Plant Glycan
Scientists at Creative Biolabs are experts in antibody preparation. Whether you are looking for any anti-glycan antibody services such as glycan identification, glycan purification or glycoantigens detection and discovery, we can provide affordable, high-quality custom services according to your specific demands with unbeatable rapid turnaround times. With integrated antibody development and engineering techniques, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive set of anti-plant glycans antibody services for our global clients.
Plant Glycans
Plants synthesize glycoconjugates which are structurally diverse and complex reflecting the diversity of plant physiological functions. In recent years, studies have shown that plants are amenable to glycol-engineering and capable of producing valuable recombinant glycoproteins with defined human-like structures largely attributing to its multiple glycan formation. Plant N-glycosylated proteins have been identified in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the Golgi apparatus and other compartments of the secretory pathway including the vacuole, the cell wall, and the extracellular space. The N-/O- glycosylation is critical for plant development and responses to stress.
The Origin of Glycans in Plants
In spite of glycan diversity, most N-glycans are synthesized from a common lipid-linked glycan precursor built of three glucose, nine mannose, and two N-acetylglucosamine. Plant N-glycans are classified into high-mannose and complex-type N-glycans whereas paucimannose N-glycans are a plant-specific subclass of complex-type N-glycans. High-mannose N-glycans are composed of 2-6 mannose residues that are linked to the trimannosyl core. Complex-type plant N-glycans lack β1,4-galactose, N-acetylneuraminic (sialic) acid and core α1,6-linked fucose. Paucimannose-type N-glycans are unique for invertebrates and plants. This kind of glycans possess only a core α1,3-fucose and/or β1,2-xylose and lack terminal GlcNAc residues or larger antennae linked to the Man3-2GlcNAc2 core.
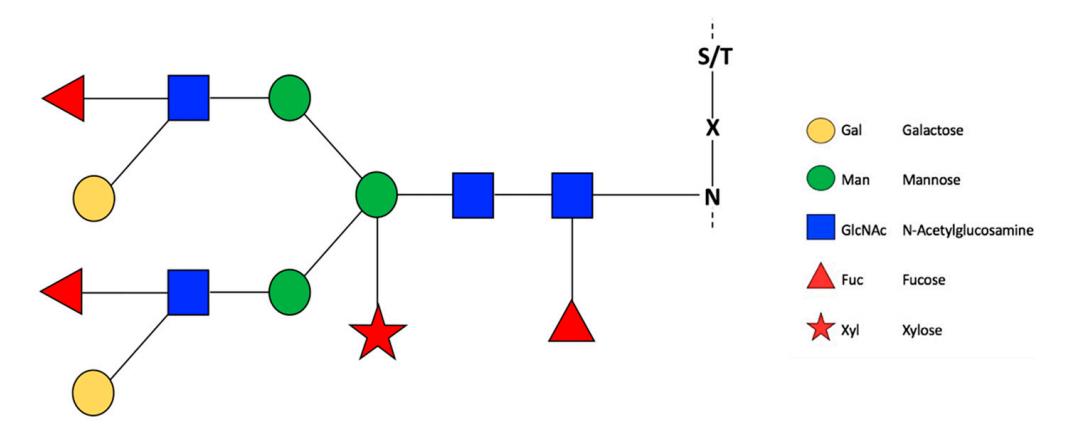 Fig.1 General representation of N-glycosylation in plants.1, 2
Fig.1 General representation of N-glycosylation in plants.1, 2
O-Glycosylation, another major type of protein glycosylation, is fundamentally different in plants. Mucin-type O-glycans have not been detected on native plant proteins and the glycosyltransferases for initiation and elongation of mucin-type O-glycans have not been found in the plant genomes. Less than a handful of proteins have been shown to be O-GlcNAc modified.
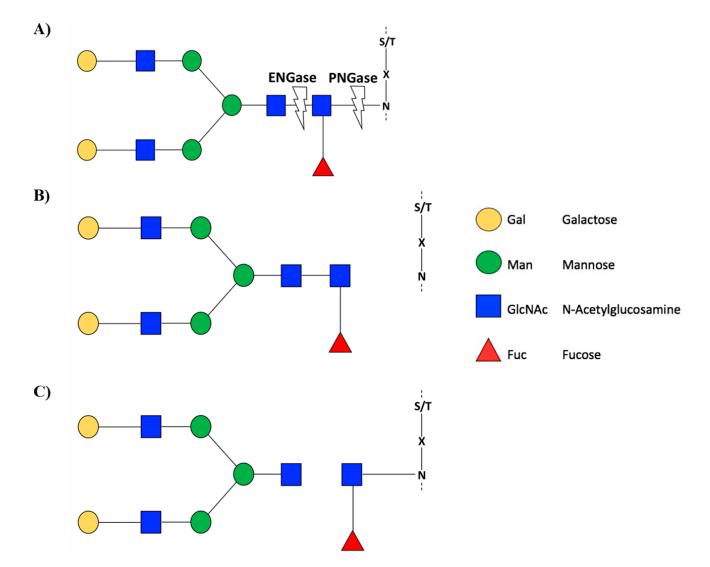 Fig.2 Schematic representation of the EnGase and PNGase enzyme activity.1, 2
Fig.2 Schematic representation of the EnGase and PNGase enzyme activity.1, 2
The Function of Glycans
The glycan modifications that take place in the ER are implicated in glycoprotein folding, quality control, sorting, degradation, and secretion. Further procession in the Golgi is vital for the trafficking and enzymatic activity of glycoproteins. Besides, mutations in ER-localized N-glycosylation enzymes often cause severe plant developmental defects, such as reduced root growth, altered leaf development, and embryo lethality. A recent study with winter wheat vernalization causes a global increase in reactivity with anti-O-GlcNAc antibodies and that devernalization decreases reactivity suggesting a role for O-GlcNAc modification in the vernalization process. Besides, O-GlcNAc has roles in both nuclear and plasmodesmata trafficking.
Experienced in antibody development and with dedicated commitment to the scientific community, Creative Biolabs has perfected our technical pipelines in the development of diverse anti-plant glycans antibody-based products. We would like to share our knowledge and passion in this field to promote the advances of science and for a better tomorrow. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References:
- Mendez-Yañez, Angela, Patricio Ramos, and Luis Morales-Quintana. "Role of glycoproteins during fruit ripening and seed development." Cells 10.8 (2021): 2095.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
