In Vitro Analysis of Human Brain Cells
Creative Biolabs offers in vitro analysis of human brain cells service to help you understand the pathogenic mechanisms underlying neurological disorders.
Brain Cells
Brain cells make up the functional tissue of the brain, which mainly consists of two types:
Neurons, also known as nerve cells, are the excitable cells of the brain that function by communicating with other neurons and interneurons (via synapses), in neural circuits and larger brain networks. The two main neuronal classes in the cerebral cortex are excitatory projection neurons, and inhibitory interneurons.
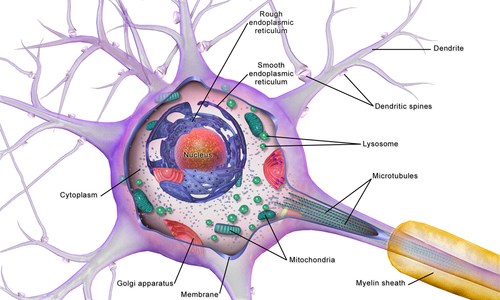 Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Glial cells, also known as neuroglia, are the supporting cells of the neurons, which provide support and nutrients to the neurons. Glial cells are grouped into macroglia of astrocytes, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes, and much small microglia.
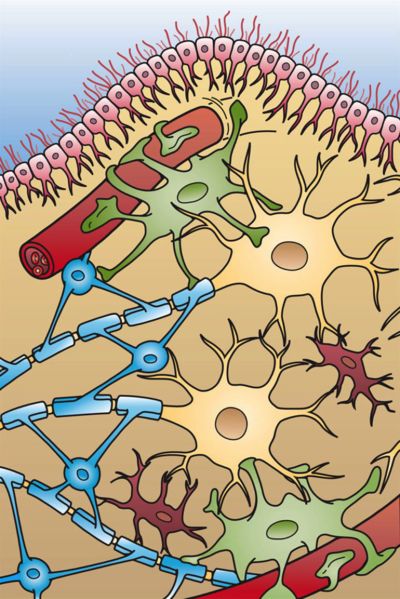 Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Synapses
Cognition and behavior depend on the efficient delivery of information between individual neurons as well as the precise communication between different brain regions. The transmission of information in the form of electrical signals between neurons occurs at specialized sites of contact termed synapses. Synapses are considered as the conveyors of information, and synaptic transmission and plasticity are considered the cellular basis of mammalian cognition and behavior. Therefore, synaptic deficits are one of the key subcellular changes occurring with many neurological disorders.
Animal Model vs Human Brain Cells
At present, the most understanding of synaptic systems that underlie cognition and behavior comes from animal model studies. Although the basic mechanistic properties of synaptic transmission and plasticity are conserved in animal species, however, there are still fundamental features of synaptic structure and function which uniquely exist in the human brain. Compared with the rodent neocortex, the adult human neocortex is thicker in proportion, more elaborate dendritic arbors and has more synapses per cell. Besides, there are marked differences between human and rodent pyramidal neurons in passive membrane properties, synaptic transmission, and synaptic plasticity.
In Vitro Analysis of Human Brain Cells Platforms
In Vitro Model Platform
In vitro models, such as CNS models and synaptic transmission, are used for the CNS drug development which contribute to the research and advancement in neurological domain.
In Vitro Analysis Technology Platform
hESCs and hIPSCs provide novel disease modeling technologies that can recapitulate human pathology in vitro, significantly improving the quality of new therapeutic agents and allow high-throughput drug screening.
Significance of In Vitro Models of Human Brain
-
Effect of in vitro models of the human brain:
-
Determine how the brain works
-
Understand the pathogenic mechanisms underlying neurological disorders
-
Discover effective treatment strategies to prevent, slow, or arrest disease progression
-
Adult human brain tissue may be the best alternative study model in human neurodegenerative conditions.
-
Brain tissue from the adult human brain may offer the most representative in vitro platform to study Alzheimer's Disease as well as other neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Adult human brain biopsy samples can be used to examine the pathology of epilepsy and brain tumors.
If you are interested in our in vitro analysis of human brain cells service, please feel free to contact us.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use




 Download our brochure
Download our brochure