T Cell-based In Vivo Skin Test Assay
The antigen-based skin test is validated to be accurate, acceptable, and cost-effective. With a deep understanding and experience in immunological research, Creative Biolabs offers cancer epitope analysis service using T cell-mediated in vivo immune response following an intradermal skin test.
Introduction of in Vivo Skin Test
The skin test method is used to measure the antigen-specific T cell response using delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH). In this test, the antigens are injected into the skin to induce a cellular response. A representative skin response is deciphered by an "induration" around the injection site resulting from responsive memory T cell metastasis and the function of secreting cytokines at the injection site. The diameter of the "induration" reflects the collective production of cytokines that can describe the whole response of immune cells. The method has many merits over other available approaches. For example, the test is simple and avoids the complex cell isolation, culturing process, and analysis using extra experimental equipment.
Creative Biolabs Services
As the skin assay is an easier and more economical test for detecting T cell response to pathogenic antigens, it is a perfect screening method for identifying potential cancer epitopes in large candidates. Creative Biolabs offers T cell-based in vivo skin test assay for our clients.
Workflow

The Procedure of the Assay
-
First Induction of T-Cell Immunity
The model animals (mice, pigs, cattle) are infected with a mixture of cancer epitope peptides. After infection, the animals are housed in cages contained within laminar flow safety enclosures in a Level III biosecurity facility.
-
Re-stimulation of T-Cell Immunity
The DTH-based skin test was performed by injecting separate candidate peptides on the flank of pigs intradermally. In cattle, the antigens are injected into two sides of the neck. Positive and negative controls are included in triplicate.
-
Results Read out and Analysis
After 24 to 72 hours, epitopes in the cancer antigen that can elicit cellular immune response would be identified by its specific skin reaction. The diameter of the induration region that is raised, thick, and hardened is measured. The diameter equals the strength of the total T-cell immunity.
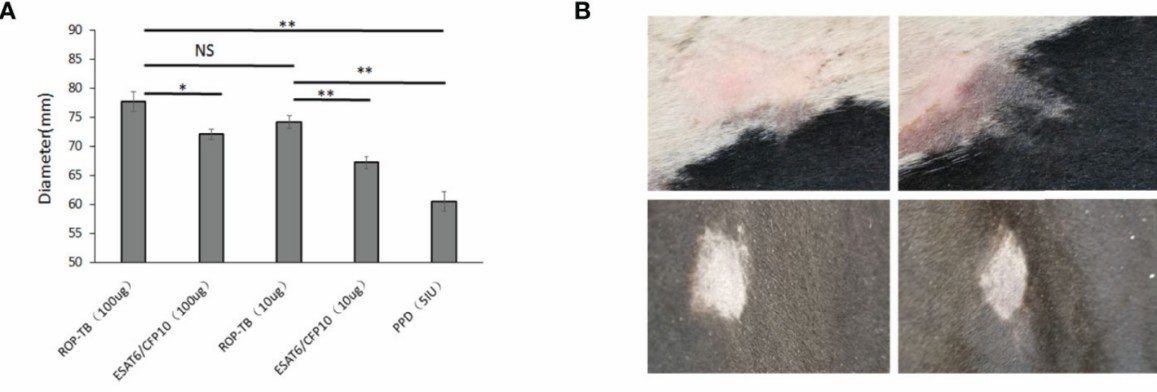 Fig.1 Results of skin reaction in guinea pigs(A) and cattle(B).1,3
Fig.1 Results of skin reaction in guinea pigs(A) and cattle(B).1,3
Highlights
-
Identifying potential cancer epitopes in large candidates.
-
Efficient and cost-effective.
-
Avoid in vitro culturing and processing.
Related Cancer Epitope Analysis Services
Multiple T and B cell-based assays are available to study the immune cells' responses upon antigen stimulation. Please refer to our Cancer Epitope Analysis Assays and choose proper approaches based on cell types, biological activities, and techniques.
-
Cell Activation
-
Cell Cytotoxicity
-
Receptor-Ligand Binding Interaction
-
3D Structure of the Epitope and Receptor Interaction
-
In Vivo Assays
As an experienced organization providing high-quality technical services to clients all over the world, Creative Biolabs has explored in vivo skin test assays for cancer epitope identification. We also provide multiple in vitro assays monitoring T and B cell response, serving as complementary measures. If you are interested in this service, please contact us for more information.
References
-
Zhang, Qing, et al. "In vitro and in vivo antigen presentation and diagnosis development of recombinant overlapping peptides corresponding to Mtb ESAT-6/CFP-10." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 872676.
-
Schaap-Johansen, Anna-Lisa, et al. "T cell epitope prediction and its application to immunotherapy." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 712488.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use



 Fig.1 Results of skin reaction in guinea pigs(A) and cattle(B).1,3
Fig.1 Results of skin reaction in guinea pigs(A) and cattle(B).1,3
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure

