The development of antibody and peptide targeting virus is very important for the diagnosis and therapy of virus infection. Creative Biolabs has accumulated extensive experience in the anti-virus biomolecular discovery. Based on our cutting-edge platforms, Anti-Virus Biomolecular Discovery, we offer high-quality anti-rabies virus biomolecular discovery services for global clients.
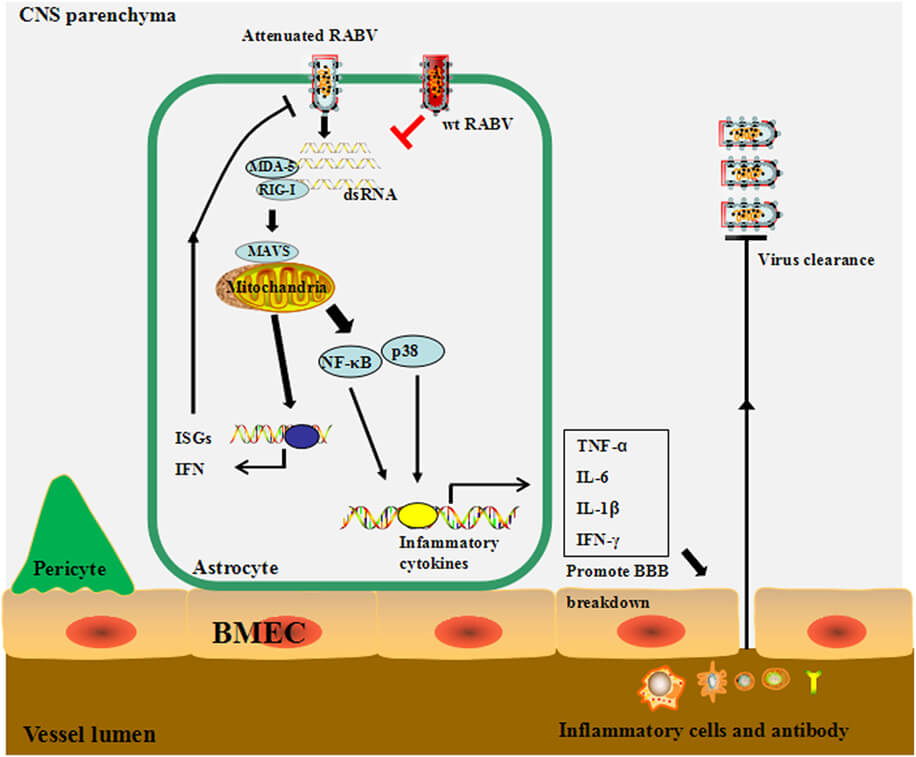 The proposed model for the mechanism through which
The proposed model for the mechanism through which
wild-type (wt) and lab-attenuated rabies virus infect astrocytes.
(Tian et al. 2018.)
Rabies virus (RABV) is the type of species of the genus Lyssavirus within the family Rhabdoviridae. The virus has a single-stranded RNA genome in the negative sense orientation that encodes five proteins in the following order: nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix protein (M), glycoprotein (G) and RNA polymerase (L). Infection with RABV causes in excess of 50,000 human deaths annually, the majority of which occur in Asia. In addition to RABV, the lyssavirus genus contains a growing number of recognized and putative members, many of which have been responsible for occasional human deaths. RABV is a zoonotic virus and has a range of reservoir host species within the mammalian orders Carnivora and Chiroptera. The most important of these reservoirs as a source of human disease is the domestic dog (Canis familiaris). In the Americas, a number of bat species are also responsible for transmission of rabies to humans, particularly the common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus) in Latin America and a number of insectivorous bat species in North America. This has emerged as a public health risk, as bites can occur without the victim realizing that an exposure has taken place, and many cases of bat-transmitted rabies have no recorded exposure to a bat prior to development of infection.
Rabies is the most severe acute viral infection of humans, with a case fatality rate of almost 100%. Although the prompt administration of rabies vaccine and rabies immune globulin after a dog bite or other recognized exposure can reliably prevent the disease, no effective therapies have been identified to rescue a patient who has developed signs of illness. The past decade has seen intense interest in the treatment of rabies, in large part because of the survival of a young patient who was treated with a combination of drugs, including the induction of "therapeutic coma". Unfortunately, numerous subsequent applications of this approach have failed. New approaches are needed for the treatment of rabies, which may combine hypothermia, antiviral drugs, and other therapeutic agents.
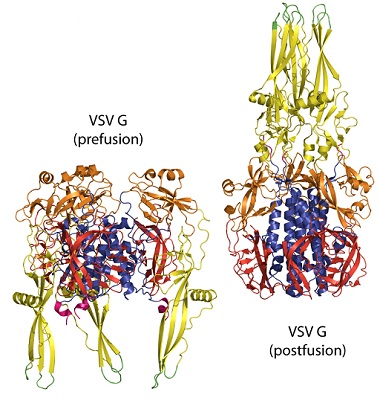
Despite the undoubted success of current commercial vaccines against rabies, there have been numerous attempts to develop alternatives, all taking advantage of the genetic manipulation revolution. Antibodies have been shown to be critical for protection against the spread of RABV. The key target for antibodies is virus glycoprotein. Glycoprotein is the only surface-exposed protein on the virion particle. The ability to clone the RABV glycoprotein into bacterial plasmids and then express the protein in a range of systems has led to a number of alternative approaches with the potential for new vaccines against rabies. In addition, glycoprotein contains a number of antigenic sites to which neutralizing monoclonal antibodies bind have been identified on this protein. These evidences strongly indicate that glycoprotein is a potential target for antibody or peptide development against rabies.
As a modularly organized protein, RABV phosphoprotein (RABV-P) contains structured and disordered regions and shows prominent structural flexibility after post-translational modification. The full-length RABV-P (P1) and four amino-terminally truncated forms of RABV-P (P2, aa 20-297; P3, aa 53-297; P4, aa 69-297 and P5, aa 83-297) are translated by a leaky ribosomal scanning mechanism. All these RABV-Ps can be found in infected cells, purified virus, and cells transfected with a plasmid encoding the complete RABV-P. RABV-P has multiple functions in the RABV-infected cells due to the presence of multiple forms of RABV-Ps. RABV-P is involved in encapsidating viral genome RNA, in assisting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in the process of transcription and translation and in inhibiting intercellular antiviral system mediated by interferons. As RABV-P is crucial for viral replication, specific antibodies or peptides against RABV-P may be good candidates to inhibit RABV replication.
With years of experience in the field of antibody development, the Anti-Virus Biomolecular Discovery platform has been successfully developed in Creative Biolabs with advanced optimization for anti-virus antibody generation. By means of this platform, our skilled scientists are proud of providing high-quality anti-rabies virus biomolecular discovery service for all our global customers. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References: