Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Quantification Service
BTK Quantitation Service offers precise measurement and analysis of BTK levels in biological samples, aiding in research and clinical assessments related to immunological and hematological disorders.
Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK)
Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a crucial role in the signaling pathways of B cells, which are an essential component of the immune system. BTK is encoded by the BTK gene located on the X chromosome and is primarily involved in the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway, which is critical for B cell development, differentiation, and activation.
B Cell Development: BTK is vital for the maturation of B cells from progenitor cells in the bone marrow.
Signal Transduction: Upon BCR engagement, BTK is activated and facilitates downstream signaling events that lead to B cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells.
Calcium Mobilization: BTK plays a role in the regulation of intracellular calcium levels, which are key for various cellular processes.
BTK Quantification Service at Creative Biolabs
Amplified luminescent proximity homotransfer assay is a sensitive assay technology often used to quantify proteins, including their phosphorylated forms. When quantifying phosphorylated (activated) BTK versus total BTK, the assay can leverage specific antibodies that discriminate between the phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of the protein. Creative Biolabs offers custom quantification services. These can be tailored to specific needs using different methodologies.
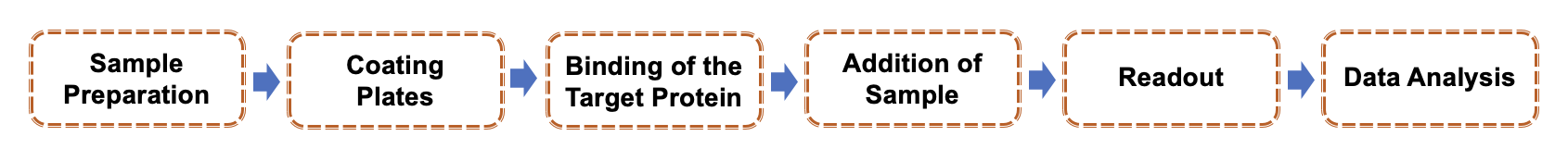
Our BTK quantification service performs as follows:
-
Sample Preparation: Extract cellular proteins from your biological samples (e.g., cell lysates) using the appropriate lysis buffer. Ensure the samples are handled to preserve the phosphorylation state of BTK.
-
Coating Plates: Use microtiter plates coated with appropriate capture antibodies. For quantifying total BTK, you would use a pan-BTK antibody that recognizes both phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms. For phosphorylated BTK, a specific phospho-BTK antibody (that recognizes only the phosphorylated form) would be used.
-
Binding of the Target Protein: Add the sample to the wells of the microtiter plate containing the capture antibody. The BTK proteins in the samples will bind to the antibodies.
-
Detection Antibodies:
-
For total BTK, a detection antibody conjugated with a donor molecule (e.g., a terbium-dyed protein) is added.
-
For phosphorylated BTK, a separate detection antibody that binds specifically to the phosphorylated form, also conjugated with a donor molecule, is used.
-
Addition of Sample: Add acceptor beads that are also tagged with a different fluorescent molecule. When the sample is in close proximity (due to the binding of the detection antibody to the BTK), the energy transfer occurs when excited, leading to a measurable signal.
-
Readout: Measure the luminescent signal using a plate reader. Signal intensity correlates with the amount of BTK or phosphorylated BTK in the sample.
-
Data Analysis
Other Services
In addition to methods based on amplified luminescence proximity homomorphism assays, Creative Biolabs offers a range of bio-immunoassays to help you achieve a variety of applications for BTK quantification.
Frequently Asked Question
Q1: How does BTK activation/deactivation work?
A1:
|
BTK Activation
|
BTK Deactivation
|
|
Mechanism of Activation
|
Downstream Effects
|
Mechanisms of Deactivation
|
Relevance
|
Binding of Antigens: BTK is activated primarily in response to the binding of antigens to the B-cell receptor (BCR), which facilitates the recruitment of BTK to the membrane.
Phosphorylation: BTK undergoes phosphorylation at specific tyrosine residues, particularly at Y223 and Y551, leading to a conformational change that activates its kinase function.
Interaction with Other Proteins: BTK activities are amplified through interactions with other signaling molecules, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and phospholipase C gamma (PLCγ).
|
Calcium Mobilization: Activated BTK promotes the release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum, which is critical for various signaling pathways.
Nuclear Signaling: Enhances the activation of various transcription factors, such as NF-κB and AP-1, leading to B-cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
|
Dephosphorylation: Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), such as SHP-1 and SHP-2, can dephosphorylate BTK, reverting it to an inactive state.
Endocytosis: Following prolonged stimulation, BTK can undergo internalization and degradation, reducing its levels in the cell.
Negative Feedback Mechanisms: Various negative regulatory pathways can inhibit BTK activity, such as the actions of certain cytokines and inhibitory receptors (e.g., CD22, FcγRIIb).
|
-
Cancer Treatment
-
Autoimmune Disorders
-
Research Implications
-
Side Effects and Efficacy
|
Contact Us
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in providing comprehensive BTK Quantification Services to support your research and development needs. If you would like to consult, cooperate, or learn more about our BTK dosing services mentioned above or any of your customization needs, please do not hesitate to contact our technicians. We are always looking forward to working with you to help advance your research goals!
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use




 Download our brochure
Download our brochure

