Heating™ Targeting Tumor Microenvironment Services for Cancer Immunotherapy
TME
Definition: Cancer cells interact closely with the extracellular matrix, stromal cells, and immune cells to promote chronic inflammation and immunosuppression, while creating a pro-angiogenic intratumoral environment that is conducive to cancer cell adaptation and growth, called the tumor microenvironment (TME).
Main ingredients: 1. Cellular components: including tumor cells and their surrounding immune cells, fibroblasts, inflammatory cells, and glial cells. 2. Matrix components: cellular interstitium, fiber components, microvascular, etc. 3. Soluble factors: IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), cytokines and chemokines.
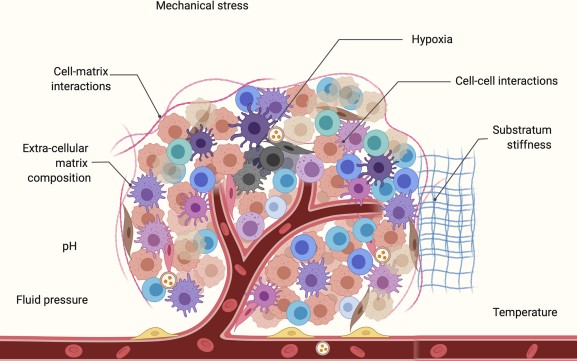 Fig.1 Major components of the tumor microenvironment.1,3
Fig.1 Major components of the tumor microenvironment.1,3
Why target TME: The immune status of TME is an important factor affecting tumor progression, which may contribute to or hinder the anti-tumor immune response. The use of immunotherapy strategies targeting TME and intervention of non-tumor cells and components can transform the immune response from tumorigenesis to tumor suppressor.
Hot Tumors and Cold Tumors
|
Hot Tumors
|
Hot Tumors
|
|
Immunoinflammatory tumors are "hot tumors" and are characterized by high T cell infiltration, elevated interferon-γ signaling pathway, PD-L1 expression, and high tumor mutational burden (TMB: The higher the TMB, the more neoantigens may be produced and the higher the tumor immunogenicity).
|
Immune desert tumors can be referred to as "cold tumors", in immune rejection tumors, CD8+ T lymphocytes are localized at the edge of invasion and cannot effectively infiltrate the tumor, and in immune desert tumors, CD8+ T lymphocytes are not present in the tumor and its surroundings.
|
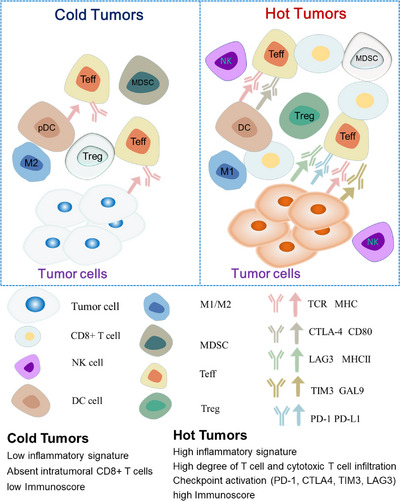 Fig.2 Distinguish between "hot and cold" tumors based on the distribution of immune cells.2,3
Fig.2 Distinguish between "hot and cold" tumors based on the distribution of immune cells.2,3
In addition to poor T cell infiltration, T cell initiation may be inhibited in the TME of cold tumors, in addition, the deposition of extracellular matrix in lesions and the establishment of a physical and chemical barrier by "stiff" matrix-induced hypoxia hinder T cell infiltration. Populations of immunosuppressive cells are also present in cold tumors, where they inhibit the function of CD8+ T cells. In summary: cold tumors lack innate immunity, or there are innate antitumor immune features in "cold tumors".
Our Service
Promote T cell initiation by increasing tumor antigen expression and restoring antigen processing and presentation mechanisms (e.g., STING agonists); Reprogramming the tumor microenvironment to facilitate T cell trafficking and allow T cells to infiltrate tumors more efficiently. These methods can help "cold" tumors transform into "hot" tumors, thereby improving the efficiency of immunotherapy. Creative Biolabs' scientists provide a reliable and comprehensive service for your immuno-oncology research by understanding the immune status of the tumor microenvironment and providing appropriate heated-cold tumor immunotherapy strategies.
STING agonists, oncolytic viruses, photothermal and photodynamic therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, among others, are able to induce immunogenic cell death (ICD) to promote T cell activation and activation.
Studies have shown that inhibition of the deubiquitinating enzyme USP8 can remodel the TME, turning "cold tumors" into "hot tumors", thereby improving the molecular mechanism of tumor immunotherapy efficacy. Creative Biolabs offers targeted tumor microenvironment heated cold tumor services to accelerate your tumor immunity.
In addition to the above two strategies, Creative Biolabs also offers nanomedicine development services. Nanomedicine facilitates the transformation from "cold tumors" to "hot tumors", mainly through four targeted pathways: physical barrier CAFs, targeting DNA/RNA, co-stimulation of embryoid bodies, and cellular stress.
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive targeted immuno-stimulatory conjugate development service that combines precise antibody engineering with strategic payload selection. We begin by identifying and optimizing antibodies with high specificity and internalization efficiency, using advanced methods like phage display and analytical assays. Tailored payloads-such as cytokines, TLR or STING agonists-are conjugated via cleavable, stable linkers, ensuring targeted immune activation. Our platform emphasizes site-specific conjugation and optimized drug-to-antibody ratios (DAR) for consistency and scalability. All conjugates undergo extensive in vitro and in vivo evaluation, focusing on immune stimulation, safety, and pharmacokinetics to ensure therapeutic potential.
Prospect and Future
The immunosuppressive microenvironment of "cold tumors" greatly reduces the effect of immunotherapy. Creative Biolabs has been continuously focusing on new technologies and new therapies to help improve the immunosuppressive microenvironment by providing different cold tumor heating strategies, and bringing new technical services to tumor immunotherapy.
If you are interested in our cold tumor heating strategies, please contact us now. Or if you have other needs in the field of cancer immunotherapy targeting the TME, you can also contact our technicians directly to get the corresponding information! Creative Biolabs' professionals are always here to help with your projects and needs!
References
-
Sheth, Maulee, and Leyla Esfandiari. "Bioelectric dysregulation in cancer initiation, promotion, and progression." Frontiers in oncology. (2022) 12 846917.
-
Wang, Lianjie, et al. "Hot and cold tumors: Immunological features and the therapeutic strategies." MedComm 4.5 (2023): e343.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Major components of the tumor microenvironment.1,3
Fig.1 Major components of the tumor microenvironment.1,3
 Fig.2 Distinguish between "hot and cold" tumors based on the distribution of immune cells.2,3
Fig.2 Distinguish between "hot and cold" tumors based on the distribution of immune cells.2,3
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure