What are Embryoid Bodies (EBs)?
Embryoid bodies are three-dimensional (3D) aggregates formed spontaneously or by directed aggregation when pluripotent stem cells, including iPSCs and embryonic stem cells (ESCs), are cultured in suspension without key growth factors that maintain pluripotency. Key characteristics of EBs:
- 3D architecture: This architecture allows for more accurate performance of complex cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. EB is not flat, but has a spherical or complex 3D structure.
- Pluripotency and differentiation capacity: EBs are composed of pluripotent stem cells capable of differentiating into cell types derived from the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm germ layers. This makes them a powerful and versatile platform for initiating differentiation into virtually any somatic cell type.
- Critical intermediate: EB formation is a common and often essential step in many agreements. Used to differentiate iPSC into specialized cells, such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, hepatocytes, etc.
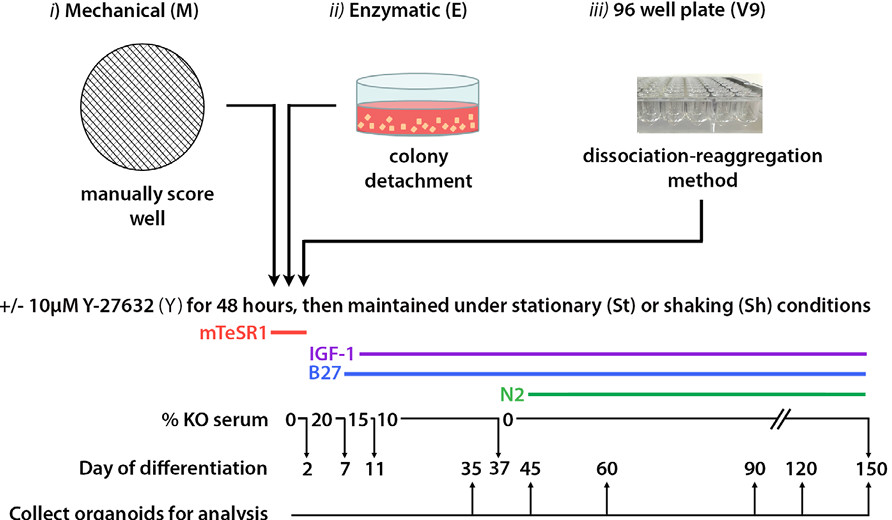 Fig. 1 Schematic showing the various methods of EB formation tested at the onset of differentiation.1,3.
Fig. 1 Schematic showing the various methods of EB formation tested at the onset of differentiation.1,3.
Service Advantages
- Precision-Controlled EB Formation: We utilize advanced technologies to control EB size and morphology, which are critical factors influencing differentiation efficiency and yield. Our protocol ensures that EBs with the best characteristics are generated for specific downstream applications.
- Chemically Defined, Xeno-Free Conditions: We prioritize the use of fully chemically defined media that do not contain animal products to ensure consistency and reduce batch-to-batch variability.
- Multiple Formation Methodologies: We provide various EB formation techniques, such as self-aggregation in low-attachment plates, hanging drop culture, and forced aggregation using specialized platforms.
- Comprehensive Multi-Parameter Characterization: We use automated image cytometry for label-free and non-destructive analysis of EBs, measuring parameters such as count, diameter, area, perimeter, form factor, smoothness, and aspect ratio.
- Proven Differentiation Potential: Our EBs are rigorously validated for their capacity to differentiate into derivatives of all three germ layers, ensuring they are a robust starting point for your specific lineage differentiation protocols.
- End-to-End Service Integration: Our services can be seamlessly integrated with upstream iPSC generation, expansion and gene editing. and downstream differentiation into specialized cells, organoid generation and functional analysis.
