All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs is a CRO solution firm launched by a team of scientists and professionals with vast knowledge and background in cell therapy research and development. We are committed to offering the best goods and services to clients globally in the academic and industrial sectors, participating in the quest of breakthrough scientific discoveries to substantially advance preclinical and clinical research.
CD70 is a single-chain membrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of about 37 kDa. CD70 belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/nerve growth factor (NGF) family and has a similar composition to other members of the TNF/NGF family. CD70 consists of an extracellular region, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular region. The extracellular region contains four conserved modules characteristic of the TNF/NGF family, with the module closest to the membrane being the signaling sequence for the release of CD70 molecules. The intracellular zone, on the other hand, contains a small intracellular region that activates CD27 and mediates the activation of immune cells, and participates in the regulatory process of the immune response. Abnormal expression of CD70 is associated with a variety of diseases, such as tumors, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases. In tumors, high expression of CD70 is associated with tumor aggressiveness, malignancy, and poor prognosis, thus becoming a potential target for tumor therapy.
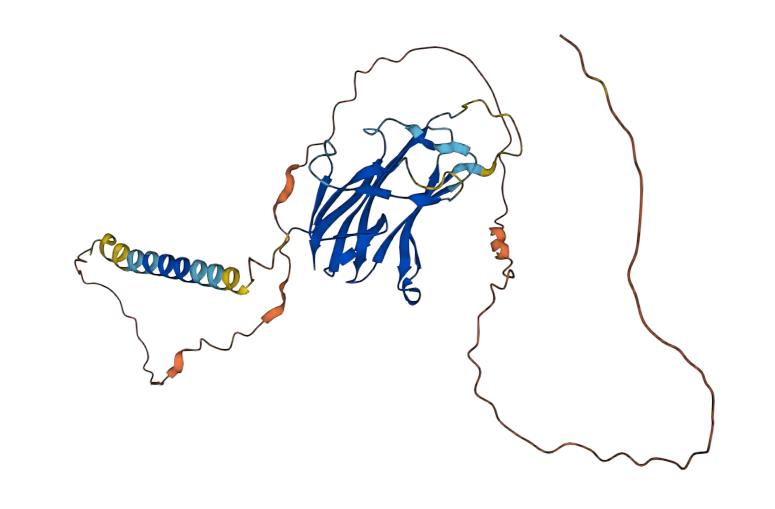 Fig.1 Structure of CD70
Fig.1 Structure of CD70
The main signaling pathway of CD70 is the CD27 signaling pathway. CD27 binding to CD70 activates several signaling pathways that promote the survival, proliferation, differentiation, and function of immune cells. CD70 is highly expressed in some tumors and activates the CD27 signaling pathway, which inhibits the killing effect of T cells, attenuates immune attack, and promotes tumor growth and proliferation. Studies have shown that CD70 is highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and positively correlates with malignancy. CD70 activation of the CD27 signaling pathway promotes multiple aspects of lung cancer cells, including proliferation, metastasis, and escape from immune surveillance, thereby promoting the development and progression of lung cancer. It has also been found that CD70 is also expressed at high levels in breast cancer patients, and both CD70 and CD27 have been detected to be closely related to multiple indicators such as tumor type, grade, and prognosis.
Moreover, the CD70/CD27 signaling pathway is involved in the immune response to various viral infections, such as hepatitis B virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Moreover, it was found that the binding of CD27 receptor and CD70 activates the IκB kinase (IKK) complex through members of the TNF receptor (TNFR)-related factor family, which allows IκB to be degraded and further activates nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) nuclear transcription factor, thus promoting the expression of inflammatory genes and the inflammatory response. But the high expression of CD70 in tumors is unique. By binding CD27, the NF-κB pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, and Akt pathway can be activated to promote the proliferation, apoptosis inhibition, and metastasis of tumor cells, thus affecting the occurrence, development, and prognosis of tumors.
