug Resistance Profiling
Leverage gene-edited and drug-resistant cell lines to study resistance mechanisms and identify biomarkers predictive of DDR-targeted therapy outcomes.
-
Target-Specific Assay Development
Apply custom panels to focus on specific DDR-related targets (e.g., PARP, BRCA1, WRN, PARG) for personalized therapeutic development and validation.
Contact us for a detailed quote!
Reference
-
Sun, Wei, et al. "Targeting DNA damage repair for immune checkpoint inhibition: mechanisms and potential clinical applications." Frontiers in Oncology 11 (2021): 648687. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 DDR pathway and targets.1
Fig.1 DDR pathway and targets.1

 Download our brochure
Download our brochure