ELISpot is a highly sensitive assay that is commonly used for the identification of antibody-secreting B cells. The scientists in Creative Biolabs offer standardized ELISpot assay to boost the Native™ antibody discovery by single B cell technology.
What is ELISpot?
The enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot (ELISpot) is an assay that was first described in 1983 for the quantification of the antibody secretion and detection of antigen-specific antibody-secreting cells (ASCs). Currently, the ELISpot assay can be performed in two different ways: the antigen or anti-immunoglobulin pre-coated, which has been one of the most commonly applied methods for determining the ability of antibody or cytokine secretion by a single cell and the number of active cells. The ELISpot assay combines enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA) with western blotting (WB), quantifying target cells by detecting the secretory molecules using specific antibodies. Therefore, this ELISpot assay is particularly suitable for identifying and counting the cytokine-producing T cells and antigen-specific ASCs, of which B-cell ELISpot assay has been established to detect and quantitate antigen-specific ASCs and memory B cells. ELISpot assay is commonly used for the ASC quantification from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in vaccine assessments and trials.
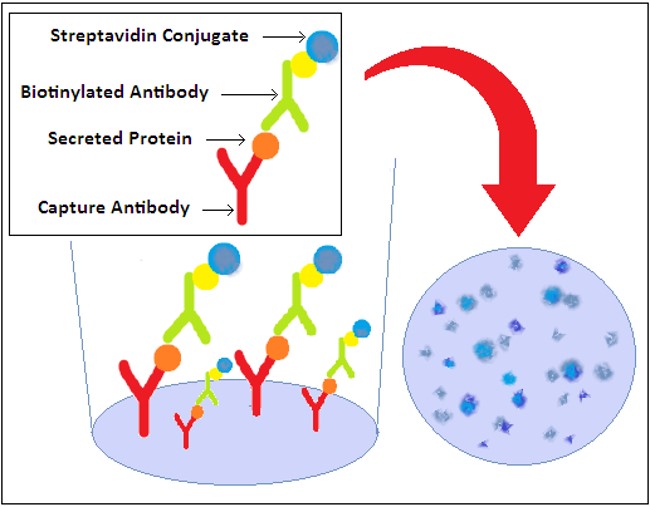 Fig.1 Illustrations of the ELISpot Assay. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wikimedia, without modification.
Fig.1 Illustrations of the ELISpot Assay. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wikimedia, without modification.
ELISpot for Antigen-Specific B Cell Identification
For the rapid discovery of Native™ antibodies with natural paring, obtaining antigen-specific ASCs is necessary and critical. B cell ELISpot plays an important role in the ex vivo identification and isolation of the antigen-specific antibody-producing plasma cells or memory B cells.
In a B cell ELISpot assay, the antigen is pre-coated onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane in a 96-well microtiter plate. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or B cells from immunized peripheral blood samples are serially diluted, added, and incubated in ELISpot plates. The antigen-specific antibodies on the membrane of ASCs are captured by the coated antigen, closely binding the individual ASC to the microplate. The enzyme or fluorescent-labeled antibody is then added to visualize the target ASCs. Thus a colored complex precipitate is formed and presents as a spot forming at the location of the ASCs. Each spot corresponds to a single antigen-specific ASC. This B cell ELISpot technique is highly sensitive but is limited to downstream analysis, which is suitable to be combined with other cell sorting techniques to identify or verify antigen-specific ASCs.
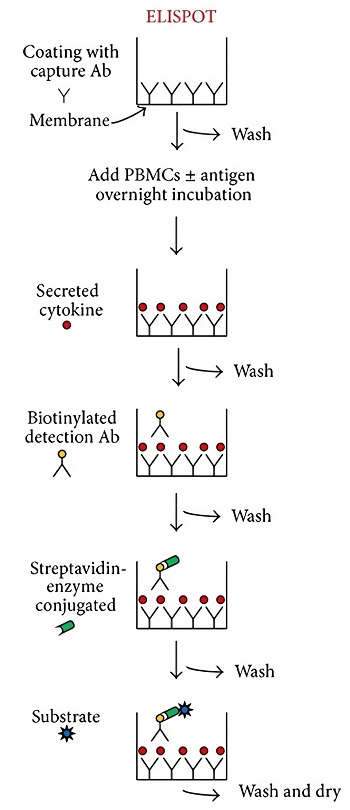 Fig.2 A schematic flowchart of ELISpot assay to detect Ag-specific ASCs.1
Fig.2 A schematic flowchart of ELISpot assay to detect Ag-specific ASCs.1
What Can We Do for You About Native™ Antibody Discovery?
Over decades of years expansion and accumulation, Creative Biolabs has become a world-leading service provider of antibody discovery and development. Based on a well-constructed B cell sorting platform, we are happy to offer a comprehensive range of Native™ antibody discovery services, which mainly including but not limited to:
If you are interested or have any questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Reference
-
Calarota, Sandra A., and Fausto Baldanti. "Enumeration and characterization of human memory T cells by enzyme‐linked immunospot assays." Journal of Immunology Research 2013.1 (2013): 637649. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Related Sections:
ONLINE INQUIRY

 Fig.1 Illustrations of the ELISpot Assay.
Fig.1 Illustrations of the ELISpot Assay.  Fig.2 A schematic flowchart of ELISpot assay to detect Ag-specific ASCs.1
Fig.2 A schematic flowchart of ELISpot assay to detect Ag-specific ASCs.1

