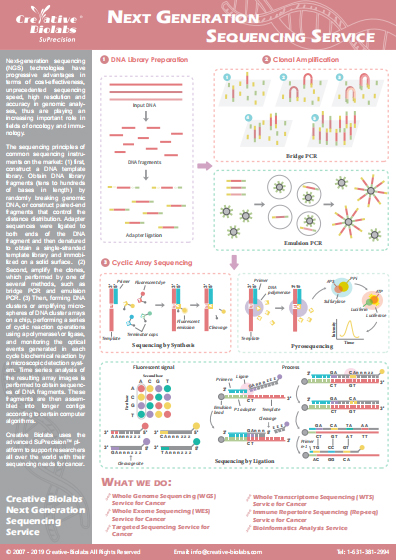
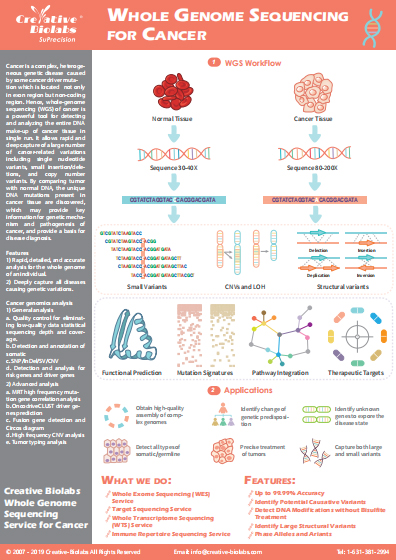
Spatial Multiplex Imaging Service
Creative Biolabs is a world-leading service provider that is committed to providing the most comprehensive cancer research strategy. In recent years, we established a powerful and innovative technology platform, spatial multiplex imaging, which enables the analysis of multiple biomarkers in a tissue section while maintaining their spatial context. This technology provides a powerful tool for tumor research involving tumor microenvironment, tumor development, invasion, and metastasis.
Introduction of Spatial Multiplex Imaging
A multicellular organism is composed of a wide variety of cell types, which brings great challenges for researching signal transduction networks containing many interacting biomolecular components and spatial relationships between different cell phenotypes in situ. Traditional immunohistochemistry (IHC) is capable of analyzing biomolecules in their original location, but it is limited to 2 to 3 biomarkers per sample. Although next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a powerful technology for the analysis of multiple biomarkers, it can’t detect biomarkers in the spatial context. While the emergence of spatial multiplex imaging (also known as multiplexed IHC) addresses these limitations. It utilizes conventional microscopes and commercially available antibodies to visually analyze multiple biomarkers in their spatial relationships, increasing the rate of discovery of new biomarkers and better demonstrating cell-cell spatial relationships. Especially, spatial multiplex imaging combining with single cell sequencing technology is a perfect combination for studying the spatial context of tumor samples to explain tumor pathology, progression, and treatment response.
Application of Spatial Multiplex Imaging in Cancer Research
- Quantitative assessment of the spatial heterogeneity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL)
- In-depth single-cell spatial profiling
Increasing evidence has reported total TIL count and TIL subpopulations represent potential predictive markers for immunotherapies. Mani et al (2016) used a multiplexed immunofluorescence (QIF) to quantify TIL to demonstrate intratumor heterogeneity in different fields of view within each section. Results showed T and B lymphocytes have more heterogeneity across the dimensions of a single section than between different sections or regions of a given breast tumor. These results may help to assess the predictive value of TIL for immunotherapies.
