All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Neuroendocrine (NEC) neoplasm is a type of less differentiated tumor that originates from various tissues and commonly occurs in the gastroenteropancreatic tract (GEP-NEC). The incidence of this cancer is rare but presents a poor prognosis for limited clinical therapeutics and knowledge of the disease. Cancer organoids are valuable preclinical models for neuroendocrine cancer studies and potential drug and therapy development. Creative Biolabs offers a functional cancer organoids platform, including organoids of multiple cancers that retain the main histopathological and molecular features of tumors and provide CAR-T efficacy assessment in vitro.
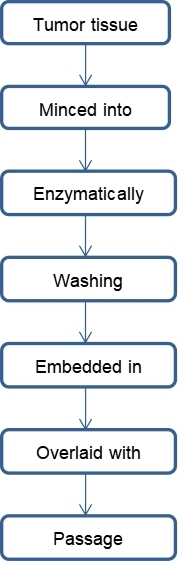 Fig.1 Workflow for NEC organoid establishment. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Workflow for NEC organoid establishment. (Creative Biolabs)
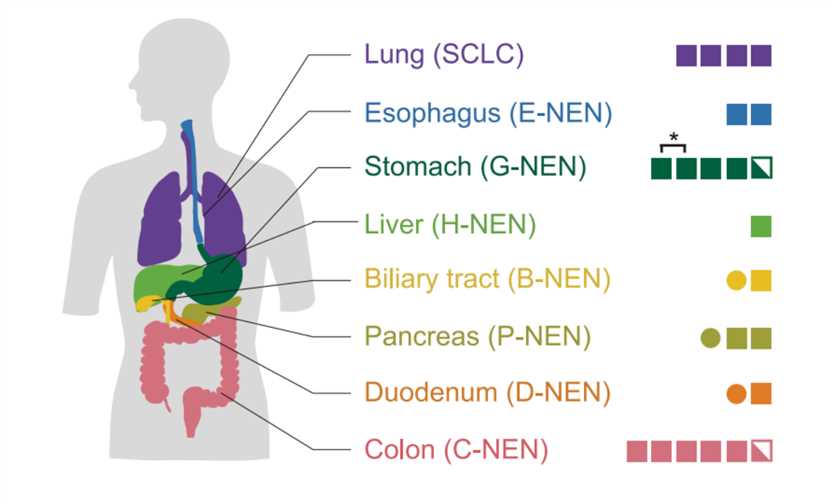 Fig.2 Neuroendocrine organoids established from different organs. (Kawasaki, et al., 2020)
Fig.2 Neuroendocrine organoids established from different organs. (Kawasaki, et al., 2020)
NEC cancer organoid models can be developed from various tissue of organs, including but not limited to this.
The original tumors established cancer organoid lines, and organoid xenografts, can be characterized to describe the correlation of the model to clinical tissues by histology, immunohistochemistry, and sequencing technology.
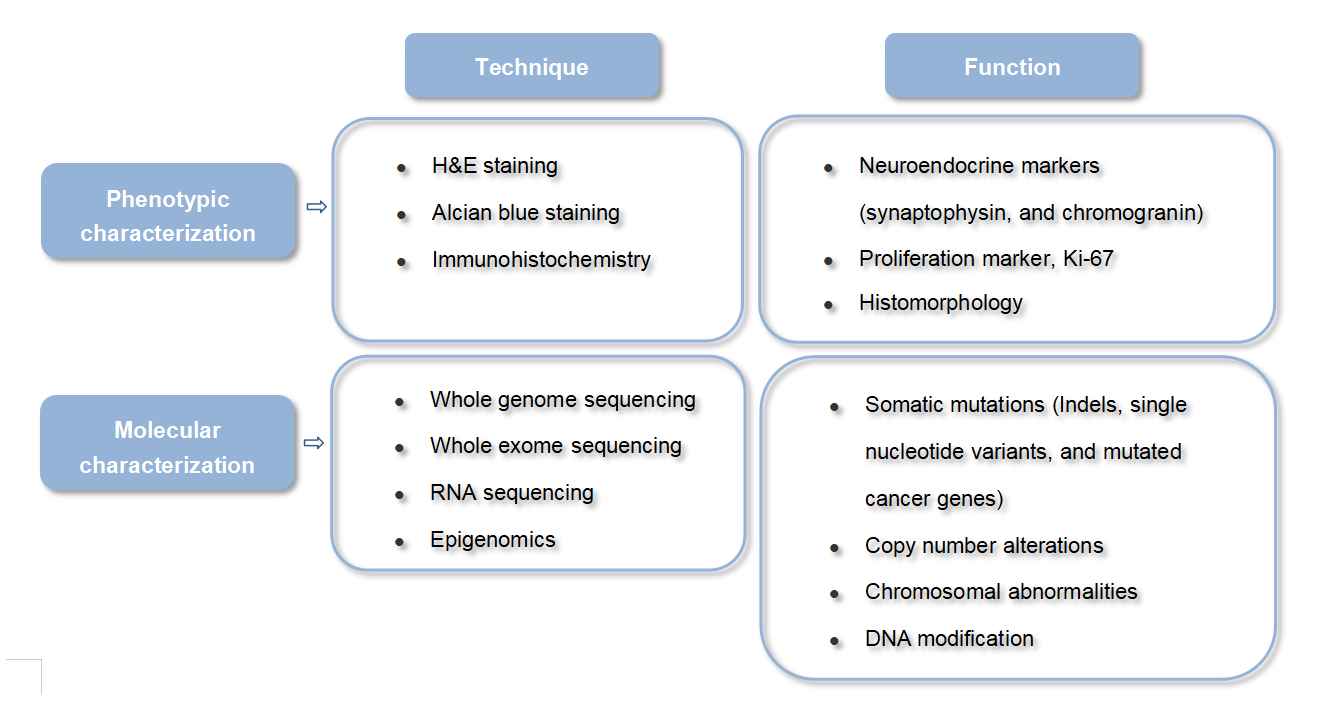
Organoid models have a broad application in neoplasm formation and pathology studies as well as clinical treatment discovery.
| Tittle: Patient-derived Neuroendocrine Cancer Organoid Models |
|
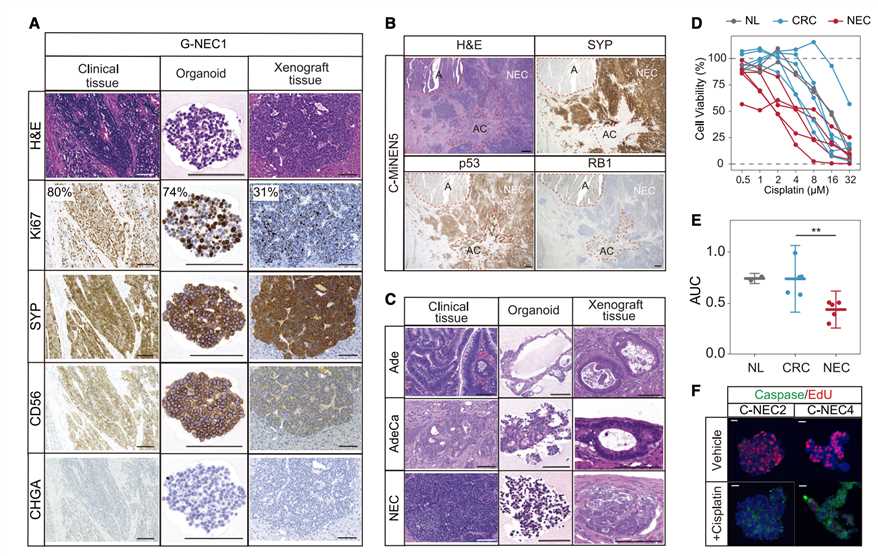 Fig.3 Histomophologically characterization of patient-derived GEP-NEC organoids and their sensitivity to drugs. (Kawasaki, et al., 2020) Picture A to C show neuroendocrine markers staining results of the clinical specimen, organoids, and organoids xenograft; Picture D to F show the drug sensitivity of colorectal-NEC is correlated to clinical cases. |
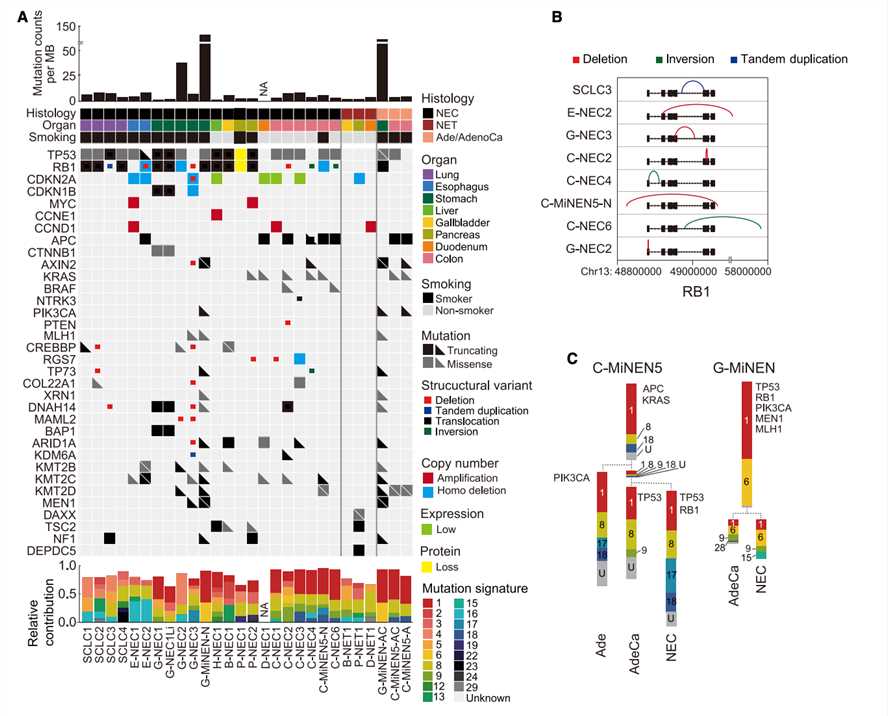 Fig.4 Genetic characterization of patient-derived GEP-NEC organoids. (Kawasaki, et al., 2020) Picture A and B show mutational signatures of organoids, and picture C shows the genetic divergence of organoids. |
Creative Biolabs offers high-quality organoids for tumor biology study and treatment investigation. If you'd like to know how we can be involved in your project, please contact us for detailed information.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION