What is iPSC Differentiation?
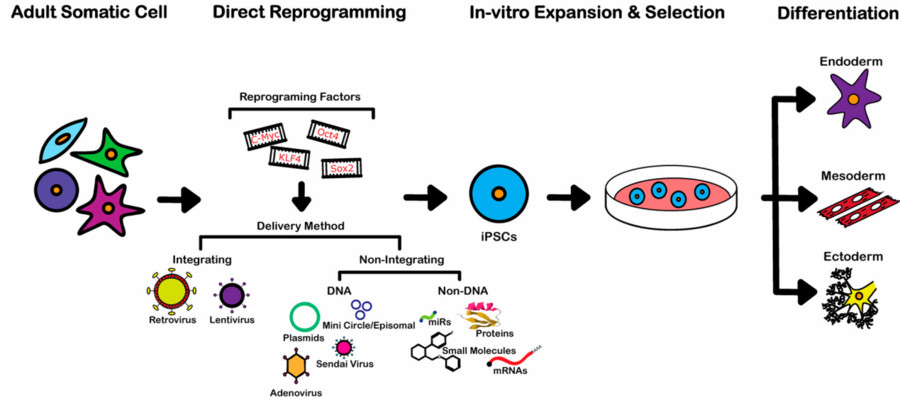 Fig. 1 Flowchart of iPS directed differentiation process.1,3
Fig. 1 Flowchart of iPS directed differentiation process.1,3
iPSCs are produced by reprogramming somatic cells through specific genetic reprogramming techniques. This process involves the introduction of specific transcription factors (Oct4, Soc2, Klf4, and c-Myc). After entering a somatic cell, the cell undergoes reprogramming and returns to an undifferentiated pluripotent state. Due to their differentiation potential, iPSCs can differentiate into specific types, such as lymphocytes, neurons, cardiomyocytes, lung cells, etc.
Differentiation of iPSC usually requires the regulation of specific growth factors and signaling molecules. It is also carried out under fixed culture conditions that mimic the development path of target cells. This ability to guide differentiation is a core aspect of stem cell research and application.
iPSC Differentiation Services
Explore our specialized iPSC differentiation services, each crafted to mirror the physiological and functional attributes of the target tissue.
| Services | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Digestive System-Cells Differentiation from iPSC | Ideal for modeling gut inflammation, nutrient absorption, or pancreas-related metabolic disorders. |
| Osteogenic Cells Differentiation from iPSC | Supports skeletal development studies, orthopedic regenerative projects, and bone-targeted drug screening. |
| Blood Cells Differentiation from iPSC | Facilitates research in hematopoiesis, immunology, anemia, leukemia, and vaccine development. |
| Ocular Cells Differentiation from iPSC | Enables advanced modeling of retinal degeneration, glaucoma, and gene therapy testing. |
| Cardiomyocytes Differentiation from iPSC | Highly valuable for cardiac toxicity assays, rhythm disorder modeling, and myocardial repair. |
| Hepatocytes Differentiation from iPSC | Applied in liver fibrosis modeling, metabolic studies, and infectious disease research (e.g., HBV, HCV). |
| Neuronal Cells Differentiation from iPSC | Supports brain-on-chip platforms, neurotoxicity screening, and neurodevelopmental disorder modeling. |
Service Advantages
-
Diverse Lineage Specialization
From neurons to hepatocytes, blood cells to ocular tissues—we don't just differentiate, we specialize. -
Optimized Protocols, Reproducible Outcomes
We rely on well-established protocols that are fully optimized for efficiency and scalability. -
Customization at Every Step
Need a co-culture setup, feeder-free protocol, or specific maturation markers? Our services are as flexible as your project demands. -
Strict Quality Control
Every cell population is characterized using high-standard tools to ensure identity, purity, and viability. -
Scalability & Experience
Proven capability to generate the cell quantities you need from small-scale research batches to larger volumes for screening or development. -
End-to-End Service
Offers integration with upstream (iPSC generation, banking, gene editing) and downstream (cryopreservation, functional testing) services.