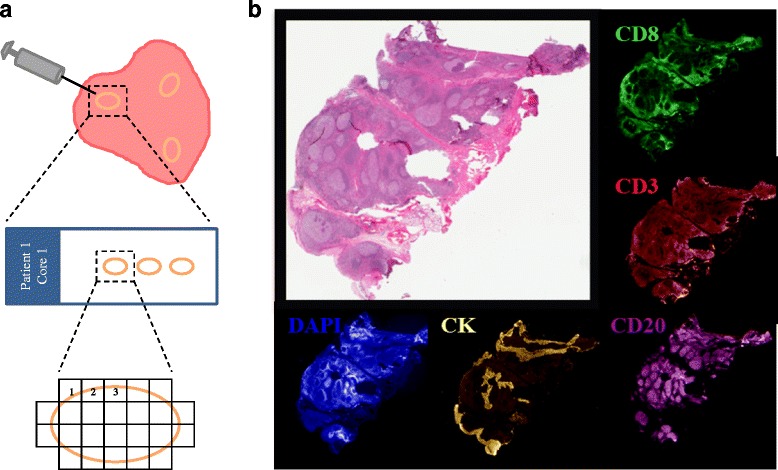 Fig.1 Average AQUA scores for tonsil whole tissue control samples. (Mani, 2016)
Fig.1 Average AQUA scores for tonsil whole tissue control samples. (Mani, 2016)
The tumor microenvironment is a dynamic cellular milieu that consists of cancer cells, the surrounding blood vessels, immune cells, fibroblasts, signaling molecules, and the extracellular matrix. Tumor development is highly associated with the physiological state of the tumor microenvironment. Elucidating the complexity of these hierarchical microenvironments is very important for demonstrating disease progression and therapeutic response. The multiplexed imaging technology provides a valuable tool for deeply deciphering the cascade of microenvironments in solid and liquid biopsies.
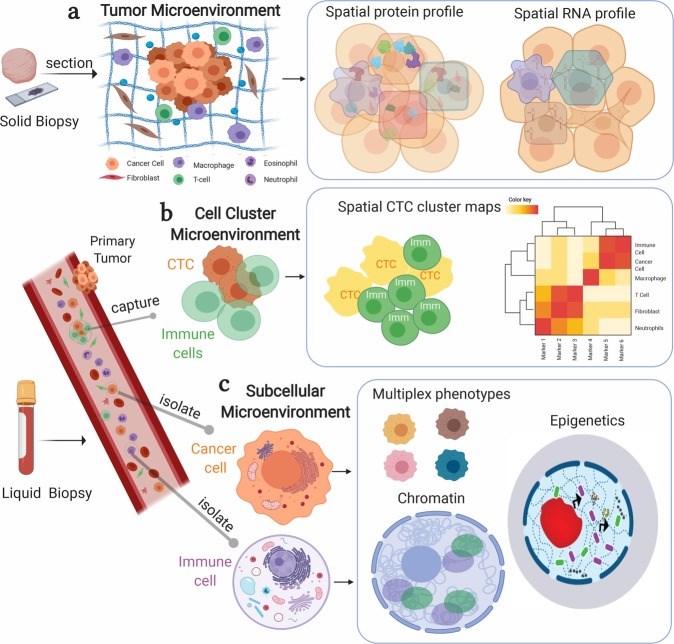 Fig. 2 Multiplex bioimaging of hierarchical spatial microenvironments in tumors. (Allam, 2020)
Fig. 2 Multiplex bioimaging of hierarchical spatial microenvironments in tumors. (Allam, 2020)
Our Capability
Based on our powerful spatial multiplex imaging platform, we support the analysis of a single 5 um tissue section with up to 50 biomarker stains. Our spatial imaging platform was developed by an excellent technical team and multiple external collaborators and has assisted several important projects on spatial. Our service portfolio includes staining, imaging, and imaging QC and analysis based on our proprietary imaging software and algorithms.
Highlights
- A spatial proteomics research platform, realizing the simultaneous labeling and high-resolution microscopic imaging of up to 50 antibodies on tissue slice samples
- Performing in-depth data analysis and mining experimental images, to achieve the in-depth analysis of the tissue microenvironment
- Quantitative research on typing of various types of cells
- Deeply exploring the biological information contained in the tissue microenvironment and facilitating analysis of cancer cells and their interaction with the immune system in the tumor microenvironment
- A cloud-based image analysis software and algorithms to support the discovery of multiple biomarkers
- Support a customized analysis according to your project’s requirement
If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
- Mani, Nikita L., et al. "Quantitative assessment of the spatial heterogeneity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer." Breast Cancer Research 18 (2016): 1-10. Distributed under open access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Allam, Mayar, Shuangyi Cai, and Ahmet F. Coskun. "Multiplex bioimaging of single-cell spatial profiles for precision cancer diagnostics and therapeutics." NPJ precision oncology 4.1 (2020): 11. Distributed under open access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.