FLT3 Assay Portfolio Service
Background Expression Pathways What We Can Offer Why Choose Us FAQs Customer Review Related Services Contact Us
Structure
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), also known as fetal liver kinase-2 (Flk-2) or stem cell tyrosine kinase-1 (STK-1), is a type III receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). The human gene is located on chromosome 13q12 and encodes a 993 amino acids protein of 110 kD. Glycosylation with complex carbohydrates leads to the active and membrane-bound 158 kDa form. FLT3 is composed of an immunoglobulin-like extracellular ligand-binding domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain (TMD), a juxtamembrane dimerization domain (JMD), and a highly conserved intracellular tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) interrupted by a kinase insert. FLT3 is characterized by the presence of five immunoglobulin-like motifs within their extracellular part. In the cytoplasm, the JMD extends and connects with the two kinase domain lobes (TK1 and TK2) that are linked by the activation loop.
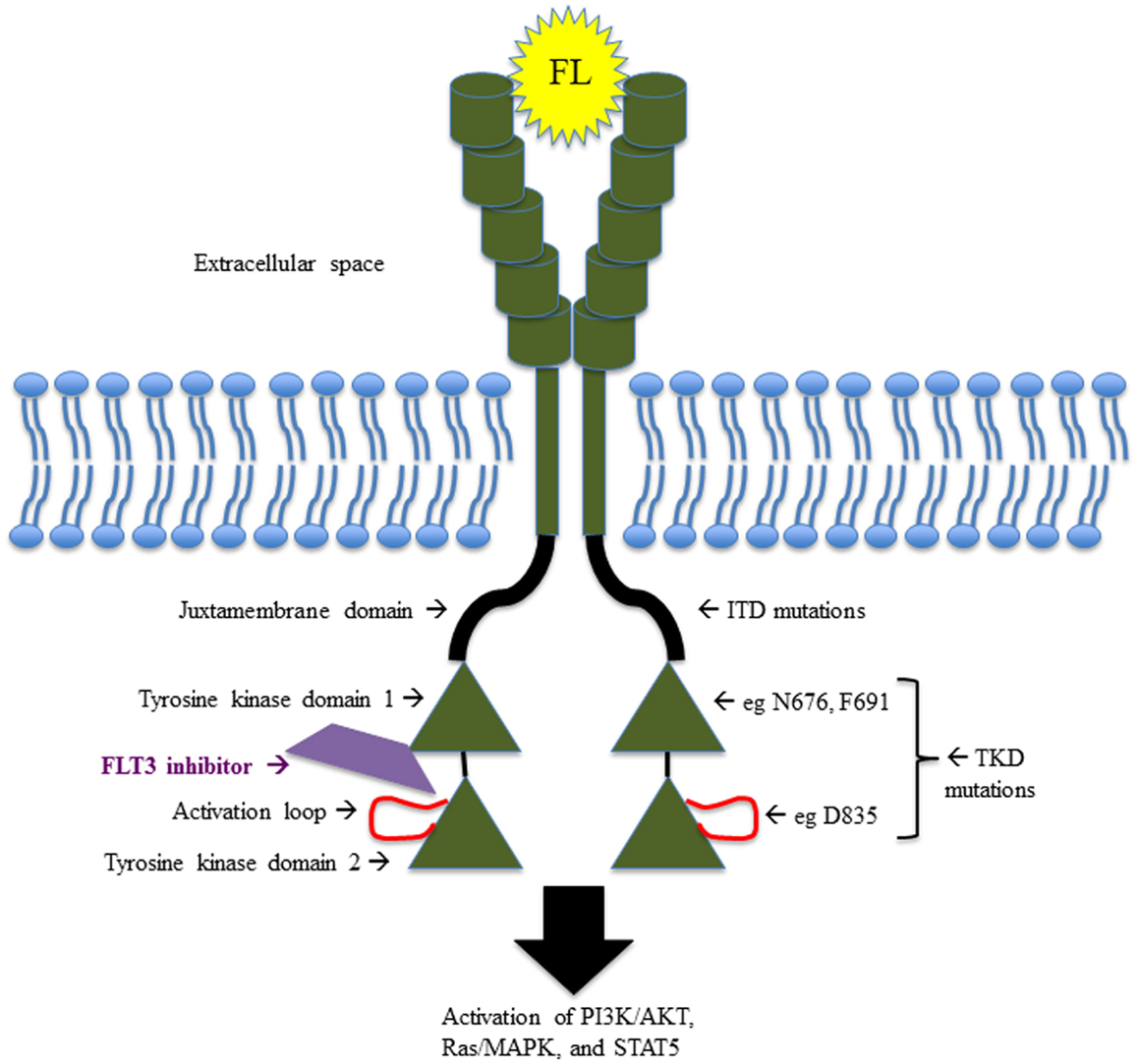 Fig.1 The structure of FLT3.1, 3
Fig.1 The structure of FLT3.1, 3
The Expression of FLT3
FLT3 is expressed in normal human bone marrow. FLT3 is predominantly expressed by hematopoietic progenitor cells and its ligand (FL) is expressed as a membrane-bound or soluble form by bone marrow stromal cells. The expression is lost or reduced during differentiation into mature lymphoid and myeloid cells. The FLT3 receptor is overexpressed on the majority of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts, and FL stimulation enhances proliferation and reduces apoptosis. FLT3 is also expressed in the human brain, placenta, and testis, though its function in these tissues remains unclear.
FLT3 Activation and Signal Pathways
The inactive form of FLT3 is maintained by interactions between the juxtamembrane (JM) domain and the kinase domain. Upon binding of the bivalent ligand through the third Ig-like domain (D3), JM is released from the kinase domain and autophosphorylation on several tyrosine residues takes place. And then auto-phosphorylation induces multiple signaling cascades. FLT3 mainly signals through Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathways, involved in proliferation and survival.
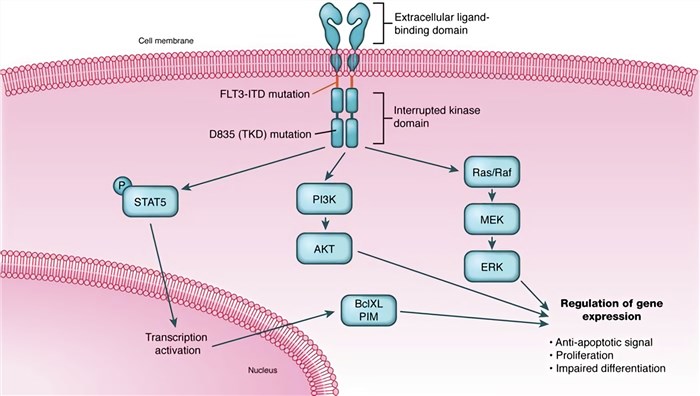 Fig.2 FLT3 mutations and signal pathways.2, 3
Fig.2 FLT3 mutations and signal pathways.2, 3
What We Can Offer?
Most AML patients overexpress the wild-type FLT3 receptor in their blast cells. In addition, FLT3 mutations are common drivers of AML formation, identified in approximately one-third of newly diagnosed adult patients, and are common in pediatric AML as well. Because of the importance of FLT3 in tumors, Creative Biolabs provides a full set of FLT3 assay portfolio services for research, including but not limited to
-
FLT3-ITD gene mutation analysis
-
Cell proliferation assay
-
Cell apoptosis assay
-
In vitro kinase assay
-
Measurement of free intracellular calcium
-
Cell chemotaxis assay
-
Western blotting
-
Immunoprecipitation
Why Choose Us?
With deep expertise and cutting-edge technology, we're your trusted partner in AML research. Our team combines scientific rigor with a proven track record in tackling complex challenges—like targeting the FLT3 receptor, a key driver in AML.
FLT3 mutations (ITD and TKD) fuel aggressive disease and poor outcomes, while resistance mutations like F691L limit treatment success. We specialize in overcoming these hurdles, offering tailored solutions backed by the latest research. When you work with us, you gain more than data—you get a strategic ally committed to advancing your AML drug discovery.
Let's turn challenges into breakthroughs. Partner with Creative Biolabs and move forward with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What types of FLT3 mutations can you analyze with this service?
A1: We offer comprehensive analysis for both FLT3-internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutations and TKD point mutations. Our assays are designed to detect a wide range of these mutations, including specific resistance-conferring mutations like FLT3-F691L.
Q2: Can you help me investigate mechanisms of drug resistance?
A2: Absolutely. Our service is designed to go beyond basic screening. We use advanced techniques like Western Blotting, immunoprecipitation, and downstream pathway analysis to investigate the specific mechanisms of drug resistance, helping you develop therapies that can overcome these challenges.
Q3: Do you work with a variety of cell lines and patient samples?
A3: Yes. Our assays have been validated on a wide range of cell lines and can also be adapted to work with primary patient-derived samples. We recommend a consultation to discuss the specifics of your sample type to ensure the most effective project design.
Customer Review
-
Assurance Against Gatekeeper Mutations
Using Creative Biolabs' FLT3 assay portfolio service in our research has significantly improved our ability to validate the potency of our lead compounds against a range of FLT3 mutations. Their detailed in vitro kinase assay data, including against the tough FLT3-F691L gatekeeper mutation, provided the evidence we needed to move forward confidently. - Dr. R.A.V.E.N.
-
Uncovering Resistance Pathways
The team's comprehensive approach was invaluable. We were struggling to understand why our compound was losing efficacy in a resistant cell line. Their thorough Western Blotting and immunoprecipitation analysis helped us uncover a parallel signaling pathway that was activated, which completely changed our therapeutic strategy. - Dr. J.O.N.E.S.
Related Services
To further support your AML research and drug discovery efforts, we recommend exploring our other complementary services:
Syngeneic Models
Syngeneic mouse models, with their functional immune systems, are ideal for preclinical testing of cancer immunotherapies. Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive service using these models to facilitate in vivo screening and evaluation of your drug candidates.
Learn More →
Aqueous Solubility Analysis Service
Aqueous solubility is a critical parameter in drug development. Creative Biolabs provides high-quality aqueous solubility analysis services with advanced methodologies. Their expert team ensures precise and reliable measurements, which helps with informed decision-making and optimizing drug candidates.
Learn More →
How to Contact Us
Creative Biolabs is your strategic partner in advancing AML research. Our FLT3 Assay Portfolio Service is meticulously designed to provide the insights and data you need to succeed in a complex and competitive field. Contact our team today to begin the conversation about your project.
References
-
Annesley, Colleen E., and Patrick Brown. "The biology and targeting of FLT3 in pediatric leukemia." Frontiers in oncology 4 (2014): 263. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00263
-
Kavanagh, Simon, et al. "Emerging therapies for acute myeloid leukemia: translating biology into the clinic." JCI insight 2.18 (2017): e95679. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.95679
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Fig.1 The structure of FLT3.1, 3
Fig.1 The structure of FLT3.1, 3
 Fig.2 FLT3 mutations and signal pathways.2, 3
Fig.2 FLT3 mutations and signal pathways.2, 3