Technical Process
- Initial cell processing: Starting materials for iPSC generation can include a variety of cells. Once cells are obtained, isolation and initial culture are carried out to expand their numbers.
- Reprogramming: We employ advanced iPSC reprogramming factor delivery strategy by virus, episomal vectors, as well as other methods (mRNA, protein) to help you obtaining the desired iPSC.
- Gene editing (if applicable): We can achieve gene knock-out, knock-in or precise point mutations in a specific way. The operating method depends on the genomic background of the experimental target and target locus.
- Directed differentiation: Directed differentiation guides pluripotent stem cells into specific cell types using signaling molecules.
- Differentiated cell function verification: This involves assessing phenotypic purity, detecting unexpected differentiation, and performing functional verification.
Table 1. Directed differentiation protocols
| Target Cell Type | Signaling Pathway Modulators |
|---|---|
| Cortical Neurons | Dual SMAD inhibition + RA/SHH |
| Pancreatic β-Cells | FGF10/Activin A → KGF/Exendin-4 |
| Cardiomyocytes | BMP4/Activin A → Wnt inhibitors |
| Hepatocytes | HGF/Oncostatin M/Dexamethasone |
| Kidney Podocytes |
Mesoderm: CHIR99021 Nephron Progenitors: FGF9 + RA Maturation: VEGF + Laminin-511 |
| Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) |
Neural Crest: CHIR99021 Eye Field: Noggin Maturation: Activin A + Nicotinamide |
| Oligodendrocytes |
Neural Induction: Dual SMADi OPC Commitment: PDGF-AA/IGF1 Myelination: T3 + NT-3 |
Cutting-Edge Technologies Driving Our Services
We integrate leading-edge technologies to ensure consistent, reliable, and functional cell outcomes.
- Single-cell RNA sequencing for transcriptomic profiling
- live-cell imaging for dynamic morphology tracking
- Flow cytometry and ICC for precise marker verification
- ELISA and enzyme activity assays for functionality testing
- CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing for precise genetic modification of iPSCs
Applications of iPSC Differentiation
Our applications ofiPSC include but not limited to:
- Basic scientific research - disease mechanism, developmental biology, cell fate determination, etc.
- Drug development and discovery - provide physiologically relevant cells for drug discovery, identification and screening, target verification, etc.
- Stem cell therapy and cell therapy - for neurodegenerative diseases, immune diseases, diabetes, etc.
- Organoid research - iPSC-derived tissue organoids.
- Toxicology screening - used to assess the safety of a compound or drug in living cells.
Published Data
This study compared two distinct astrocyte differentiation protocols: a long, serum-free (LSF) method and a short, serum-containing (SSC) method. The LSF protocol is a widely used approach based on previous methods, while the SSC protocol is an in-house technique relevant to Parkinson's disease research. The SSC method uses homogeneous neural stem cells that can generate both astrocytes and dopaminergic neurons. RNA sequencing and imaging were used to evaluate astrocyte maturity and activation. The study also compared iPSC-derived astrocytes with postmortem human astrocytes to assess their suitability for disease modeling.
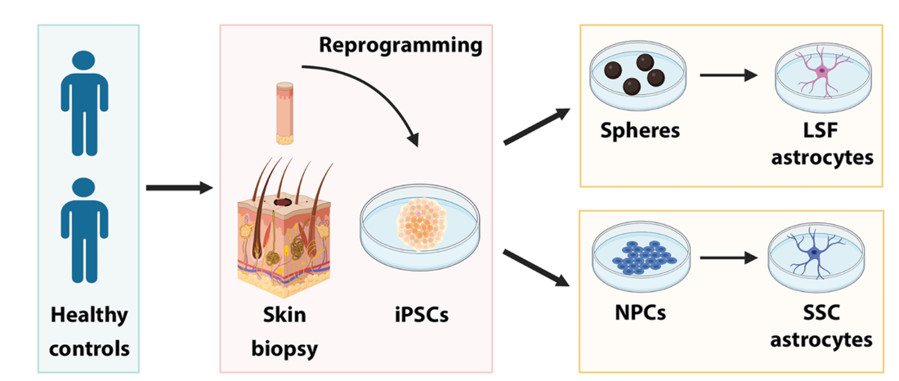 Fig. 2 Scheme representing the main steps required to obtain astrocytes with the different protocols.2,3
Fig. 2 Scheme representing the main steps required to obtain astrocytes with the different protocols.2,3
FAQs
What if I need a highly specific or rare cell type—can you customize the protocol?
Absolutely. Our platform is built for customization. We can modify growth factor exposure, timing, 3D matrix composition, feeder layers, or combine multiple lineage steps. For rare or novel targets, we can develop differentiation protocols de novo, either from published sources or proprietary R&D, with milestones and pilot stages clearly defined.
How long does an iPSC differentiation project typically take?
Timelines depend on the complexity of the lineage and any custom modifications. We provide a detailed chart and weekly updates throughout the project.
Can your iPSC-derived cells be used for clinical applications?
Our standard iPSC differentiation services are for research use only (RUO).
Can I request isogenic controls or gene-edited iPSC lines before differentiation?
Yes. We provide isogenic iPSC line development. You can request either gene knockouts, point mutations, or knock-ins (e.g., GFP reporters). These modified iPSCs can then be differentiated into your desired lineage under the same protocol, giving you powerful side-by-side comparators for functional assays or disease modeling.
Do you provide co-culture models using iPSC-derived cells?
Absolutely. We support co-culture systems involving multiple iPSC-derived lineages (e.g., neurons + astrocytes, hepatocytes + Kupffer cells), or iPSC-derived cells with primary stromal/immune cells. These models are ideal for studying intercellular signaling, barrier integrity, inflammation, and cell-cell interactions.
How are your services priced?
Our pricing is based on lineage complexity, QC depth, and deliverable format. Volume-based discounts and multi-project contracts are available. Please contact us for a tailored quote.
Our company is your trusted partner for iPSC-based innovations. Our solutions are backed by scientific rigor, technical expertise, and unwavering commitment to your success.
Let's differentiate—together.
Get in touch for a free consultation or project quote today.
References
- Menon, Siddharth, et al. "An overview of direct somatic reprogramming: the ins and outs of iPSCs." International journal of molecular sciences 17.1 (2016): 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010141
- Mulica, Patrycja, et al. "Comparison of Two Protocols for the Generation of IPSC-Derived Human Astrocytes." Biological Procedures Online, 25.1 (2023): 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12575-023-00218-x
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
What Our Clients Say
“We ordered iPSC-derived retinal pigment epithelial cells for our in vitro AMD model. The pigmentation, morphology, and phagocytosis activity were all in line with primary RPE standards. Plus, their shipping and documentation were flawless.”
— Dr. Meena Vasudevan, Senior Investigator
“Their team worked with us from reprogramming fibroblasts to generating mesodermal progenitors and osteoblasts. They updated us weekly and responded to every question promptly and scientifically.”
— Dr. Martin Herzog, Research Lead
“From establishing our iPSC line to generating functional cardiomyocytes, the service was exceptional. The cells exhibited robust beating and proper responses to cardioactive drugs. Their technical team was always available for in-depth discussions."
— Dr. Lena Chen, Director of Cardiovascular Research
“Their CRISPR-edited iPSC lines for our rare disease model arrived ahead of schedule, complete with comprehensive genomic validation data. When we requested a custom neuronal differentiation protocol, their scientists provided an optimized workflow within 48 hours.”
— Prof. Elena Torres, Chief of Genetic Therapeutics
Get Started with Confidence














1. Contact Us
via the Inquiry Form or Email
2. Define Your Needs
Cell Type, Function, Quantity, Modifications
3. Kickstart the Project
Our Expert Team Guiding Every Step
Created August 2025