Time dependent Evolution Analysis Service for Microbial Community in Metastasis
Background Service What we can offer Workflow Highlights FAQs Contact
Are you struggling to decode the complex and dynamic role of the microbiome in cancer progression? Creative Biolabs' time-dependent evolution analysis service for microbial communities in metastases provides longitudinal, multi-omics profiling and integrates high-resolution time-series data, in order to elucidate the interactions between microbiome and tumor across temporal scales, thereby expediting biomarker discovery and therapeutic design.
Introduction
Metastatic progression is increasingly recognized as a chronologically orchestrated process in which the microbiome co-evolves with disseminated tumor cells. Longitudinal metagenomic profiling reveals that microbial consortia undergo stage-specific transitions, from initial hitchhiking during epithelial-mesenchymal escape, through dormancy-associated anaerobe dominance, to post-reactivation blooms that sculpt the pre-metastatic niche. Our service integrates dense temporal sampling, multi-omics data streams, and advanced state-space modeling to decode these microbial trajectories.
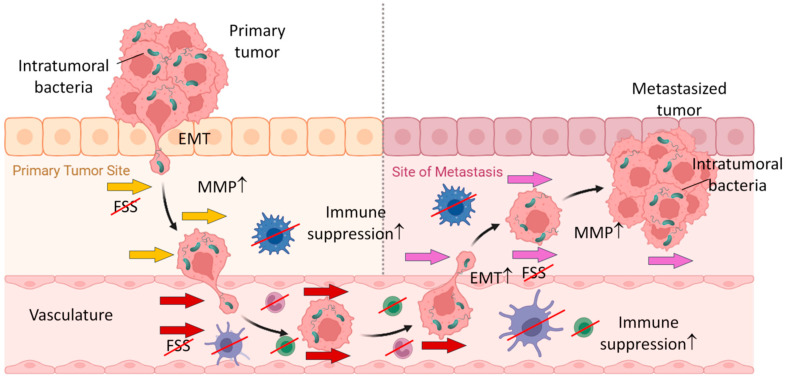 Fig.1 The important role of microbiome in tumor metastases.1
Fig.1 The important role of microbiome in tumor metastases.1
Time-dependent Evolution Analysis Service for Microbial Communities in Metastases at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs' time dependent evolution analysis service for microbial communities in metastases transcends static, single-point analyses to deliver a dynamic understanding of the tumor microbiome. We address key challenges by identifying microbial communities that translocate to metastatic sites, elucidating their impact on the immune microenvironment, and uncovering novel biomarkers predictive of therapeutic response.
What We Can Offer?
-
We seamlessly integrate metagenomic sequencing data with host-level information, including RNA-seq, metabolomics, and clinical data, to provide a holistic view of host-microbe interactions.
-
We have advanced time-series methodologies including Local Similarity Analysis (LSA) and Dynamic Bayesian Networks (DBNs), to precisely map microbial community dynamics and infer causal relationships over time.
-
Drawing on extensive experience in predictive modeling, we deliver robust algorithms that link discrete microbial signatures to pivotal clinical endpoints, enabling precise patient stratification and accurate forecasting of therapeutic efficacy.
Our Service Process
Required Starting Material:
-
Paired longitudinal patient biopsy samples, for example pre- and post-treatment biopsies, or metagenomics sequencing data.
-
Comprehensive clinical data associated with each time point, including treatment regimens and patient outcomes.
-
Supplementary multi-omics layers (such as RNA-seq, metabolomics) are welcomed but optional.
Key Steps:
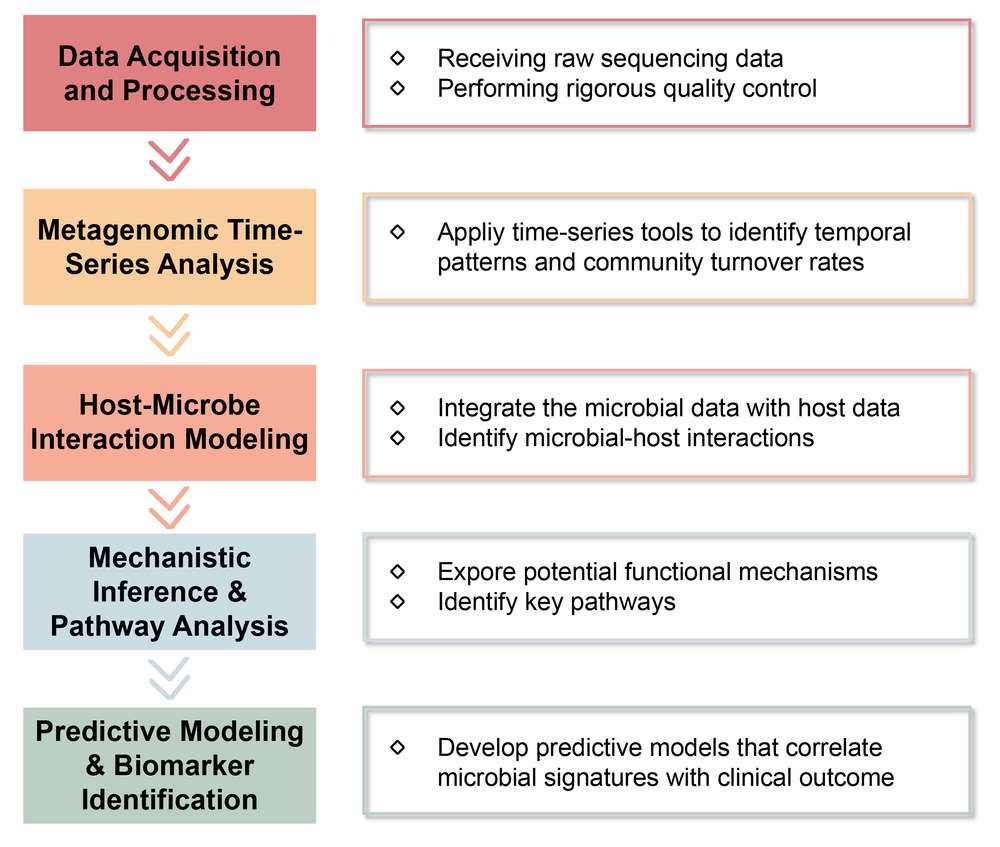
Final Deliverables:
-
Raw and processed data files.
-
A list of identified microbial biomarkers.
-
Visualization of microbial community dynamics.
Key Advantages
-
Customized Analytical Pipelines: We offer fully customizable solutions in order to address your unique research questions, from biomarker discovery to mechanistic pathway elucidation.
-
Well-Established Quality System: We have rigorous SOPs and traceable QC metrics underpin every step of data handling, delivering results that are both reproducible and audit-ready.
-
Expert Support: Our bioinformaticians and cancer biologists work in tandem to guarantee that every computational insight is anchored in robust biological context.
FAQs
Q1: What if my data set is small or has limited time points?
A1: Although time-series analysis benefits from larger datasets, our algorithms have been optimized for limited series. During onboarding, we will benchmark your dataset against clinically validated reference cohorts and recommend the most suitable analytical approach to maximize the value of your data.
Q2: What types of cancer can your service be applied to?
A2: Our service is applicable to various cancer types with available longitudinal metagenomic and clinical data. We have extensive expertise and published experience in pan-cancer analysis, with particular strengths in cancers where the microbiome is known to play a significant role, such as colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancers.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in exploring new mechanisms, discovering novel targets, and identifying new therapeutic directions. Our time-dependent evolution analysis service for microbial communities in metastases provides high-precision sequencing services, analyzes complex longitudinal datasets and integrates bioinformatics insights with tumor biology to elucidate the dynamic processes and critical mechanisms of microbial changes during tumor metastasis.
Customer Reviews
"Using Creative Biolabs' Time-Dependent Evolution Analysis in our research has significantly improved our understanding of microbial translocation. Their dynamic models helped us prove how specific gut microbes reach and colonize metastatic tumors, a finding that would have been impossible with static sequencing data." -L. K. O***, Scientist
"The predictive models we received from Creative Biolabs were remarkably accurate. They allowed us to identify a robust microbial biomarker for patient stratification, saving us significant time and resources in a critical clinical trial." -E. M. S***, Clinical Research Director
"The team's ability to integrate our metagenomic and RNA-seq data was a major advantage. We gained a holistic view of the host-microbe interplay, which not only confirmed our hypotheses but also revealed novel therapeutic targets." -A. J. L***, Head of R&D
Contact us to discuss your project and we will provide a streamlined service process tailored to your research objectives, enabling you to effectively decipher microbiome dynamics and ultimately achieve your research goals more efficiently.
Reference
-
Furuta, Saori. "Microbiome-Stealth Regulator of Breast Homeostasis and Cancer Metastasis." Cancers vol. 16,17 3040. 31 Aug. 2024. Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173040
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 The important role of microbiome in tumor metastases.1
Fig.1 The important role of microbiome in tumor metastases.1