Technical Workflow
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| iPSC Culture and Quality Check | We maintain iPSCs in chemically defined media on coated surfaces. Cells are passaged using enzyme-free methods to preserve colony integrity and ensure high viability before EB formation. |
| Cell Preparation for EB Formation | iPSCs are dissociated into either small clumps (for self-aggregation) or single cells (for forced aggregation) using carefully optimized EDTA or enzyme treatment times. |
| EB Formation (Selected Method) | Cells are resuspended in an appropriate medium, transferred to a selected platform, and incubated to form EB. |
| EB Harvesting and Analysis | EBs are harvested and subjected to our comprehensive characterization pipeline. |
| Transition to Differentiation or Shipping | Fully characterized EBs are either directly transferred to your specified differentiation protocol or prepared for shipment to your laboratory. |
Key EB Formation Methods We Offer
| Formation Method | Key Principle | Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Suspension | Spontaneous aggregation in low-attachment vessels | Simple, scalable for large batches | Projects requiring many EBs, less stringent size uniformity |
| Hanging Drop | Gravity-enforced aggregation in suspended droplets | High size uniformity, controlled cell number | Protocols requiring highly reproducible EB size |
| Dielectrophoresis (DEP) | Electric field-guided aggregation in specific patterns | Rapid, precise size control, can pattern different cell types | Complex engineered tissues, studying aggregation mechanics |
Cutting-Edge Technologies
We integrate advanced technologies to ensure superior EBs.
- Automated Image Cytometry: For rapid, non-destructive, quantitative analysis of EB morphology.
- Dielectrophoresis Platforms: For unprecedented control over initial aggregate formation and size.
- Chemically Defined Media Systems (E8/E6): To ensure culture consistency and eliminate variability from animal-derived components.
- Advanced 3D Culture Systems: Including ultra-low attachment plates and synthetic hydrogels to support EB development and prevent unwanted adhesion.
Applications of Our EB Services
The high-quality EBs we provide are fundamental to numerous applications.
- Disease Modeling: Generate organoids (e.g., cerebral, retinal) from iPSCs to study neurodevelopmental disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and more.
- Drug Screening & Toxicology: Use EB-derived differentiated cells in high-throughput compound screening and safety pharmacology in a more physiologically relevant 3D context.
- Developmental Biology Studies: Reviewing and studying early human development processes.
- Basic Research: Study the effects of cell fate determination, aggregation dynamics, and genetic or chemical perturbations on early differentiation events.
Published Data
In this study, researchers compared a PBMC-derived iPSC line to a fibroblast-derived iPSC line in conjunction with either an EB or a monolayer-based (MB) differentiation protocol. Both cell lines and differentiation protocols were investigated regarding their ability to generate OCs and their inherent robustness and ease of use. First, both cell lines' ability to remain undifferentiated while propagating in a feeder-free system was assessed. This was followed by evaluating mesodermal differentiation and characterization of hematopoietic progenitor cells produced under the differentiation strategy.
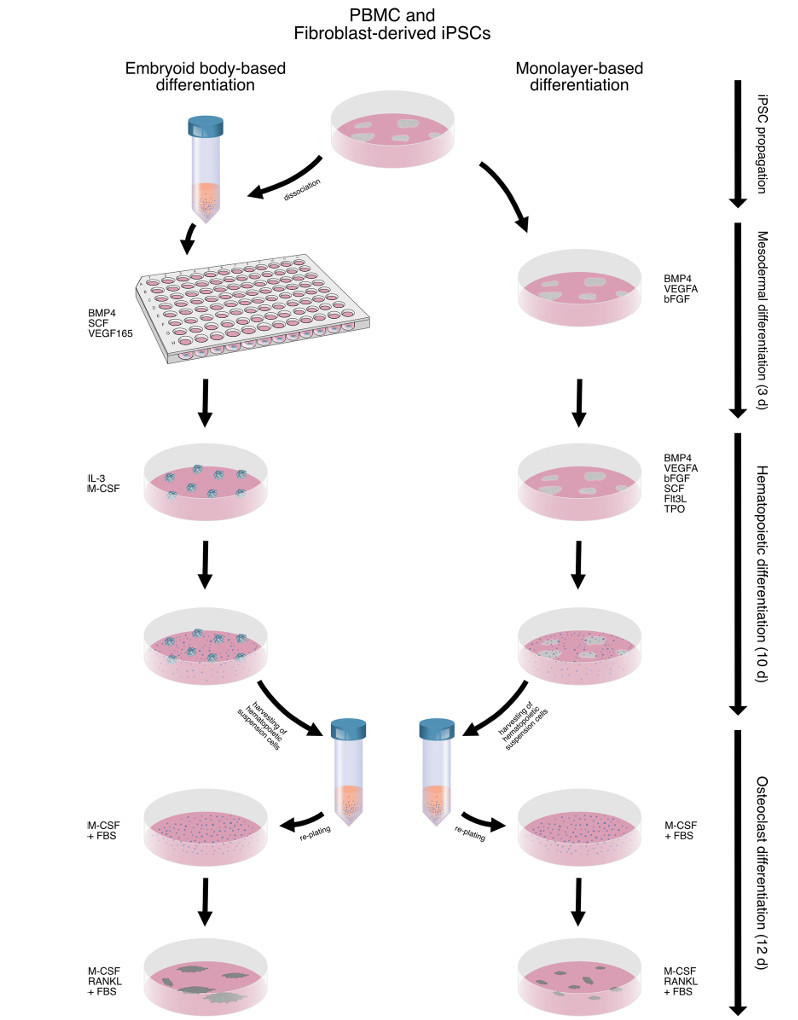 Fig.2 Schematic outline of the differentiation process and the comparison between EB
Fig.2 Schematic outline of the differentiation process and the comparison between EB and monolayer-based (MB) differentiation.2,3
What Our Clients Say
"The team's expertise in dielectrophoresis-generated EBs was a game-changer. We received EBs of a consistent, optimal size that differentiated into neural lineages with unprecedented efficiency for our cortical organoid project."
— Dr. Anna Petrova, Neuroscience Research Lead
"Switching to their chemically defined EB formation service eliminated the batch variability we struggled with using serum-containing media."
— Dr. Ben Carter, Director of Stem Cell Core
"We needed a custom EB formation protocol from a genetically edited iPSC line for a rare disease model. They developed and optimized a workflow quickly, and the resulting EBs exhibited excellent potential for downstream hepatic differentiation."
— Prof. Sarah Miller, Institute of Genetic Medicine
FAQs
Q: Why is EB size important, and how can you control it?
A: EB size significantly impacts differentiation efficiency and lineage choice. We offer precise control over EB size through methods. We will work with you to determine the ideal size for your target cell type.
Q: Do you offer EB formation for both iPSCs and ESCs?
A: Yes, our protocols and services are applicable to both iPSCs and ESCs.
Q: Can you form EBs from my specific iPSC line?
A: Absolutely. We have experience working with a wide range of iPSC lines. We can receive your cell line, expand it, and proceed with EB formation. We also offer complete integration with our upstream iPSC generation and banking services.
Q: How long does the EB formation process take?
A: The typical timeline from receiving confluent iPSCs to delivering characterized EBs is approximately 2-3 days. Some advanced methods can initiate EB formation even more rapidly.
Q: Are the EBs you provide ready for differentiation?
A: Yes. Upon delivery, the EBs are fully formed, characterized, and can be directly transferred into your chosen differentiation medium to begin specific lineage induction.
Take the Next Step with Creative Biolabs














1. Contact Us
via the Inquiry Form or Email
2. Define Your Needs
Cell Type, Function, Quantity, Modifications
3. Kickstart the Project
Our Expert Team Guiding Every Step
Creative Biolabs is your dedicated partner in harnessing the power of embryoid bodies. We combine scientific expertise with state-of-the-art technology to provide a foundational service that enhances the reliability and success of your stem cell research.
Let's pioneer new paths in stem cell research together. Get in touch for a free consultation and project quote today.
References
- Mellough, Carla B., et al. "Systematic comparison of retinal organoid differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells reveals stage specific, cell line, and methodological differences." Stem cells translational medicine 8.7 (2019): 694-706. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.18-0267
- Blümke, Alexander, et al. "Comparison of osteoclast differentiation protocols from human induced pluripotent stem cells of different tissue origins." Stem Cell Research & Therapy 14.1 (2023): 319. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03547-6.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Created September 2025