CD70 has emerged as one of the important targets in oncology therapy, and many studies are underway, including preclinical and clinical trials. Some of these studies suggest that CD70-based CAR-T cell therapy may have important efficacy and promising applications. CD70 CAR-T cell therapy can safely and effectively treat patients with CD70-positive malignant B-cell lymphoma without significant serious side effects. In addition, many studies have also found that CD70-based CAR-T cell therapy can inhibit the growth and metastasis of CD70-positive tumors in vivo, thus demonstrating significant anti-cancer effects. CD70 as a target for CAR-T cell therapy is still in the early stages of research. Currently, the main research is focused on CAR-T cell therapy for CD70-positive chemotherapy-refractory, in vivo and in vitro multiple myeloma, lung cancer, lymphoma and leukemia, and other malignancies. Its main research interests involve immunotherapy, malignancies, CAR design, and clinical trials. In particular, CAR design has undergone great innovation. The key to CAR design for CD70 CAR-T cell therapy in experiments is how to improve the affinity and specificity of CARs to enhance the therapeutic effect of CAR-T cells. A well-designed CAR structure can improve the targeting and stability of CAR-T cells while avoiding the risk of the immune system's response to CAR.
Table 1. Ongoing CD70 -Targeted CAR Cell Therapy Clinical Trials
| NCT Number | Title | Status | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Phases |
| NCT04662294 | CD 70 CAR-T for Patients With CD70 Positive Malignant Hematologic Diseases | Recruiting | Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Non-hodgkin's Lymphoma|Multiple Myeloma | Zhejiang University|Yake Biotechnology Ltd. | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT05353530 | Phase I Study of IL-8 Receptor-modified CD70 CAR-T Cell Therapy in CD70+ and MGMT-unmethylated Adult Glioblastoma (IMPACT) | Not yet recruiting | Glioblastoma | University of Florida|United States Department of Defense|AM Rosen Foundation | Phase 1 |
| NCT05420519 | Clinical Study of CD70-targeted CAR-T Therapy for Advanced/Advanced Renal Cancer | Recruiting | Metastatic Tumor|Renal Cell Carcinoma|Advanced Cancer | Chongqing Precision Biotech Co., Ltd | Phase 1 |
| NCT05518253 | A Clinical Study of CD70-targeted CAR-T in the Treatment of CD70-positive Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors | Recruiting | Metastatic Tumor|Advanced Solid Tumor|Renal Cell Carcinoma|Ovarian Cancer|Cervix Cancer | Weijia Fang, MD|Chongqing Precision Biotech Co., Ltd|Zhejiang University | Phase 1 |
| NCT05468190 | A Clinical Research About CD70-positive Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors Treated by CD70-targeted CAR-T | Recruiting | Metastatic Tumor|Advanced Solid Tumor|Renal Cell Carcinoma|Ovarian Cancer|Cervix Cancer | Chongqing Precision Biotech Co., Ltd | Phase 1 |
| NCT05420545 | A Clinical Study of CD70-targeted CAR-T in the Treatment of CD70-positive Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors | Recruiting | Metastatic Tumor|Advanced Solid Tumor|Renal Cell Carcinoma|Ovarian Cancer|Cervix Cancer | Chongqing Precision Biotech Co., Ltd | Phase 1 |
| NCT05667155 | Clinical Study of Cord Blood-derived CAR NK Cells Targeting CD19/CD70 in Refractory/Relapsed B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | Recruiting | B-cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma | Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University | Phase 1 |
| NCT05438368 | GD2/CD70 Bi-specific CAR-T Cell Therapy | Recruiting | Cancer Disease | Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05437341 | PSMA/CD70 Bi-specific CAR-T Cell Therapy | Recruiting | Cancer Disease | Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT02830724 | Administering Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes Transduced With a CD70-Binding Chimeric Antigen Receptor to People With CD70 Expressing Cancers | Recruiting | Pancreatic Cancer|Renal Cell Cancer|Breast Cancer|Melanoma|Ovarian Cancer | National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT04429438 | Multi-CAR-T Cells Targeting B Cell Lymphomas | Recruiting | B Cell Lymphoma (BCL) | Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute|The Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University|Shenzhen Children's Hospital | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05436496 | CD19/70 Bi-specific CAR-T Cell Therapy | Recruiting | B Cell Malignancies | Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT04502446 | A Safety and Efficacy Study Evaluating CTX130 in Subjects With Relapsed or Refractory T or B Cell Malignancies (COBALT-LYM) | Recruiting | T Cell Lymphoma | CRISPR Therapeutics AG|CRISPR Therapeutics | Phase 1 |
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION