Human Pancreas Cell MIA PaCa-2-based Proliferation Assay Service
Human Pancreas Cell MIA PaCa-2
MIA PaCa-2 is a human tumor cell line that is extensively utilized in research, especially in studies that are related to pancreatic cancer. This cell line exhibits highly aggressive characteristics, robust growth, and proliferation capabilities in vitro. It is frequently used to assess the effectiveness and mechanisms of different anticancer drugs, particularly in the context of pancreatic cancer research. MIA PaCa-2 cells demonstrate sensitivity to multiple chemotherapeutic agents, making them a crucial model for investigating treatment strategies for pancreatic cancer.
MIA PaCa-2-based Proliferation Assay
Investigating how a compound affects MIA PaCa-2 cell proliferation is essential for identifying potential cancer therapies, elucidating their mechanisms of action, and evaluating toxicity and safety. In the MIA PaCa-2-based proliferation assay, staurosporine was used as a control. Staurosporine has a significant impact on pancreatic cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. It effectively increases the apoptosis rate in cell lines. The mechanism involves the activation of caspase-9, an essential component of the apoptotic pathway. Additionally, Staurosporine reduces the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl2 and Bad in pancreatic cancer cells, further promoting cell death. This compound serves as a suitable positive control for in vitro apoptosis assays in these pancreatic cancer cell lines, highlighting its potential therapeutic relevance.
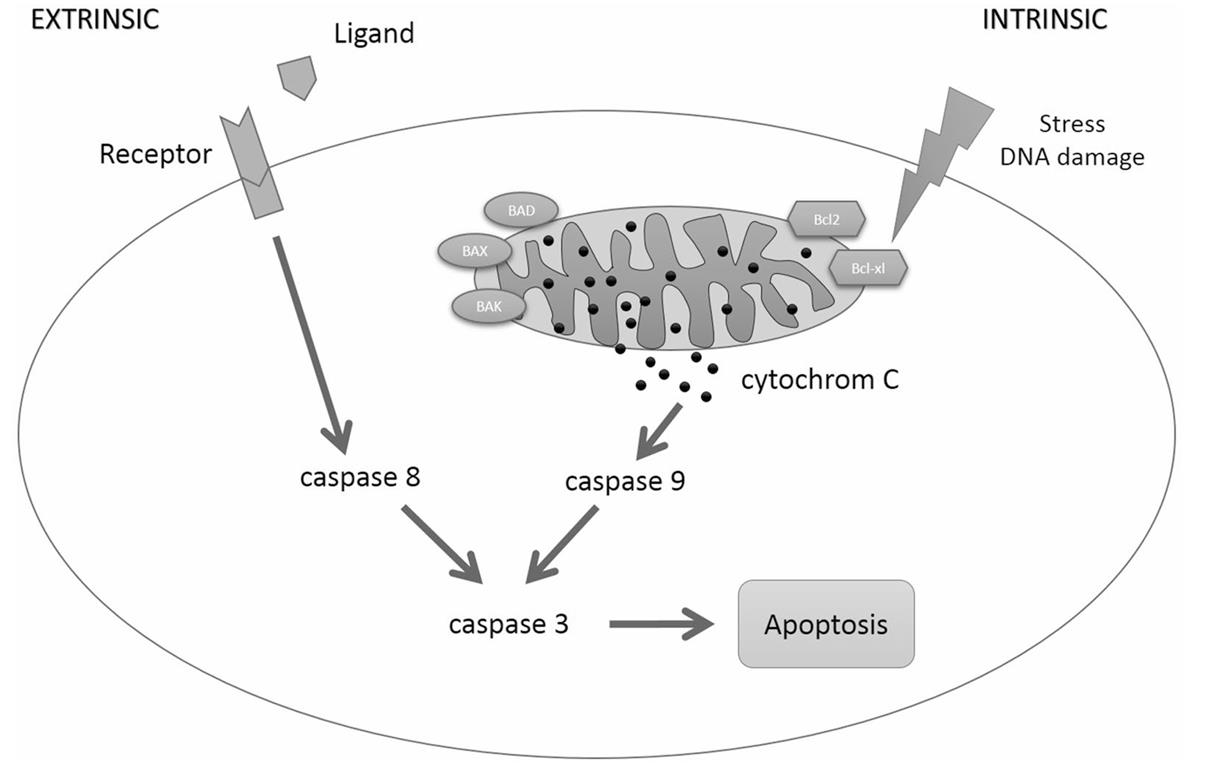 Fig. 1 Staurosporine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.1
Fig. 1 Staurosporine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.1
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of cell proliferation assay services. You might also be interested in another proliferation assay involving a different pancreatic cancer cell line HPAC. For more details or any other needs, please contact us.
Reference
-
Malsy, M., et al. "Staurosporine induces apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma cells PaTu 8988t and Panc-1 via the intrinsic signaling pathway." Eur J Med Res 24.5 (2019). Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig. 1 Staurosporine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.1
Fig. 1 Staurosporine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure