A novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) originally detected in Wuhan, China, has caused an outbreak of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) and becomes a global public health concern, spurring an urgent need for the discovery of antiviral drug, neutralizing antibodies (NAbs), antiviral peptides, and vaccine. There are no specific vaccine or therapeutic agents currently available for SARS-CoV-2.
With years of experience in anti-infectives biomolecular discovery, Creative Biolabs has accumulated abundant experience in the development of antiviral agents. Especially, we have devoted tremendous efforts and dedication to developing NAbs and functional peptides targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). As a reference, we can help our worldwide customers rapidly explore prophylactic and therapeutic antibody & antiviral peptide to combat SARS-CoV-2.
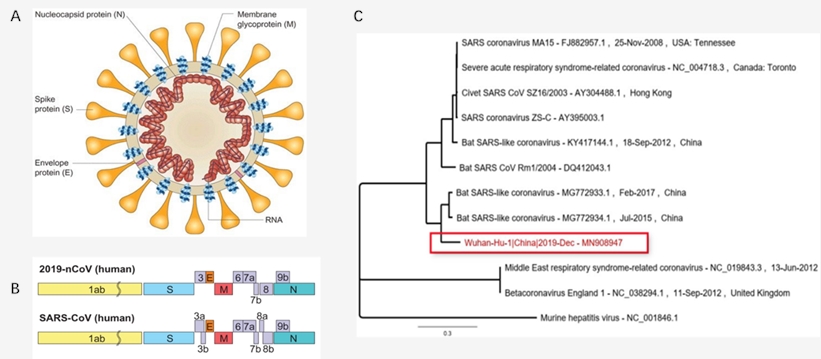 Fig.2 The diagram, genome and phylogenetic tree of SARS-CoV-2. (Chan, 2020)
Fig.2 The diagram, genome and phylogenetic tree of SARS-CoV-2. (Chan, 2020)
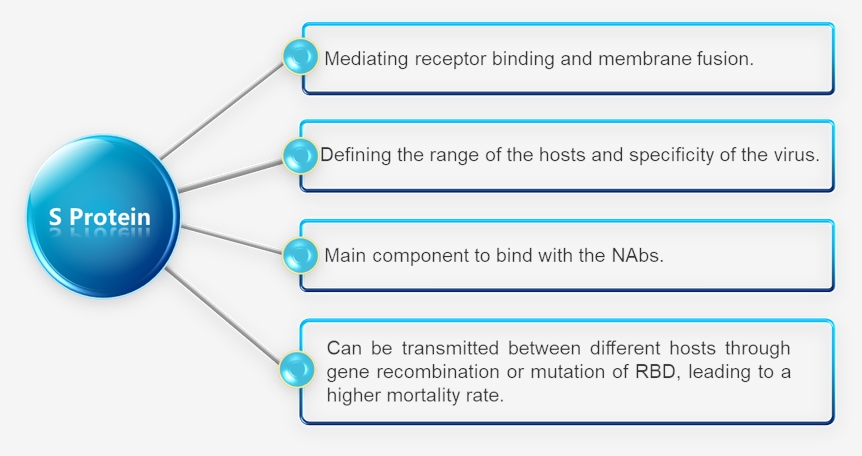
Based on previous studies of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, S protein is the most important and promising target to develop NAbs targeting SARS-CoV-2. As a large type I transmembrane protein, S protein is consisted of two subunits: S1 and S2.
Besides the essential role in the virus binding and entry processes, S protein plays multiple roles in the virology and pharmaceutical field.
Administration of NAbs has become an increasingly attractive option for prophylaxis and treatment of CoV infections. In the prophylaxis and therapy of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, NAbs have shown great potential, moreover, NAbs-mediated protection can also prevent the escape of mutant viruses from cytotoxic T-lymphocytes that are commonly associated with rapid disease progression and severity. Under the great pressure of SARS-CoV-2 prevention and control, it is desirable to develop effective neutralizing Ab-based passive immunotherapy for this zoonotic respiratory pathogen and make it rapidly adapt in humans.
Based on SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, our scientists have developed several NAbs targeting the S glycoprotein. These NAbs can be mapped to multiple epitopes within and outside the RBD of S1 subunit and provide protection against lethal SARS/MERS infection in a murine model following passive immunization.
Based on SARS-CoV-2, Creative Biolabs has rapidly integrated all-round resources and existing research results. Combined with our accumulated extensive experience and Anti-Virus Biomolecular Discovery platform, we can provide comprehensive antiviral products discovery services to help our clients rapidly develop effective NAbs & antiviral peptides to prevent, treat and diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo. What’s more, the antibody responses may improve immunity and will guide future vaccine and therapeutic development efforts. At Creative Biolabs, we have developed several different methods that can be used to generate specific and humanized NAbs, including the immunization of transgenic mice, cloning of small chain variable regions from convalescent patients, naive human antibody phage display libraries and the immortalization of convalescent B cells.
Besides the customized service of NAb and peptide discovery, we also provide SARS-CoV-2 Related Products to support COVID-19 research.
If you are doing some research about the outbreaks of SARS-CoV-2 infection, please feel free to contact us for more professional technical support.
References: