Mouse Lung Cell KLN205-based Proliferation Assay Service
Unlock Lung Cancer Insights with Precision: Mouse Lung Cell KLN205 Proliferation Assay
Lung cancer research continues to demand accurate and efficient tools to evaluate therapeutic compounds. At Creative Biolabs, we offer advanced cell-based assays designed to assess the functional impact of various compounds on lung cancer cells. Among our services, the mouse lung cell KLN205-based proliferation assay stands out as an effective tool for studying antagonistic activities against KLN205 carcinoma cells. This assay offers insights into cell growth inhibition, providing critical data for lung cancer drug development.
Technical Methods
This assay is a functional assay that uses the KLN205 mouse carcinoma cell line to evaluate the antagonistic effects of test compounds. Luminescence is used as the detection method to measure cell proliferation and viability. By quantifying key metrics such as GI50, TGI, and LC50, this assay offers reliable insights into the inhibitory effects of candidate compounds on lung cancer cell proliferation.
|
Assay Type
|
Cell Type
|
Model
|
Detection Method
|
Control Inhibitor
|
|
Functional
|
KLN205
|
Antagonist
|
Luminescence
|
Staurosporine
|
Procedure
-
KLN205 cells are pre-incubated overnight in 96-well plates at 37°C with 5% CO2.
-
The test compound is added to the wells.
-
Cells are incubated for an additional 72 hours.
-
Luminescence is measured using a microplate reader.
-
Key metrics are recorded:
-
GI50: Concentration at which cell growth is reduced by 50%.
-
TGI: Minimum concentration required to completely inhibit growth.
-
LC50: Concentration causing a 50% reduction in cell viability.
Advantages
This assay provides a powerful and precise method to evaluate the antagonistic effects of compounds on lung cancer cells. Using luminescence as the detection method allows for high sensitivity and reproducibility. Our Mouse Lung Cell KLN205-based Proliferation Assay offers reliable results for assessing compound efficacy, cell viability, and growth inhibition. This assay is highly suited for preclinical drug screening, helping to ensure that only the most effective and promising compounds advance through the development process.
Applications
-
Drug screening for potential lung cancer treatments
-
Evaluation of growth inhibitors in lung carcinoma
-
Determination of therapeutic efficacy and cytotoxicity of compounds
-
Preclinical studies on antagonistic drug mechanisms targeting lung cancer cells
Publication Sharing
This study demonstrates the utility of KLN205 cells in proliferation assays, particularly in evaluating the impact of gene expression modulation on cell growth. Antisense oligonucleotide (LNA-oligo) targeting aldolase A (ALDA) expression significantly reduced ALDA levels in KLN205 cells under glucose-deprived conditions. The reduction in ALDA expression corresponded with a marked decrease in cell proliferation, underscoring the role of ALDA in cellular metabolic processes essential for tumor cell growth. These findings highlight the relevance of KLN205 cells as a model for assessing the effects of metabolic stress and gene expression alterations on cancer cell proliferation.
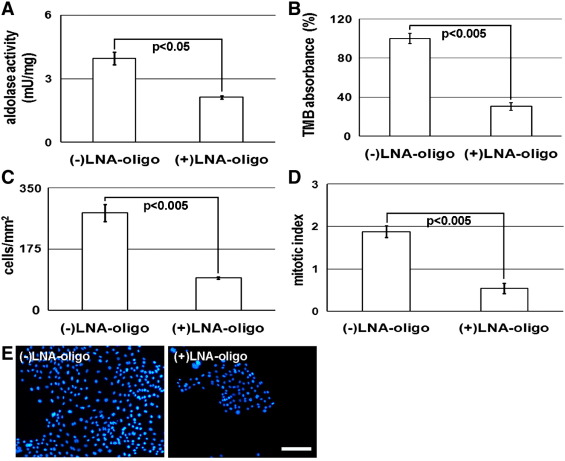 Fig.1 The effect of antisense oligonucleotide (LNA-oligo) on ALDA expression and proliferation of the KLN-205 cells in the absence of glucose.1
Fig.1 The effect of antisense oligonucleotide (LNA-oligo) on ALDA expression and proliferation of the KLN-205 cells in the absence of glucose.1
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How is the assay result measured?
A1: The results are measured using luminescence, which detects cell viability and proliferation rates.
Q2: Is this assay suitable for high-throughput screening?
A2: Yes, the 96-well plate format and luminescence detection make it compatible with high-throughput screening setups.
Q3: Can the assay be customized for specific compounds or conditions?
A3: Yes, we can tailor the assay to test specific conditions or adjust parameters based on your research needs.
If you're looking to evaluate the growth inhibition potential of your compounds in lung cancer models, our mouse lung cell KLN205-based proliferation assay provides the reliable and actionable data you need. Contact Creative Biolabs today to discuss how this assay can support your research and development efforts in the fight against lung cancer.
Reference
-
Mamczur, Piotr, et al. "Nuclear localization of aldolase A correlates with cell proliferation." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 1833.12 (2013): 2812-2822. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 The effect of antisense oligonucleotide (LNA-oligo) on ALDA expression and proliferation of the KLN-205 cells in the absence of glucose.1
Fig.1 The effect of antisense oligonucleotide (LNA-oligo) on ALDA expression and proliferation of the KLN-205 cells in the absence of glucose.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure