Revolutionizing Biomedical Research: The Emergence of TERT-Immortalized Rhesus Macaque Kidney Cells
Non-human primates (NHPs) are critical to biomedical research, offering models that closely replicate human diseases. Among these, rhesus macaques stand out, particularly in the study of viral infections. Their physiological and genetic similarities to humans make them indispensable for understanding complex diseases and testing novel therapies.
Recent advancements in cellular biology have led to the development of immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cells. By utilizing lentiviral transduction techniques, cells are engineered to express telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), achieving immortalization. This breakthrough has generated TERT-immortalized cell lines, marking a significant leap forward in NHP research.
Materials and Methods
The Materials and Methods of the article outline the procedures and techniques used to generate and analyze TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cells. Here are the main points covered:
- Retroviral Transduction for Stable Cell Lines: Lentivirus-based transducing virus was produced using 293T cells transfected with vector pLenti-IHy-TERT, HIV gag-pol (SCA), and VSV-G expression plasmid. The transduction process involved seeding cells, adding transducing virus, spinoculation, and selecting with hygromycin.
- Analysis of Viral Entry Using Pseudotyped Retroviral Particles: Pseudoviral particles were produced in 293T cells and used to infect target cells, assessing the susceptibility to viral entry with different viral glycoproteins.
- Induction of MX1 and IFNB1 Expression: To analyze the interferon (IFN) system's response, cells were treated with IFN or infected with VSV ncp*, inducing IFN production. RNA was then harvested for quantitative PCR analysis.
- Virus Replication Kinetics and Titration: Viral infection studies included single-step growth kinetics and virus titration using plaque assays for herpesviruses and a modified focus forming assay for ZIKV.
- Quantitative Real-Time PCR: RNA isolation, DNase treatment, cDNA synthesis, and quantitative PCR were performed to analyze gene expression, specifically focusing on MX1 and IFNB1, using specific primers.
- Flow Cytometry: This technique was used to analyze cell surface markers, such as podoplanin, after cells were stained with specific antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry.
- Cell Proliferation Assay: Cell proliferation was assessed using the carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) Cell Division Tracker Kit, tracking division through CFSE dilution.
- Microscopy: Phase contrast microscopy was employed to visualize cells, with images taken at 20x magnification and processed for brightness and scale bar adjustments.
- Statistical Analysis: Data were graphed and statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism software.
These methods facilitated the generation, characterization, and functional analysis of the monkey immortalized kidney cell lines, highlighting their utility in viral infection studies and the intact IFN response system
Results
The Results of the article provide comprehensive insights into the characteristics and functionalities of the TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cell lines. Here are the main findings described:
- Establishment of Immortalized Cell Lines: Three TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cell lines were established, exhibiting less heterogeneity, smaller cell body, faster growth, and spindle-like morphology typical of mesenchymal cells. These lines were named MaMuK2345C, MaMuK2345MW, and MaMuK8639, developed from kidney tissues of both male and female rhesus macaques.
- TERT Expression and Cell Marker Analysis: The immortalized cells expressed TERT (indicative of successful immortalization) and the podocyte marker podoplanin (PDPN), with weak expression of the podocyte marker protein Nephrin detected in all three cell lines.
- Functional IFN System: The cell lines maintained a functional interferon (IFN) system, responding to IFN treatment or virus infection by expressing IFNB1 and the IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) MX1, albeit at levels lower than in the human lung cell line A549 used as a control.
- Susceptibility and Permissiveness to Virus Infection: The cell lines were found to be both susceptible and permissive to viral infection, allowing for entry driven by glycoproteins from various viruses, including Indiana vesiculovirus (VSV), Ebola virus (EBOV), Nipah virus (NIV), influenza A virus (IAV), and Lassa virus (LASV). They supported replication of Zika virus (ZIKV) and primate herpesviruses (PaHV2 and CeHV2), with PaHV2 replicating to high levels in all cell lines and CeHV2 showing reduced efficiency compared to control Vero76 cells.
These results indicate the potential of the TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cell lines as valuable tools in biomedical research, particularly for studies on viral infections and the innate immune response.
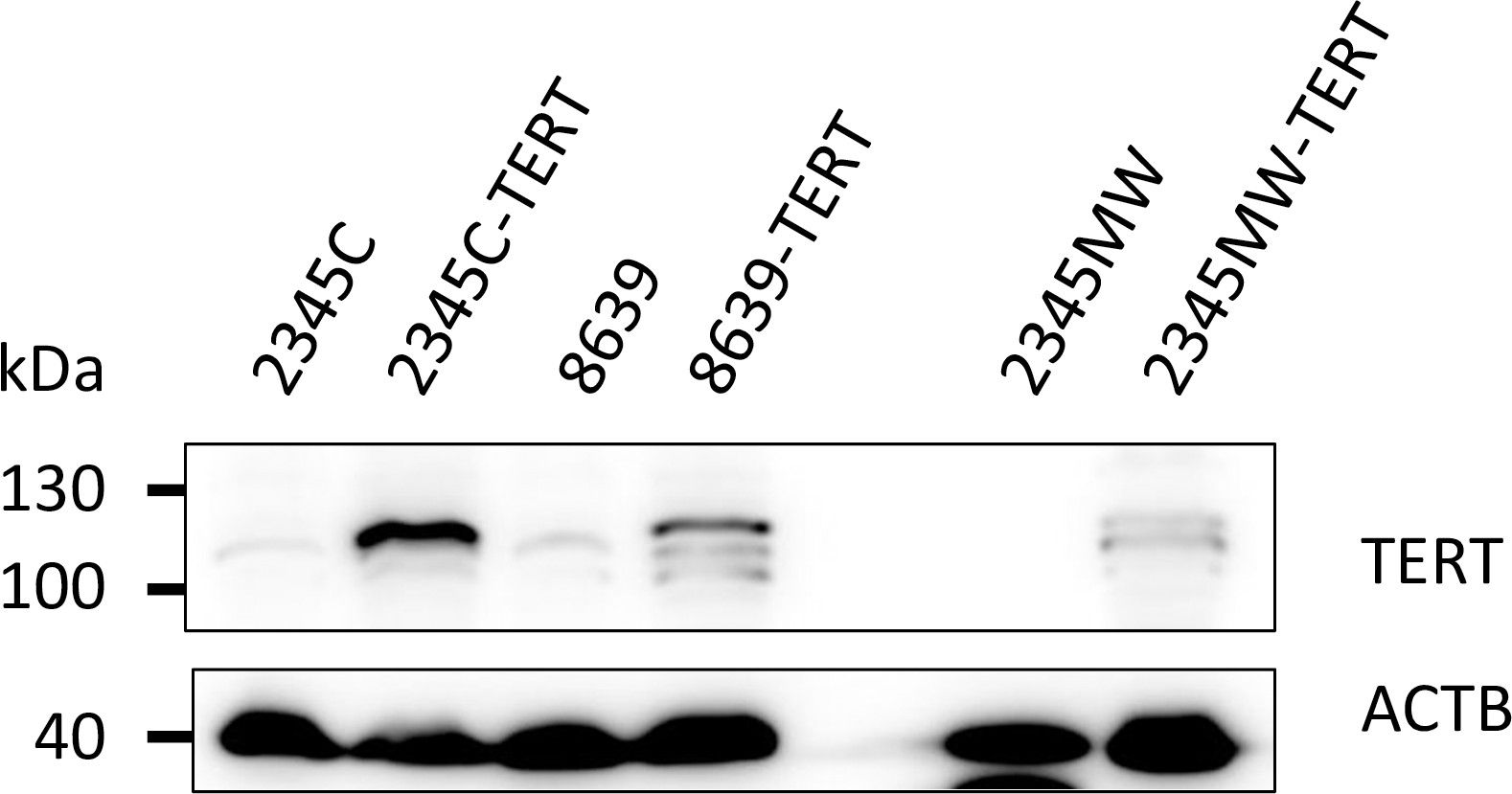 Fig.1 Immortalized kidney cells express the immortalization gene TERT.1
Fig.1 Immortalized kidney cells express the immortalization gene TERT.1
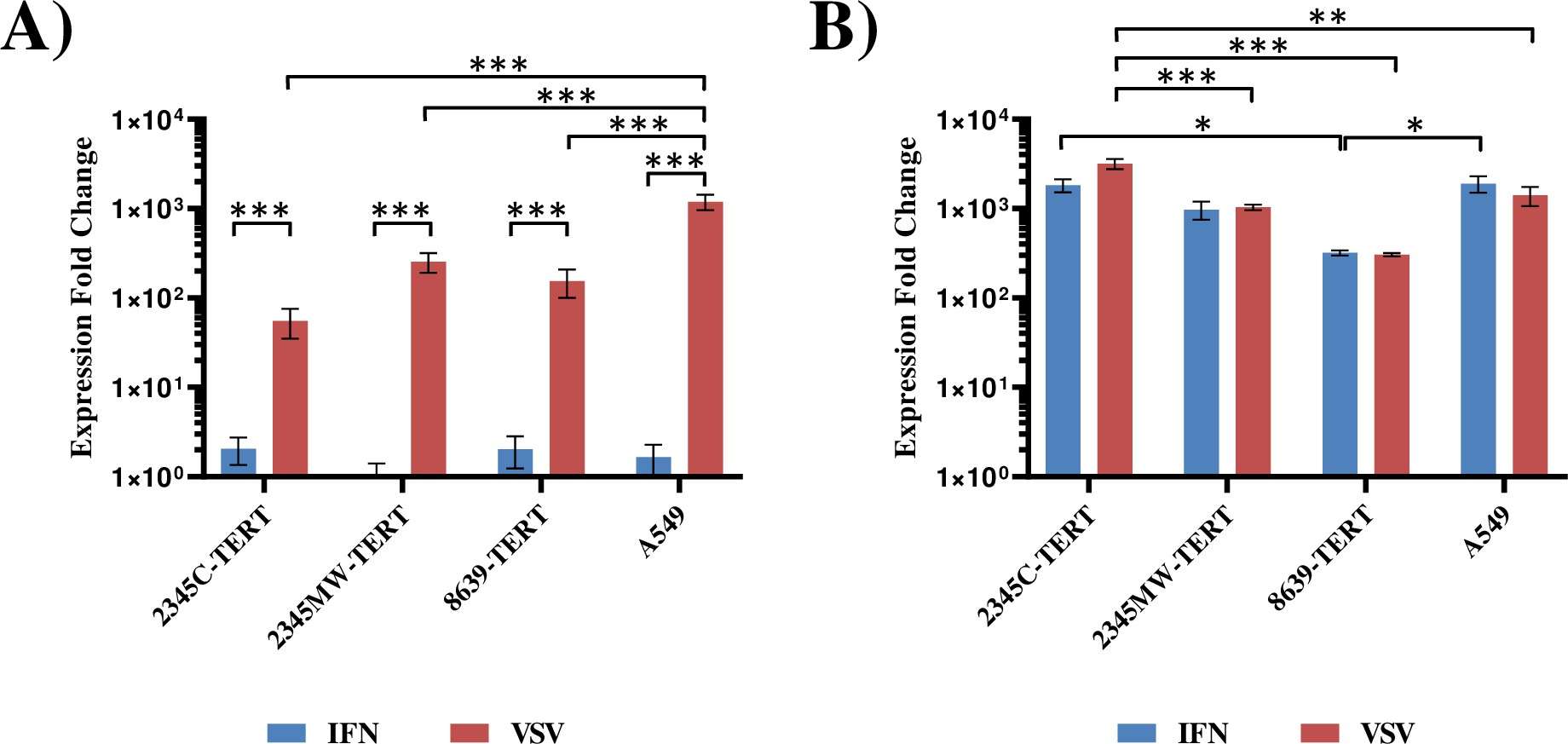 Fig.2 Immortalized kidney cells express IFNB1 and/or MX1 upon stimulation with IFN or VSV infection.1
Fig.2 Immortalized kidney cells express IFNB1 and/or MX1 upon stimulation with IFN or VSV infection.1
Discussion
The article presents a detailed analysis of the significance and implications of the study on TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cell lines. Here are the main points covered:
- The study generated and characterized three TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cell lines, which showed susceptibility to infection by various viruses and permissiveness to infection with primate simplexviruses and ZIKV.
- A comparison with the LLC-MK2 rhesus macaque kidney cell line, noting the epithelial morphology of LLC-MK2 versus the spindle-like morphology of the newly generated cell lines, which suggests a mesenchymal and possibly podocyte lineage.
- The importance of the interferon (IFN) system in analyzing viral infections is highlighted, as an intact IFN system can significantly limit viral replication. The newly generated cell lines possess an intact IFN system, as shown by strong induction of IFN beta and the ISG MX1 by both IFN treatment and viral infection.
- The cell lines allowed entry driven by glycoproteins from multiple virus families, indicating their potential susceptibility to a wide range of viruses. Notably, differences in susceptibility to infection were observed even between cell lines derived from the same animal, highlighting the influence of cellular heterogeneity and culture conditions.
- Productive infection was demonstrated for two primate herpesviruses (PaHV2 and CeHV2) as well as ZIKV, with virus titers comparable or higher than those in Vero cells, despite the functional IFN system. However, CeHV2 growth was less efficient in the rhesus macaque kidney cells compared to Vero cells, which may reflect species-specific restrictions.
- The study concludes that the TERT-immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cell lines with an intact IFN system could be valuable tools for comparative infection research and translational research, potentially aiding in the study of diverse viruses including primate herpesviruses and ZIKV.
Comprehensive Support from Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we recognize the transformative potential the research above holds for biomedical research. Our NHP immortal cell line products are developed with the highest standards to provide researchers with reliable, high-quality tools for their studies. These cell lines are not just products; they are a gateway to accelerating scientific discoveries and advancing healthcare solutions. Here's a table showcasing some relevant products:
Given the emphasis on the use of NHP immortalized cells for biomedical research, the following services from Creative Biolabs can meet your needs:
- NHP Biospecimen Custom Collection Service: Creative Biolabs excels as a one-stop provider for non-human primate (NHP) derived biospecimens, offering both standardized and customized collection and production services to meet unique project requirements. Their service advantage lies in their ability to provide a wide array of biospecimens from a large NHP colony, ensuring tailored support for research needs across diverse scientific fields, thus fostering significant preclinical breakthroughs.
- NHP Based Pharmacology and Pharmacodynamics Service: Creative Biolabs is an expert in providing comprehensive non-human primate (NHP)-based pharmacology and pharmacodynamics services to expedite research projects globally, leveraging a dedicated team with extensive drug development experience. Their advantages include a robust NHP platform offering both in vitro and in vivo services, optimized protocols ensuring precision, and a wide array of services tailored to meet specific research needs, facilitating smooth transitions from preclinical studies to clinical applications.
Reference
- Reiter, Stefanie, et al. "Development of immortalized rhesus macaque kidney cells supporting infection with a panel of viruses." Plos one 18.5 (2023): e0284048. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Online Inquiry
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Enter your email here to subscribe.
SubmitFollow us on


 Cynomolgus Monkey PBMCs
Cynomolgus Monkey PBMCs