Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider of novel antibody and peptide discovery against bacteria. Anti-Bacteria Biomolecular Discovery is one of our most distinctive platforms. Based on this platform, we can offer optimal solutions to help our global clients to discover the high-quality antibody and peptide targeting Staphylococcaceae.
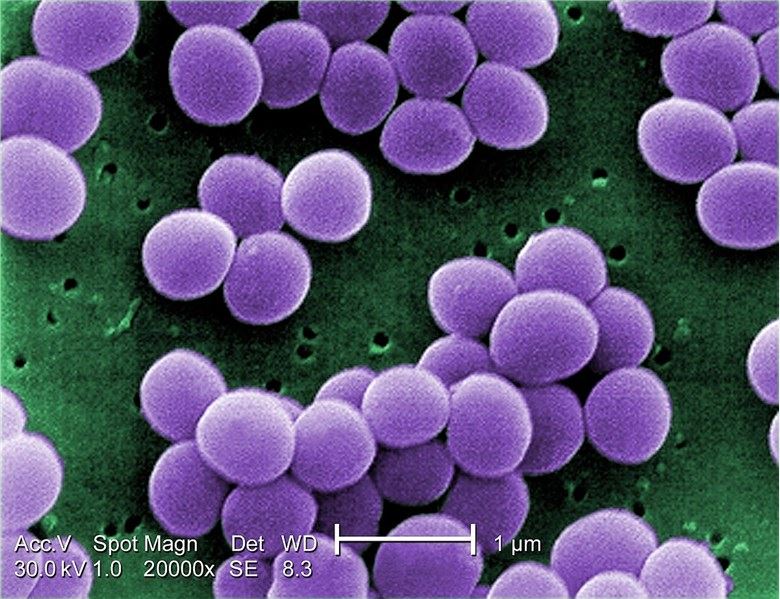 Fig. 1 Scanning electron micrograph
Fig. 1 Scanning electron micrographStaphylococcus belongs to the Staphylococcaceae family in the order Bacillales, a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. They appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters under the microscope. A wide variety of diseases in humans and animals can be caused by Staphylococcus through either toxin production or penetration. Staphylococcus aureus is the second-most common bacterial pathogen isolated from humans. It causes a variety of infections including soft tissue, skin, and bone infections and life-threatening endocarditis, sepsis and pneumonia. Furthermore, the emergence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) increases the complication for treatment of Staphylococcus infection, which brings challenges to researches on vaccines and novel immunotherapies development.
Currently, many antigens of S. aureus including secreted toxins, microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMMs), lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and quorum sensing peptide have been identified as candidate targets for mAbs targeting S. aureus infection. A recent study reports that S. aureus surface protein A (SasA), composed of 2,271 amino acids, is one of the surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMMs) and regarded as a potential target for a mAb-based immunotherapy against S. aureus infections, especially MRSA infections. In both sepsis and peritoneal infection models, a protective mAb (2H7) targeting the conserved domain of SasA improves the survival of BALB/c mice infected by two prevalent MRSA clones and enhanced bacterial clearance in kidneys.
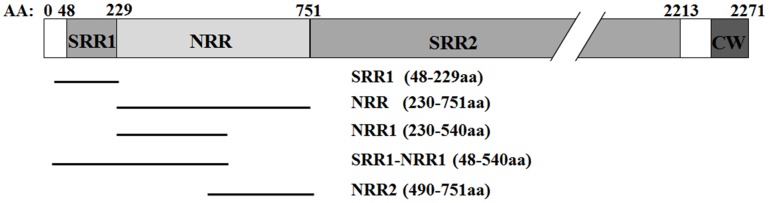 Fig. 2 Sequence analysis of SasA (Yang et al. 2016).
Fig. 2 Sequence analysis of SasA (Yang et al. 2016).
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), generally containing 12-100 amino acids, are evolutionarily conserved and crucial components of the innate immune system in all complex organisms. They can protect the host from various pathogenic bacteria and viruses. With the widespread use of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance has emerged. In order to overcome this issue, the discovery of AMP becomes very important. Giving the fact that some unique clones exhibiting antibacterial activity against S. aureus is selected and isolated from a metagenomic library, Creative Biolabs devlopes custom peptide libraries and peptide array, which facilitates the discovery of AMP targeting Staphylococcus by using the pathogen as a target organism.
With years of experience in the field of antibody development, Creative Biolabs is honored to offer first-in-class service for the discovery of antibodies and peptides targeting Staphylococcus for multiple downstream applications. We have established a powerful AntInfectTM Platform containing phage display, antigen-specific B lymphocytes cytometry technology, and hybridoma technology, which is optimal for antibacterial antibodies and peptides discovery. If you are interested in our services, please free to contact us for more information.
Reference