As a leader of antibody discovery, Creative Biolabs offers the comprehensive solutions for discovery of antibody targeting Eimeria. Our experts have established a cutting-edge platform, Anti-Parasite Biomolecular Discovery which facilitates the generation of antibody against Eimeria.
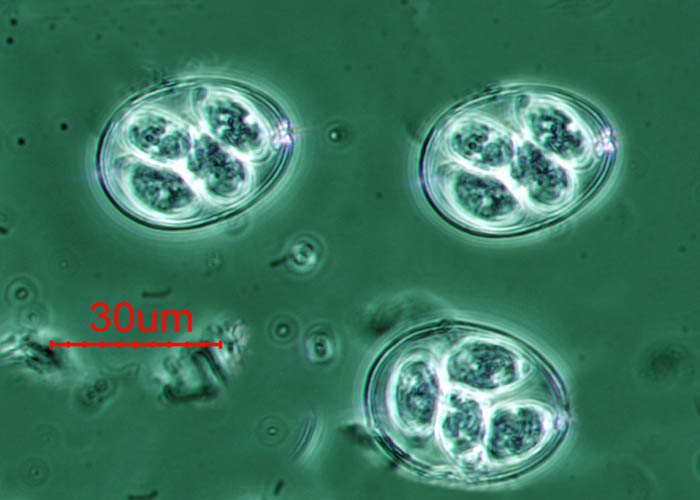 Fig.1 Eimeria maxima oocysts.
Fig.1 Eimeria maxima oocysts.
Eimeria is a genus of apicomplexan parasites including various species such as E. alpacae, E. tenella, E. ivitaensis, E. lamae, and E. macusaniensis. Species of this genus infect a wide variety of hosts and tend to be host specific. These parasites are the leading cause of disease coccidiosis in animals such as cattle, poultry, and smaller ruminants including sheep and goats. The severity of the disease is directly dependent on the number of infective Eimeria oocysts that are ingested.
Eimeria infections result in life-long immunity to that specific parasite species but do not provide cross-protection to other species. For these reasons, vaccines for control seem promising, of which live attenuated vaccines are the most effective. However, the search for highly immunogenic antigens and overcoming antigenic variation of the parasites remains a challenge. Studies have been found some proteins or peptides present in parasites or spores are associated with invasion and survival of parasites, making them potential targets for Eimeria-specific antibodies discovery.
EtCDPK3 is a novel calcium-dependent protein kinase in E. tenella. It is involved in the invasion and survival of E. tenell at intracellular stages. Due to the absence of this kinase from the host, it can be regarded as a useful target for the development of immunotherapy against E. spp.
ECP contains 235 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 25.4 kDa. It has been revealed that EPC may play a role in invasion and development of the first-generation merogony stage of E. tenella. And inhibition of ECP using specific antibodies reduces the ability of E. tenella sporozoites to invade host cells.
IMP1 is a new protective protein in apicomplexan parasites, which is also found in E. tenella. The C-terminal derivative of IMP1 in E. tenella might be considered as a candidate in the development of subunit vaccines/antibodies against Eimeria infection.
EtcatL is a cysteine protease with 470 amino acids. It is expressed mainly at the endogenous stages and the initial phase of the sporulation. And the protein has been indicated as an effective immunogen and as a vaccine candidate molecule.
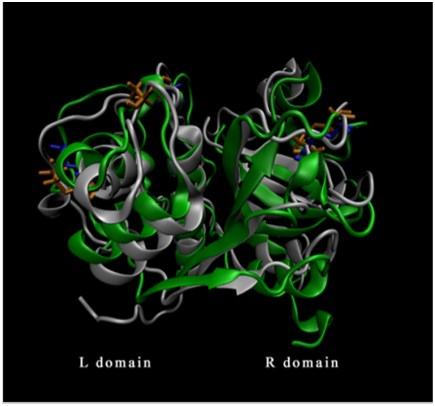 Fig.2 The structure of EtcatL (Liu et al. 2015).
Fig.2 The structure of EtcatL (Liu et al. 2015).
Creative Biolabs has years of experience in antibody discovery and development. Equipped with the innovative Anti-Parasite Biomolecular Discovery platform, we guarantee high-quality services for global customers. This cutting-edge platform is constituted with the most comprehensive solutions, thus providing an unprecedented capability to produce antibodies with high anti-Eimeria activity. If you are interested in the discovery of antibody targeting Eimeria, please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Reference