Overview Service Features Published Data FAQs Scientific Resources Related Services
With years of experience, Creative Biolabs has developed a series of innovative stem cell-based platforms to provide chondrogenesis differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) service for our global customers. Our full-service packages are designed to meet the clients' project and specific requirements for MSC differentiation.
Overview of Chondrogenesis Differentiation of MSC
MSC as a Source for Chondrogenesis
In the adult human, MSCs in bone marrow retain the capacity to proliferate and differentiate along with multiple cartilages. Recently, MSCs are interested as a promising cell source for in vitro chondrogenesis due to their ease of isolation and high expansion capacity. MSCs can be isolated from many vascularized tissues as they reside within the joint that may be considered a potential reservoir of chondroprogenitor cells. Common in vitro protocols for chondrogenic differentiation of MSC successfully induce expression of multiple cartilage-specific molecules, including collagen type II and aggrecan, and result in a chondrocyte-like phenotype.
Factors that Influence Chondrogenic Differentiation of MSCs
The development of cartilage is initiated by a phase of condensation of mesenchymal precursor cells during embryogenesis. The cell-cell contact arising from condensation involving N-cadherin appears to be crucial for the onset of chondrogenesis. Therefore, functional N-cadherin is necessary for chondrogenesis of mesenchymal cells both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, high cell density and cell-cell contact could facilitate chondrogenic induction of MSCs compared with monolayer culture. MSCs have an intrinsic differentiation program of endochondral bone formation induced by exposure to these specific reagents.
Services at Creative Biolabs
MSCs can fulfill the requirements demanded of cells for tissue engineering of cartilage, as they can be conveniently manipulated in vitro to differentiate to chondrocytes for these purposes. In addition, MSCs can faithfully reproduce a chondrocyte phenotype, including hypertrophic stages. The potential of chondrogenic differentiation from MSCs is shown in many matrix-free and matrix-based cell culture systems. Now, the induction of in vitro chondrogenesis from MSCs displays well-established standard procedures. As a global leader of stem cell-based custom services, Creative Biolabs focuses on a powerful model system containing a condensed cell culture system and uses inducers to efficiently promote the chondrogenesis of MSCs to meet our customers' specific requirements.
Based on our deep understanding of various strategies, our scientists have built up one-stop solutions and considered different factors for the chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs, including but not limited to:
-
A basal medium contains dexamethasone, ascorbate, insulin, transferrin, and selenous acid for chondrogenic induction conventionally.
-
BMP2, BMP4, BMP6, and the insulin-like growth factor IGF1 may be regarded as promoters of chondrogenesis in MSCs when used with the TGFβ (the well-established potent inducers of chondrogenesis).
-
Environmental factors such as mechanical stimulation and hypoxia are reported to modulate chondrogenesis of MSCs in vitro.
With professional scientists devoted to MSC differentiation, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing the first-in-class chondrogenesis differentiation of MSC service for our customers worldwide. Our services will greatly contribute to the success of your MSC programs. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Features of Our Services
-
Customized differentiation protocols - We work closely with our clients to develop and optimize differentiation protocols that are tailored to their specific research needs. Our team of experts has extensive experience in chondrogenic differentiation and can provide guidance on the most appropriate conditions for successful differentiation.
-
Scalability - Our service is designed to accommodate projects of all sizes, from small-scale research studies to large-scale drug development programs. We have the capabilities to differentiate MSCs in large quantities while maintaining consistent quality and reproducibility.
-
Flexible deliverables - Depending on our clients' needs, we can provide differentiated cells in various formats, including cell pellets, monolayer cultures, or 3D tissue constructs. We can also perform additional assays, such as histological staining or gene expression analysis, to further characterize the differentiated cells.
-
Quality control - We rigorously monitor the differentiation process by assessing key markers of chondrocyte differentiation, such as collagen type II, aggrecan, and Sox9 expression. This ensures that the differentiated cells are of high quality and suitable for downstream applications.
Our service offers a robust and reliable solution for biotechnology companies looking to advance their research or development efforts in the field of cartilage regeneration.
Published Data
Below are the findings presented in the article related to chondrogenesis differentiation of MSCs.
Umbilical cord-derived hydrogels can be used as 3D scaffolding materials to support cell adhesion, proliferation, migration and differentiation due to their biochemical composition similar to cartilage. Therefore, Faiza Ramzan, et al. established a protocol to formulate hydrogels from decellularized human umbilical cord (DUC) tissues and evaluate their application in the proliferation and differentiation of UC-MSCs along the cartilage spectrum.
After inoculation of UC-MSC into hydrogels, they were cultured in either basal or chondrogenic medium for 28 days, and the expression of chondrogenic marker genes including TGF-β1, BMP2, SOX-9, SIX-1, GDF-5, and AGGRECAN was significantly increased. In addition, it was found that hydrogel concentration significantly affected the expression of chondrogenic marker genes. The overall results suggest that DUC-hydrogel is compatible with MSCs and supports their chondrogenic differentiation in vitro.
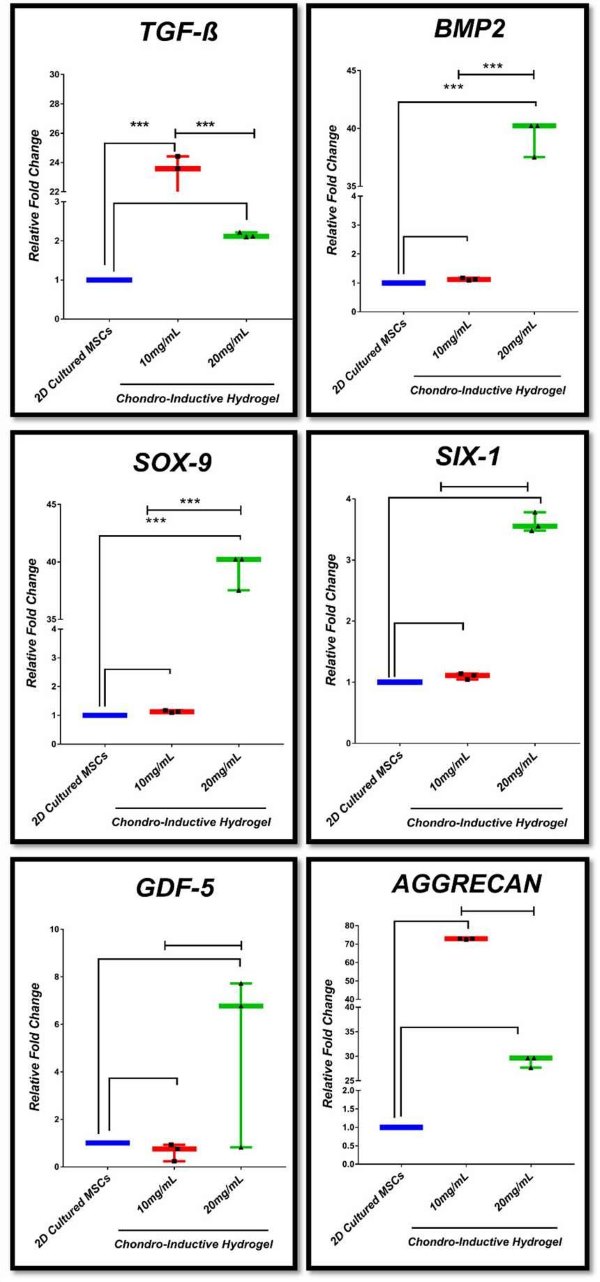 Fig. 1 Gene expression profile of chondrogenic markers in 3D hydrogel-cultured MSCs.1
Fig. 1 Gene expression profile of chondrogenic markers in 3D hydrogel-cultured MSCs.1
FAQs
-
Q: Are there any specific requirements or preparations needed from the client's end?
A: Generally, we handle most of the preparations for the differentiation process. However, if you are providing the MSCs, we would need information on the source, passage number, and any relevant handling procedures to ensure compatibility with our protocols. We also encourage clients to share any specific requirements or preferences they might have for the differentiation process to tailor the service to their needs.
-
Q: How long does the chondrogenesis differentiation process typically take?
A: The chondrogenesis differentiation process typically takes around 21 to 28 days, depending on the specific requirements of the project. This timeframe includes the initial preparation of MSCs, their induction into the chondrogenic lineage, and the final analysis to confirm successful differentiation. We maintain regular communication with our clients to provide updates on the progress of their projects.
-
Q: How do you ensure the consistency and reproducibility of your differentiation results?
A: To ensure consistency and reproducibility, we employ standardized protocols and utilize high-quality reagents and MSCs. Our experienced team conducts multiple rounds of validation and optimizes each step of the differentiation process. We also include control samples in every batch to monitor the process's consistency and rigorously analyze the data to ensure reproducibility across different experiments.
-
Q: What are the costs associated with the chondrogenesis differentiation service, and are there any discounts for bulk orders?
A: The cost of our chondrogenesis differentiation service varies based on the specific requirements of each project, such as the source of MSCs, the extent of customization, and the types of analyses needed. We offer competitive pricing and provide detailed quotes after discussing your project's details. Discounts may be available for bulk orders or long-term collaborations, so please contact our sales team to discuss pricing and potential discounts.
Scientific Resources
Reference
-
Ramzan, Faiza, et al. "Decellularized human umbilical tissue-derived hydrogels promote proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells." Bioengineering 9.6 (2022): 239. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part C of the original image.
For
Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
 Fig. 1 Gene expression profile of chondrogenic markers in 3D hydrogel-cultured MSCs.1
Fig. 1 Gene expression profile of chondrogenic markers in 3D hydrogel-cultured MSCs.1