Flow Cytometry-based H2A.X Activation Assay Service
Introduction
DNA damage in cells can occur due to a variety of endogenous or exogenous factors, including cytotoxic chemical agents, environmental stressors, and physical insults such as radiation. Among the different types of DNA lesions, double-strand breaks (DSBs) are particularly deleterious and represent a severe threat to genomic integrity. The histone variant H2A.X plays a critical role in the cellular response to DSBs, undergoing rapid phosphorylation at serine 139 to form γ-H2AX. This phosphorylation event serves as a sensitive and early marker of DSBs, facilitating the recruitment of DNA repair machinery. Creative Biolabs specializes in assessing H2A.X activation using flow cytometry-a highly effective method for quantifying γ-H2AX levels in individual cells.
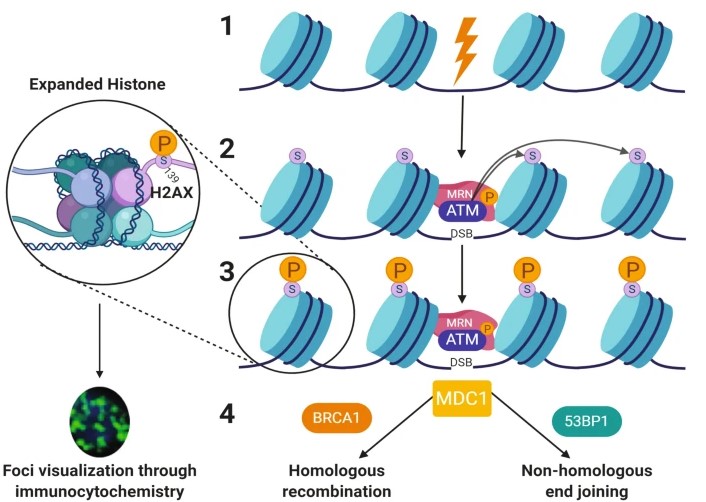 Fig.1 H2AX in DNA damage and repair pathway.1,3
Fig.1 H2AX in DNA damage and repair pathway.1,3
Assessment of H2A.X Activation by Flow Cytometry
Creative Biolabs offers state-of-the-art services for the assessment of H2A.X activation by flow cytometry, providing researchers with critical tools to study DNA damage and repair mechanisms. Our high-throughput, sensitive, and customizable assays are backed by rigorous scientific methodologies, ensuring reliable and actionable data for advanced research and clinical applications.
Service Content
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive services for the assessment of H2A.X activation, encompassing:
-
Sample Preparation: Culturing cells, treating them with DNA-damaging agents, and preparing them for staining.
-
Staining Protocol: We provide optimized dyeing solutions according to the specific project needs of our customers.
-
Flow Cytometric Analysis: Quantifying γ-H2AX levels using advanced flow cytometers.
-
Data Analysis: Interpreting the fluorescence data to provide insights into DNA damage and repair kinetics.
-
Custom Requests: Tailoring protocols and assays to meet specific research needs, available on a custom basis.
Features of Our Service
Sensitivity and Accuracy
By utilizing fluorescence intensity measurements and optimizing image resolution, our assay offers high sensitivity in detecting γ-H2AX foci. This allows for accurate dose-response relationships and precise quantification of DNA repair kinetics, which are critical for assessing individual radiosensitivity.
|
Speed and Precision
Our high-throughput γ-H2AX assay provides rapid and precise results by leveraging the capabilities of FC and advanced image analysis software. The protocol ensures minimal sample handling and quick immunolabeling, making it ideal for large-scale population studies.
|
Scientific Backing
|
Summary
|
Recent advancements, such as the development of high-throughput γ-H2AX assays using imaging flow cytometry (IFC), have further refined the accuracy and speed of γ-H2AX quantification. These techniques allow for the assessment of DSBs and their repair kinetics with unprecedented precision, enabling researchers to harness this information for predictive diagnostics and therapeutic decision-making.
|
|
Result:
|
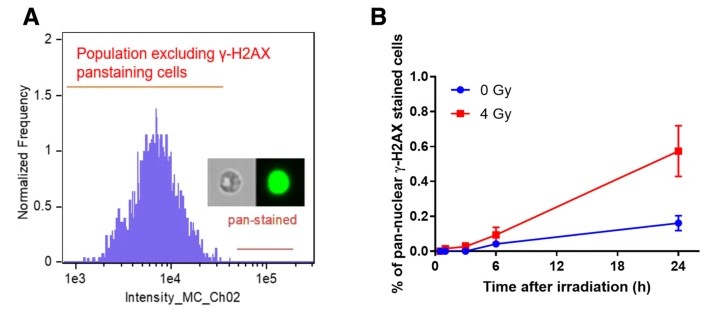
Fig.2 Detection of pan-nuclear γ-H2AX stained cells in irradiated and non-irradiated cells.2,3
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What makes flow cytometry a superior method for assessing H2A.X activation?
A1: Flow cytometry allows for the rapid, quantitative analysis of γ-H2AX levels across thousands of cells in a single run. This high-throughput and quantitative nature makes it superior to traditional methods, which are often time-consuming and less precise.
Q2: How does the quantification of γ-H2AX fluorescence intensity correlate with DNA damage?
A2: Fluorescence intensity is directly proportional to the number of γ-H2AX foci, which represents the occurrence and severity of DNA DSBs. Higher fluorescence intensity indicates more extensive DNA damage and/or more active DNA repair processes.
Creative Biolabs is committed to advancing the field of DNA damage and repair assessment with our sophisticated, high-throughput γ-H2AX assays, empowering researchers with the precision and speed required for groundbreaking discoveries and applications in personalized medicine.
References
-
Noubissi, Felicite K., et al. "Detection and quantification of γ-H2AX using a dissociation enhanced lanthanide fluorescence immunoassay." Scientific Reports 11.1 (2021): 8945.
-
Lee, Younghyun, et al. "Development of a high-throughput γ-H2AX assay based on imaging flow cytometry." Radiation Oncology 14 (2019): 1-10.
-
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 H2AX in DNA damage and repair pathway.1,3
Fig.1 H2AX in DNA damage and repair pathway.1,3

 Download our brochure
Download our brochure

