Cynomolgus Monkey Heart (NHP-TI001)

Tag: Cynomolgus Monkey, Tissue Block
- This product provided by Creative Biolabs is isolated from Cynomolgus monkeys' heart. The sample is negative for Herpes-B Virus, as well as SRV, SIV, and STLV-1, and can be used for a variety of in vitro tests and assays such as PCR, Western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescent flow cytometry.
Detailed Product Description
- Source: Healthy cynomolgus monkey
- Applications: Given their robust resemblances to humans across physiological, behavioral, immunological, and genetic aspects, non-human primates serve as crucial models in a broad range of biomedical research, especially in bridging translational research from small animal models to humans. Creative Biolabs offers both standard formats and personalized non-human primate tissue preparations, catering to diverse in vitro testing applications.
- System: Cardiovascular System
- Organ/Tissue: Heart
- Shipping: Dry ice
Technical Specifications
- Preservation Methods: Snap frozen
- Quality Assurance: Tissue blocks are prepared by histologists with years of experience to be sure of excellent morphology and high quality.
- Packaging: Securely packaged to maintain the tissue quality during shipping.
The article focuses on the detailed study of the heart muscle in Cynomolgus monkeys, particularly emphasizing the role and diversity of tropomyosin (TPM) isoforms. Tropomyosin, a key protein in muscle contraction, exists in different forms (isoforms) that contribute to the heart's function. The research highlights the genetic similarity between Cynomolgus monkeys and humans, with about 90% DNA similarity, making these monkeys a valuable model for biomedical research, especially for studying human heart diseases.
Significant findings include the cloning and sequencing of various sarcomeric TPM isoforms from Cynomolgus monkey hearts and skeletal muscles. The study reveals a unique expression pattern of these isoforms in the monkey heart, with TPM1α being the dominant sarcomeric isoform present, unlike human hearts where other isoforms like TPM1κ, TPM2α, and TPM3α are also detected. This suggests notable differences in cardiac protein expression between humans and monkeys, potentially influencing heart function and disease.
Quantitative analyses provide insights into the expression levels of different TPM isoforms in Cynomolgus monkey heart and skeletal muscles, facilitating comparisons with human TPM expression. This research is crucial for understanding heart muscle function and its variations across species, offering a foundation for developing treatments for heart diseases.
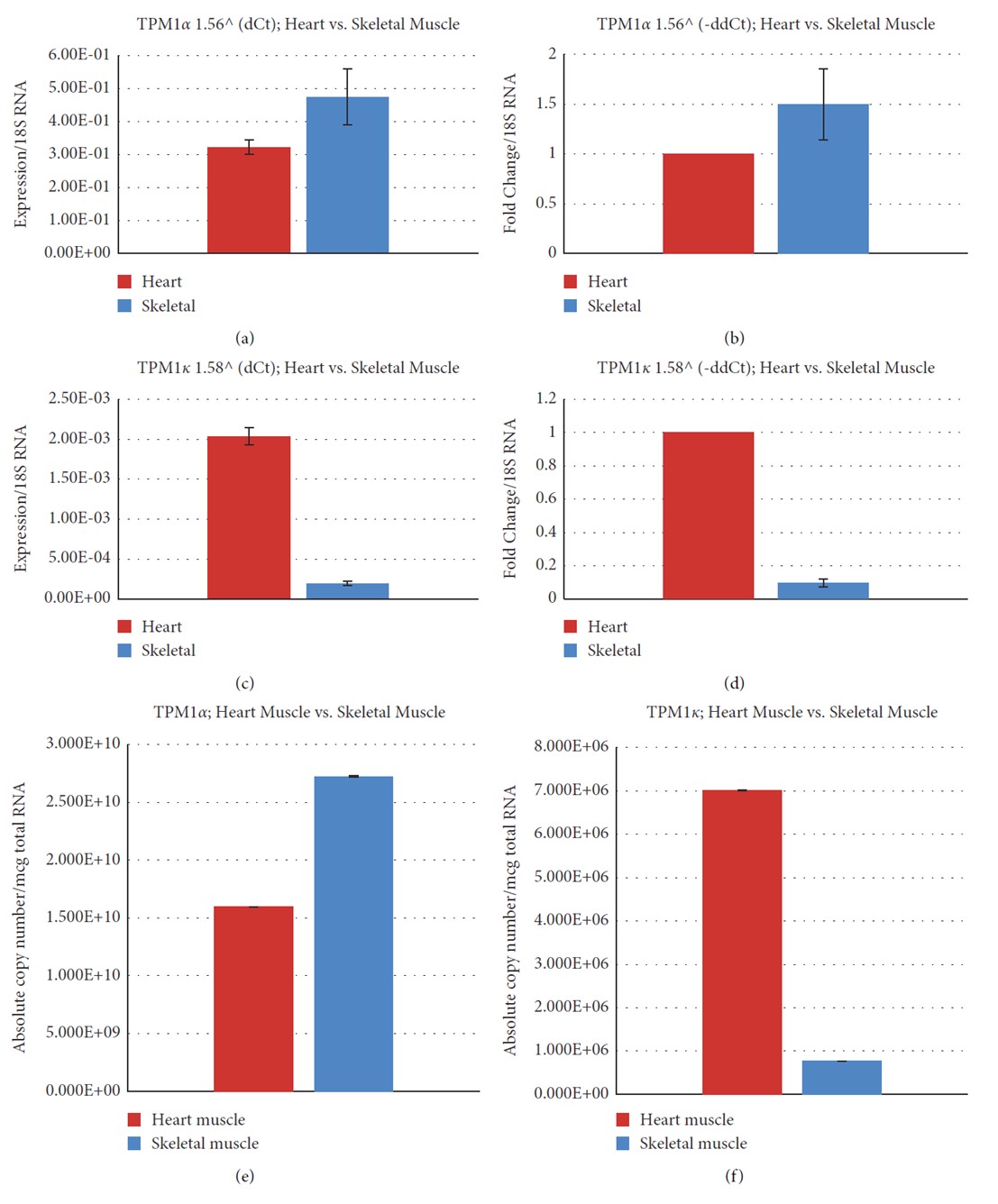 Fig.1 Relative and absolute expression of TPM1& and TPM1' in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM1& using the dCt method. (b) Fold change of TPM1& using the ddCt method. (c) Relative expression of TPM1' using the dCt method. (d) Fold change of TPM1' using the ddCt method. (e) Estimation of the absolute copy number of TPM1&. (f) Estimation of the absolute copy number of TPM1
Fig.1 Relative and absolute expression of TPM1& and TPM1' in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM1& using the dCt method. (b) Fold change of TPM1& using the ddCt method. (c) Relative expression of TPM1' using the dCt method. (d) Fold change of TPM1' using the ddCt method. (e) Estimation of the absolute copy number of TPM1&. (f) Estimation of the absolute copy number of TPM1
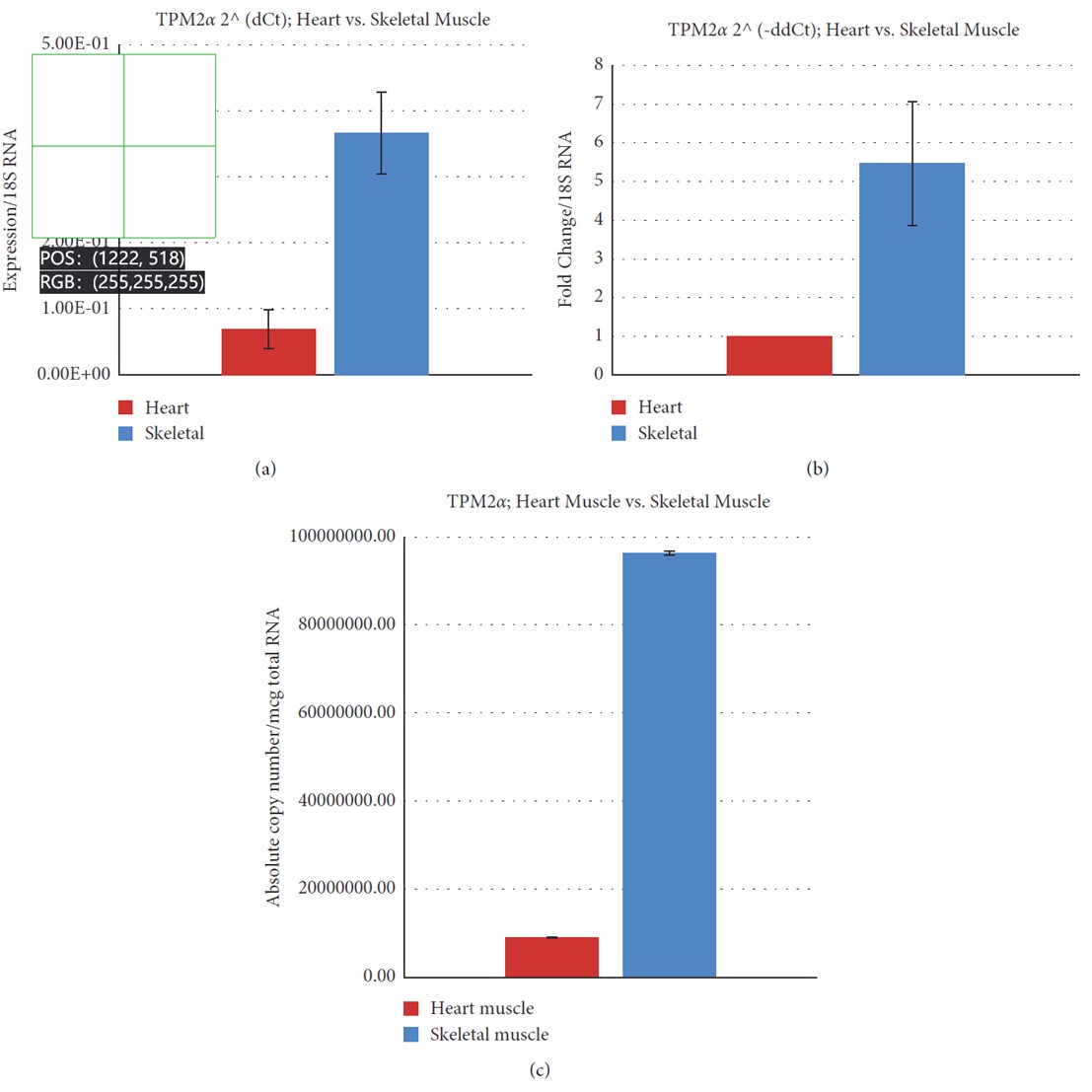 Fig.2 Relative and absolute expression of TPM2& in Cyn striated muscles.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM2& using the dCt method in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle. (b) Fold change of TPM2& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle using the ddCt method. (c) Determination of the absolute copy number of TPM2a in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.
Fig.2 Relative and absolute expression of TPM2& in Cyn striated muscles.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM2& using the dCt method in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle. (b) Fold change of TPM2& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle using the ddCt method. (c) Determination of the absolute copy number of TPM2a in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.
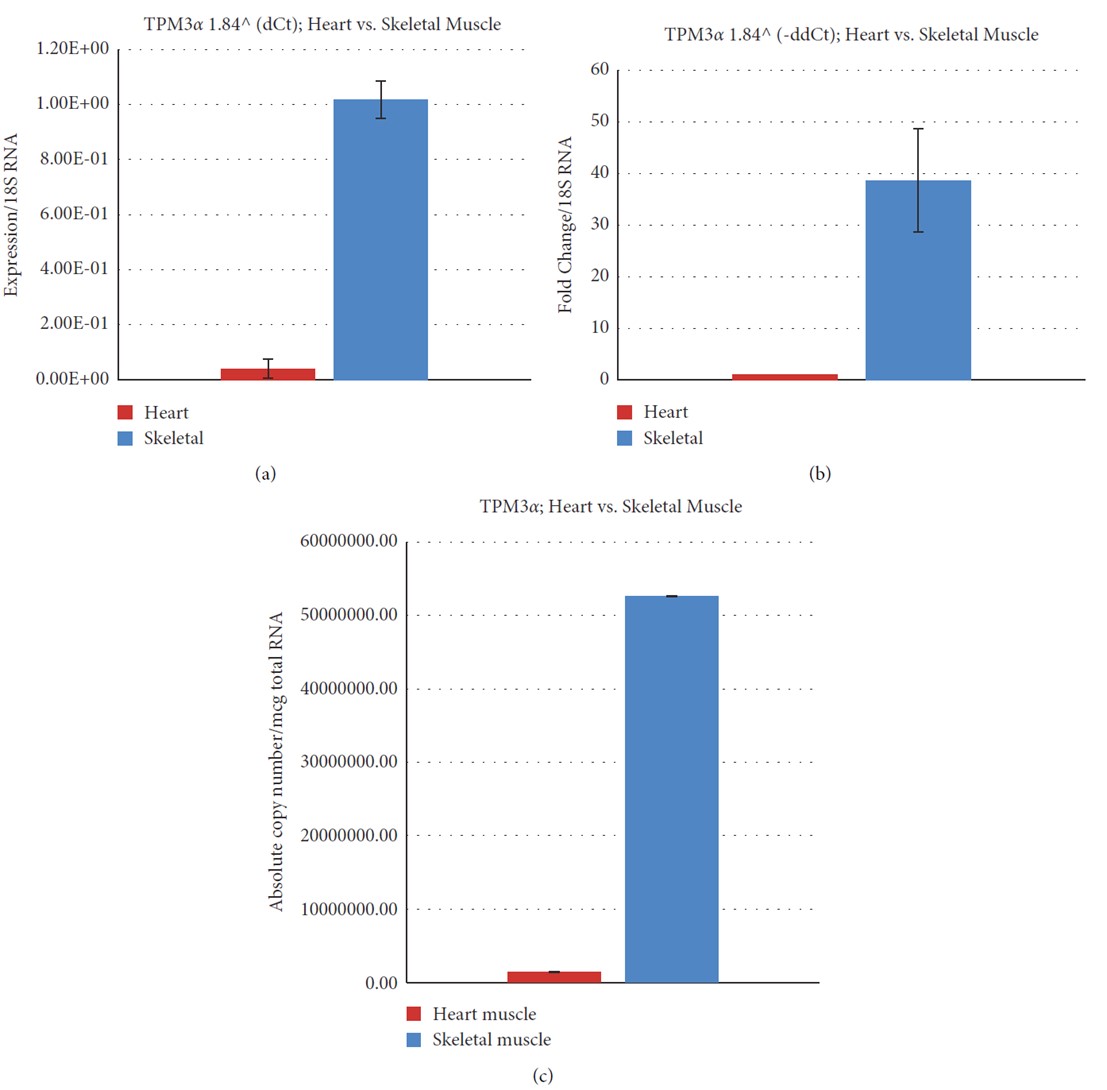 Fig.3 Relative and absolute expression of TPM3& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM3& using the dCt method. (b) Fold change of TPM3& using the ddCt method. (c) Estimation of the absolute copy number of TPM3& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.
Fig.3 Relative and absolute expression of TPM3& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM3& using the dCt method. (b) Fold change of TPM3& using the ddCt method. (c) Estimation of the absolute copy number of TPM3& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.
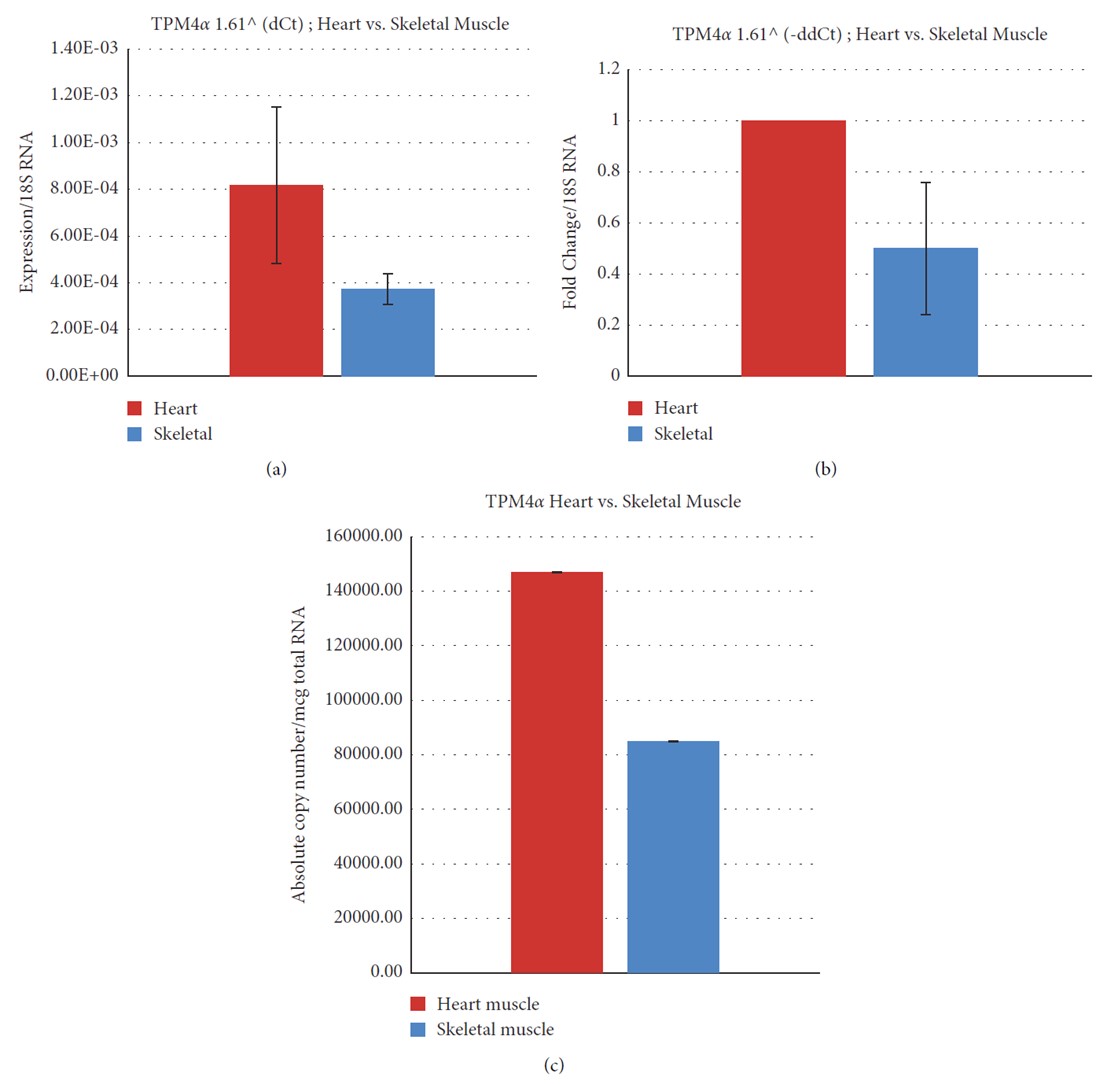 Fig.4 Relative and absolute expression of TPM4& in Cyn striated muscles.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM4& using the dCt method in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle. (b) Fold change of TPM4& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle using the ddCt method. (c) Determination of the absolute copy number of TPM4a in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.
Fig.4 Relative and absolute expression of TPM4& in Cyn striated muscles.1 (a) Relative expression of TPM4& using the dCt method in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle. (b) Fold change of TPM4& in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle using the ddCt method. (c) Determination of the absolute copy number of TPM4a in the Cyn heart and skeletal muscle.
Reference
- Dipak K. Dube., et al. "Tropomyosin Isoform Diversity in the Cynomolgus Monkey Heart and Skeletal Muscles Compared to Human Tissues" Biochemistry Research International.(2023). Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
-
Q 1: How is the tissue preserved for shipping?
A: We offer both flash-frozen and formalin-fixed options, based on your research needs.
-
Q 2: Can I request specific sections of the heart?
A: Yes, we can provide specific heart sections upon request. Please contact us with your requirements.
-
Excellent Cynomolgus Monkey Heart
Would buy and use it again. Worth recommending!
Click the button below to contact us or submit your feedback about this product.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Enter your email here to subscribe.
SubmitFollow us on


 Cynomolgus Monkey PBMCs
Cynomolgus Monkey PBMCs