With a set of advanced equipments and a highly professional technical team, Creative Biolabs is proud of providing high-quality service for anti-Fasciola antibody discovery based on our effective Anti-Parasite Biomolecular Discovery platform. We have served hundreds of global customers within a few years, and have accumulated rich experience in generation of anti-parasite antibodies, thus making us the best partner in your anti-Fasciola projects.

Fasciola is a genus of trematodes and a leading agent for fasciolosis, a disease that affects a wide range of livestock and causes economic losses of large proportions. Two species of trematodes (F. hepatica and F. gigantica) have been identified to cause fascioliasis. F. hepatica is distributed worldwide and infects the livers of various mammals including humans. Symptoms in human fascioliasis vary depending on whether the disease is chronic or acute. During the acute phase, the immature worms begin penetrating the gut, causing symptoms of fever, nausea, swollen liver, skin rashes, and extreme abdominal pain. The chronic phase occurs when the worms mature in the bile duct and can cause symptoms of intermittent pain, jaundice, and anemia. In cattle and sheep, classic signs of fasciolosis include persistent diarrhea, chronic weight loss, anemia, and reduced milk production.
Fasciolosis induced by Fasciola infections has been identified as an important cause of both production and economic losses in the dairy and meat industries. According to conservative estimates, the annual loss of animal productivity due to fasciolosis in the world exceeds $3.2 billion. Furthermore, fasciolosis is also recognized as an emerging human disease that threatens human health seriously. WHO has estimated that 2.4 million people are infected with Fasciola, and a further 180 million are at risk of infection. Hence, it is very important to develop the Fasciola-specific antibodies for Fasciola infections diagnosis because immunodiagnostic tests have a sensitivity above 90% during all stages of the diseases. Besides, developing therapeutic antibodies against Fasciola is also required, which can perform an excellent role in resistance to challenge infection with F. hepatica and F. gigantica.
The challenge for developing Fasciola-specific antibody is to discovery highly immunogenic antigens or the site of parasite invasion. Up to now, there has been found several potential targets for antibody development.
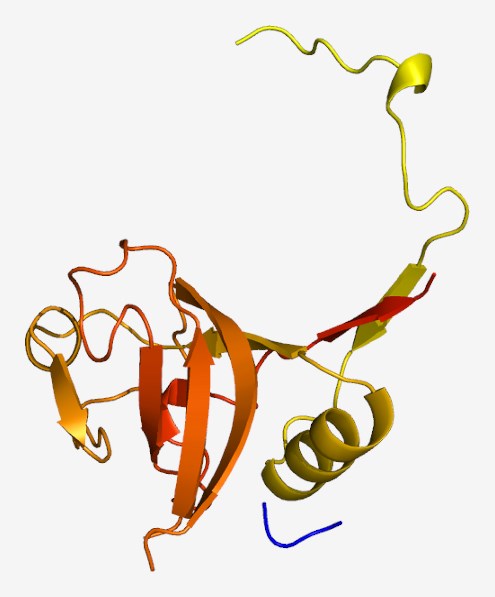
Cathepsin L is a cysteine proteinase secreted by Fasciola species. It is involved in nutrient acquisition by catabolizing host proteins to absorbable peptides, facilitates the migration of the parasite through the host intestine and liver by cleaving interstitial matrix proteins (such as fibronectin, laminin, and native collagen), and is implicated in the inactivation of host immune defenses by cleaving immunoglobulins. Besides, cathepsin L has been shown to suppress Th1 immune response in infected laboratory animals, making the infected animals susceptible to concurrent bacterial infections. Hence, cathepsin L is regarded as an essential target for parasite intervention strategies. Besides, fluke Cathepsin L cysteine proteinases are also reported as sensitive and specific markers for the immunodiagnosis of fasciolosis in ruminants.
FgGPx plays a key role in the antioxidant reaction that protects F. gigantica from damage by free radicals released from host immune cells. FgGPx is expressed in all stage of F. gigantica from eggs, metacercariae, newly excysted juveniles, 4-week-old juveniles, to adults. It has been revealed that a mouse-derived anti-rFgGPx antibody reacts with the native FgGPx without cross-reactivity with other parasites.
FgSAP-2 protein is a member of the family of lipid-interacting proteins which participate in the cytolysis of target cells. This protein is expressed only in late juvenile and adult F. gigantic, suggesting FgSAP-2 acts as a specific immunodiagnostic marker and a vaccine candidate for fasciolosis.
As a leading service provider in anti-parasite antibody discovery, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to offering the best solutions to facilitate the discovery of antibodies against Fasciola to meet your special purposes. Our professional expert team has successfully established an advanced AntInfectTM Platform which streamlines antibody discovery program and increases the efficiency of antibody generation. If you are interested in anti-parasite antibody discovery, please free to contact us for more information.