Cellular Metabolite Assay Service
Cellular Metabolite from Tumor Cell: The Marker of Cancer
Metabolites serve not only as substrates and products of biological processes but also play a crucial role in regulating enzymatic activity. Metabolite levels reflect the balance between production and consumption. However, an accumulation of aberrant metabolites directly suppresses immune cell function, raising metabolic and non-metabolic dysregulation and the risk of cancer. Therefore, studying the cellular metabolite can help characterize the profile of cancer cells and aid in anti-cancer drug development.
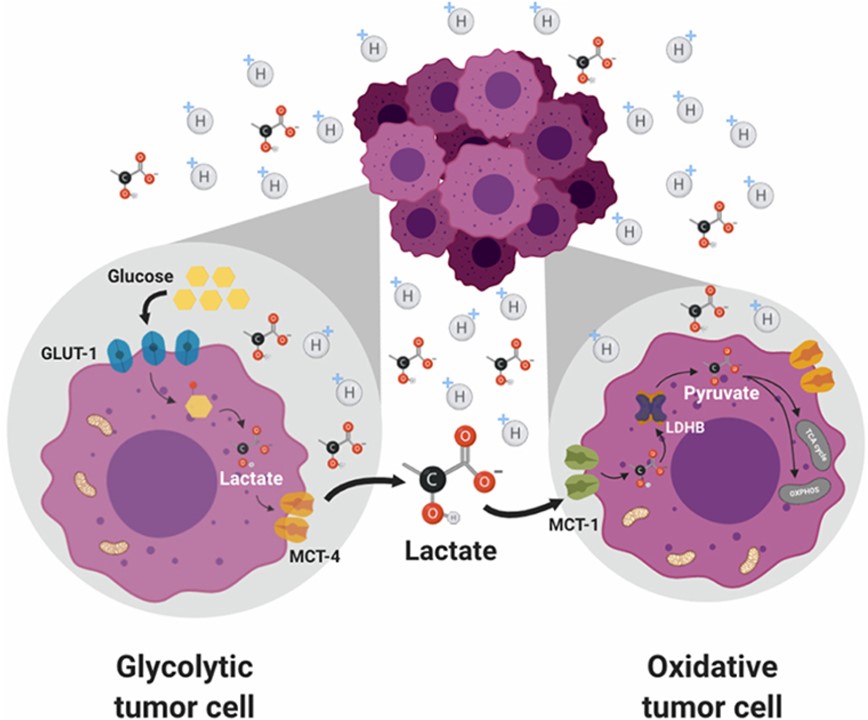 Fig.1 Metabolic symbiosis.1, 4
Fig.1 Metabolic symbiosis.1, 4
Our Cellular Metabolite Assay Service
Creative Biolabs provides a rapid and sensitive cellular metabolite assay service for global customers to characterize the profile of a cancer cell. Our cellular metabolite assay utilizes a bioluminescent-based method that is combined with metabolite oxidation and NADH production. The reductase utilizes the generated NADH to produce luminescence. It is worth noting that the luminescent signal increases proportionally with the number of metabolites in the sample. Hence, we use the luminescent intensity as an indicator for our cellular metabolite assay. At Creative Biolabs, we have full confidence in delivering high-quality results that meet the needs of our global customers' research projects within a quick turnaround time.
In our cellular metabolite assay service, we can target multiple types of metabolites, which include but are not limited to the following
|
Glycolysis Pathway
|
Fatty Acid Metabolism
|
Urea Metabolism
|
|
Glucose
|
Triglyceride
|
Urea
|
|
Pyruvate
|
Free fatty acid
|
Glutamate
|
|
Lactate
|
Pyrophosphate
|
L-arginine
|
Key Advantages for Better Outcomes
-
A single sample can obtain more information about multiple types of metabolites across an extended spectrum of concentrations.
-
Our cellular metabolites assay is more sensitive and easier to operate when compared to common methods.
-
Our highly qualified research team together with comprehensive and customized services, provides a one-stop solution.
Data Support
Case 1: Mutations in Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1/2) and their primary effector, 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), have been discovered to expedite the development of cancer in various human malignancies. This study focused on the molecular mechanism and metabolic alterations that occur in cells due to IDH1/2 mutations. The findings showed that mutations in IDH1/2 caused an increase in the accumulation of 2-HG within cells, as well as the expression of Glut1. Persistently elevated glucose absorption and lactate generation suggest deregulated glucose metabolism.
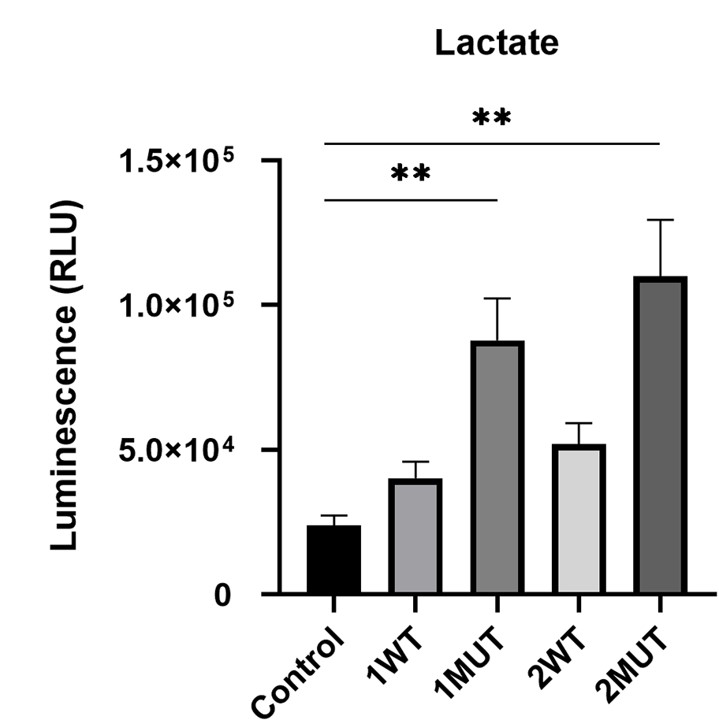 Fig.2 IDH1/2 mutations increase intracellular lactate levels.2, 4
Fig.2 IDH1/2 mutations increase intracellular lactate levels.2, 4
Case 2: There is growing evidence that miRNA dysregulation has a role in human cancer. The results showed that miR-422a expression was significantly decreased in gastric cancer (GC) cells. MiR-422a overexpression in GC cells triggered a transition from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation and inhibited PDK2 activity, limiting cell proliferation and migration. These results point to the miR-422a-PDK2 axis as a potential target for anti-cancer medication development.
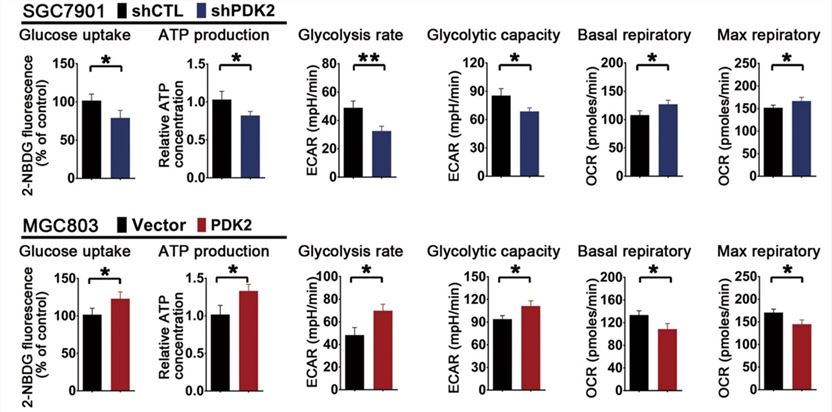 Fig.3 The effects of PDK2 on glucose metabolism.3, 4
Fig.3 The effects of PDK2 on glucose metabolism.3, 4
If you want to know more about our cellular metabolite assay service, please don't hesitate to get in touch with us at your convenience.
References
-
de la Cruz-López, Karen G., et al. "Lactate in the regulation of tumor microenvironment and therapeutic approaches." Frontiers in oncology 9 (2019): 1143.2.
-
Liu, Xun, et al. "Cancer-associated IDH mutations induce Glut1 expression and glucose metabolic disorders through a PI3K/Akt/mTORC1-Hif1α axis." PLoS One 16.9 (2021): e0257090.
-
He, Z. Y., et al. "MiR-422a regulates cellular metabolism and malignancy by targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9: 505."
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Metabolic symbiosis.1, 4
Fig.1 Metabolic symbiosis.1, 4

 Fig.2 IDH1/2 mutations increase intracellular lactate levels.2, 4
Fig.2 IDH1/2 mutations increase intracellular lactate levels.2, 4
 Fig.3 The effects of PDK2 on glucose metabolism.3, 4
Fig.3 The effects of PDK2 on glucose metabolism.3, 4
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure