Along with over a decade of extensive experience in antibody development, Creative Biolabs can develop novel VHH to meet our clients' various project requirements. From the target identification to the final VHH antibody production, our one-stop solution
can offer a series of pathways to achieve the project goals, which can free up your valuable time and effort on the innovative side of the project.
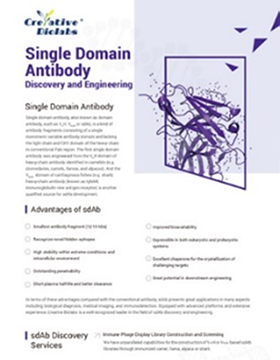
Based on the unique advantages of small size, high stability, and outward solubility, single domain antibodies play an important role in many fields, including but not limited to:
In this case study, a soluble protein was used as the screening target. Creative Biolabs got 13 single domain antibody (sdAb) binders specific to this target from our pre-constructed antibody library.
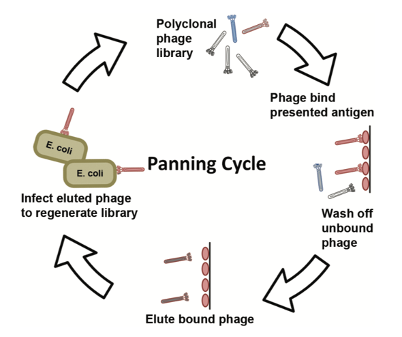
This project used a solid phase screening strategy to immobilize the target on the surface of the well plate. After three rounds of bio-panning, we obtained good enrichment and a significant difference compared with the control group. This indicates that some specific binders against this target have been obtained.
After the panning, we randomly selected multiple clones for monoclonal phage ELISA detection against the target and performed DNA sequencing on the positive clones.
Through DNA sequencing, we finally obtained 13 clones that showed uniqueness at the CDR level. Two of these clones showed significantly higher abundance. We then prepared these unique clones into soluble (phage-free) solutions for quality control soluble ELISA validation.
The article highlights significant progress in Alzheimer's disease research through the use of a single-domain antibody (sdAb), named DesAb-O, which selectively detects and neutralizes toxic Aβ42 oligomers in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
DesAb-O shows remarkable specificity for Aβ42 oligomers compared to other amyloid forms, demonstrating a potent ability to identify and counteract these neurotoxic aggregates both in vitro and in neuronal cell cultures. This breakthrough
offers dual benefits: enhancing early Alzheimer's diagnosis by pinpointing specific biomarkers in CSF, and potentially developing new therapeutic strategies targeting the toxic oligomers associated with disease progression. By mitigating the effects
of these oligomers, DesAb-O could significantly impact the treatment and management of Alzheimer's disease, marking a promising step forward in the fight against this debilitating condition.
1. What is a single domain antibody (sdAb)?
A single domain antibody (sdAb) is the smallest functional fragment of an antibody, consisting only of a single monomeric variable antibody domain. Unlike conventional antibodies, which are composed of both heavy and light chains, sdAbs lack the light
chains and the constant regions, making them much smaller and more versatile.
2. How are sdAbs different from conventional antibodies?
Single domain antibodies offer several advantages over traditional antibodies due to their small size, robust structure, and high solubility. These attributes allow sdAbs to bind to epitopes that are inaccessible to conventional antibodies, providing
enhanced tissue penetration and stability under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or denaturing environments.
3. What are the primary sources of sdAbs?
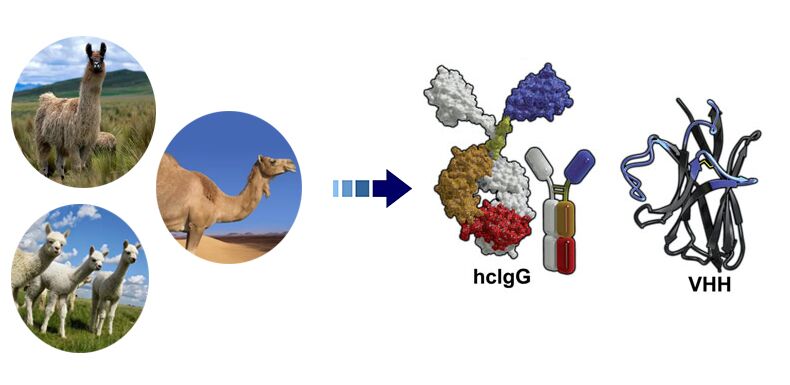
Single domain antibodies are primarily derived from the heavy-chain-only antibodies found in camelids, such as llamas and camels, or from cartilaginous fishes like sharks. These organisms produce antibodies that naturally lack light chains, which have
been adapted for therapeutic and diagnostic applications in humans.
4. What are the applications of sdAbs in medicine?
Single domain antibodies are used in various medical applications including as therapeutic agents in cancer, infectious diseases, and inflammatory disorders. They are also employed in diagnostic assays due to their ability to bind specifically to small
and cryptic antigens, enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of these tests.
5. What makes sdAbs ideal for therapeutic use?
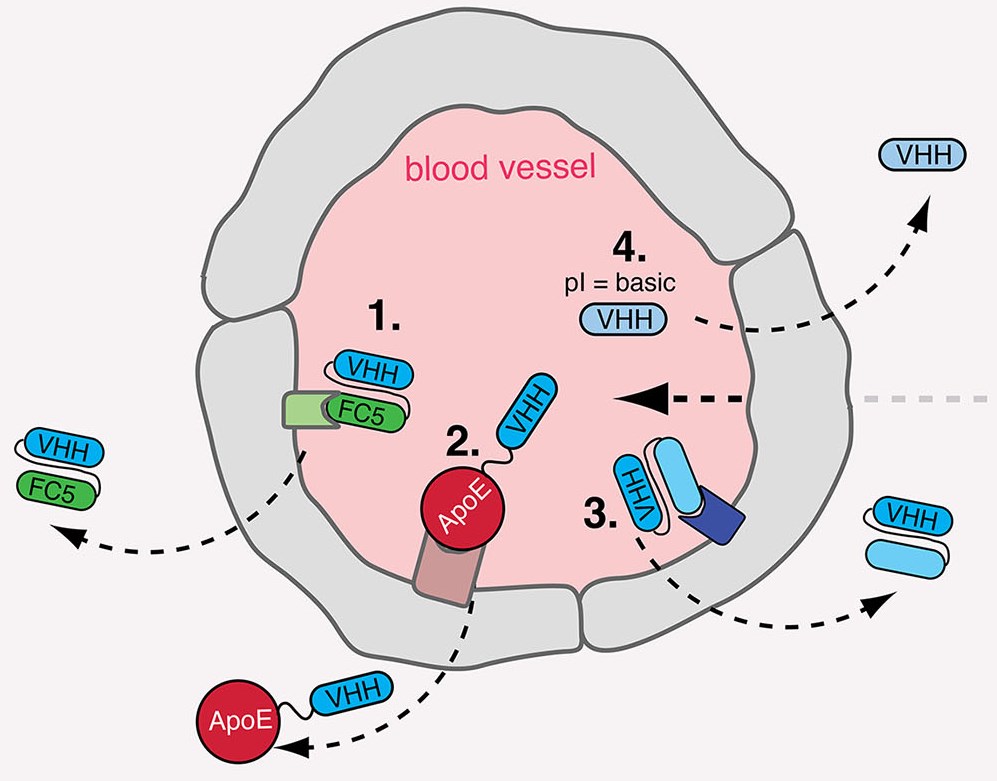
The small size and unique structure of sdAbs allow for rapid tissue penetration and fast clearance from the bloodstream, which is beneficial for reducing systemic toxicity. Their ability to remain stable under harsh conditions also makes them suitable
for oral administration and topical applications, expanding their use beyond injectable forms.
6. How are sdAbs developed?
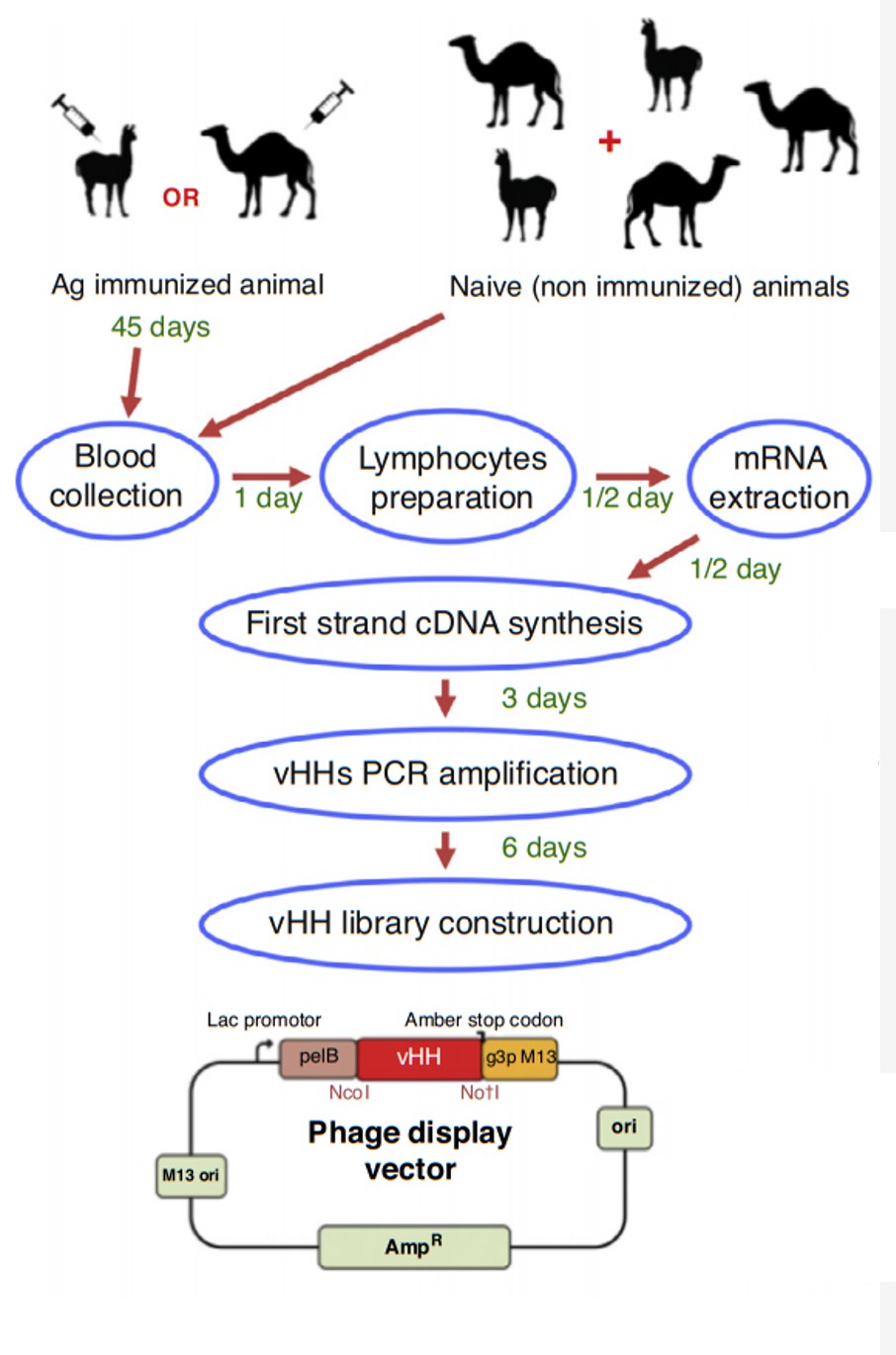
Single domain antibodies are typically generated through immunization of camelids or sharks and subsequent recovery of the variable domains from the immune cells. Alternatively, phage display libraries can be constructed to screen for sdAbs that bind
with high affinity to desired antigens, allowing for the selection of candidates without the need for animal immunization.
7. What is the role of sdAbs in targeted drug delivery?
Single domain antibodies can be conjugated to drugs, toxins, or other therapeutic agents to form targeted delivery systems. Their precise binding to specific cellular targets allows for the direct delivery of the therapeutic agent to diseased cells, minimizing
the impact on healthy tissues and reducing side effects.
8. What future advancements are expected in sdAb technology?
Future advancements in single domain antibody technology are likely to focus on improving their pharmacokinetics, reducing immunogenicity, and enhancing their therapeutic index.

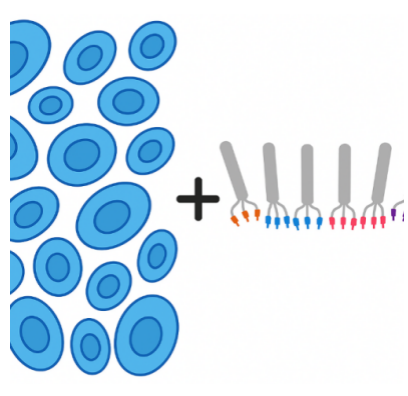
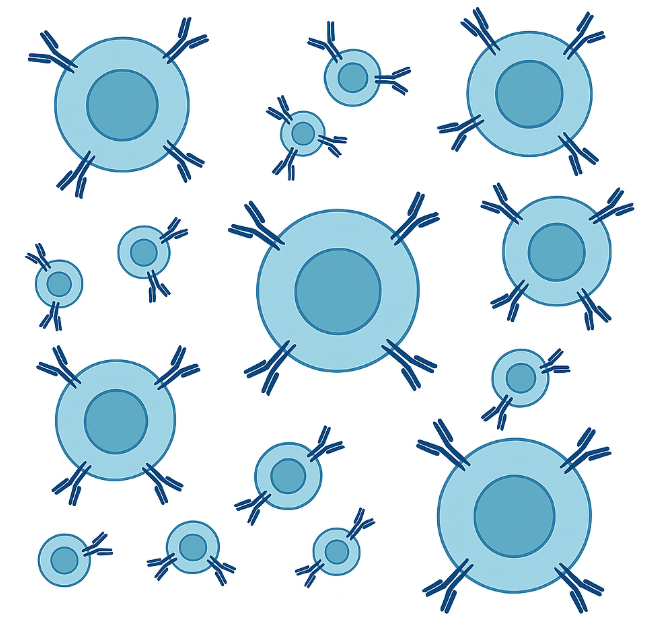
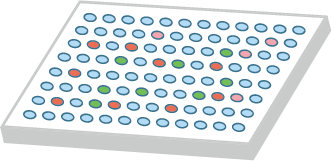
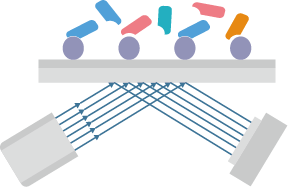
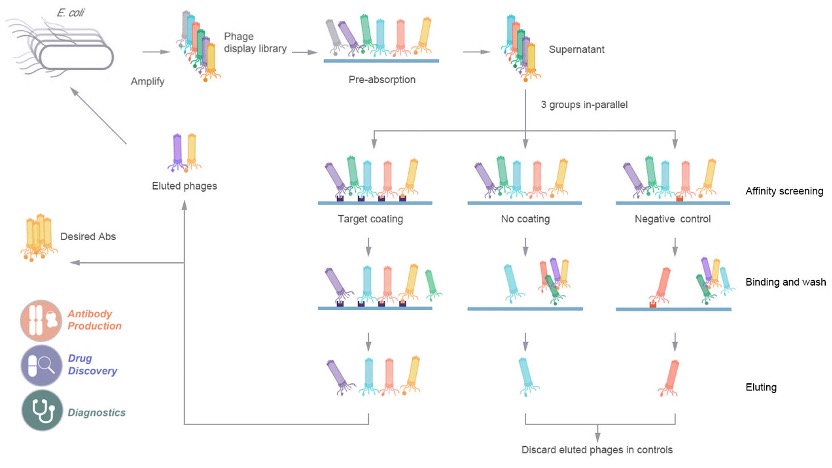 Figure 1. Flow diagram of phage display-based screening using premade HuSdL-1™ library.
Figure 1. Flow diagram of phage display-based screening using premade HuSdL-1™ library.
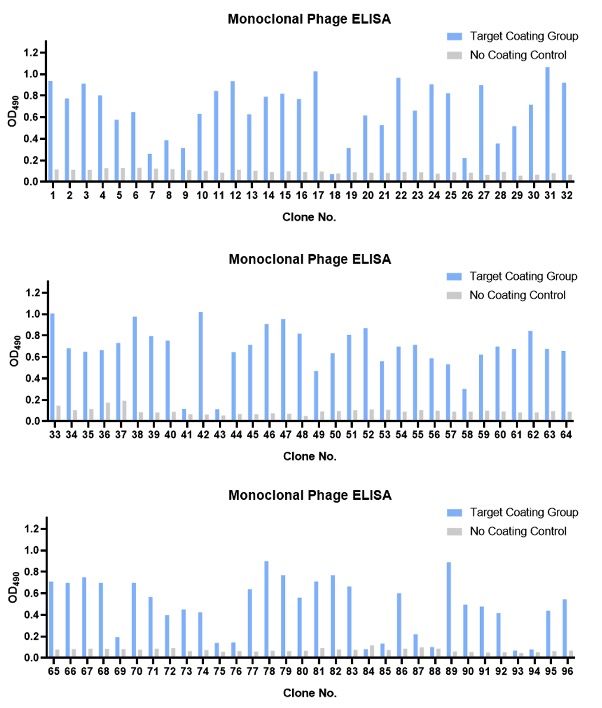 Figure 2. Monoclonal phage ELISA of the 96 randomly picked clones.
Figure 2. Monoclonal phage ELISA of the 96 randomly picked clones.
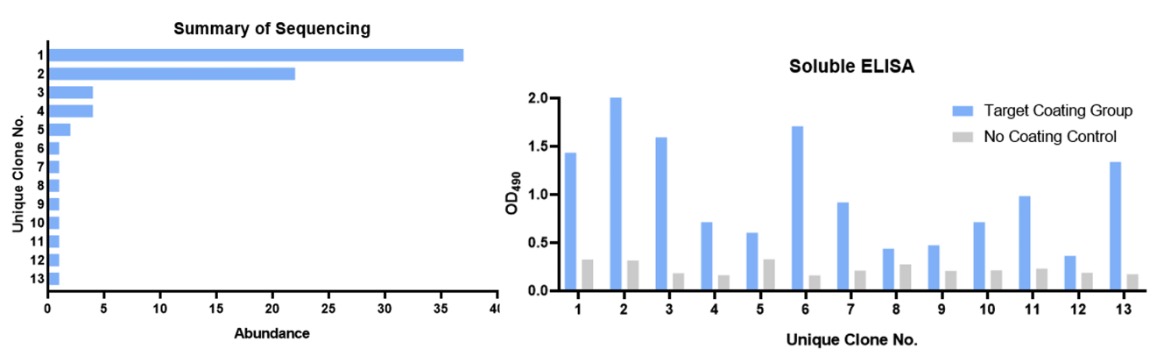 Figure 3. Summary of DNA sequencing and QC soluble ELISA of the 13 unique sdAb candidates.
Figure 3. Summary of DNA sequencing and QC soluble ELISA of the 13 unique sdAb candidates.
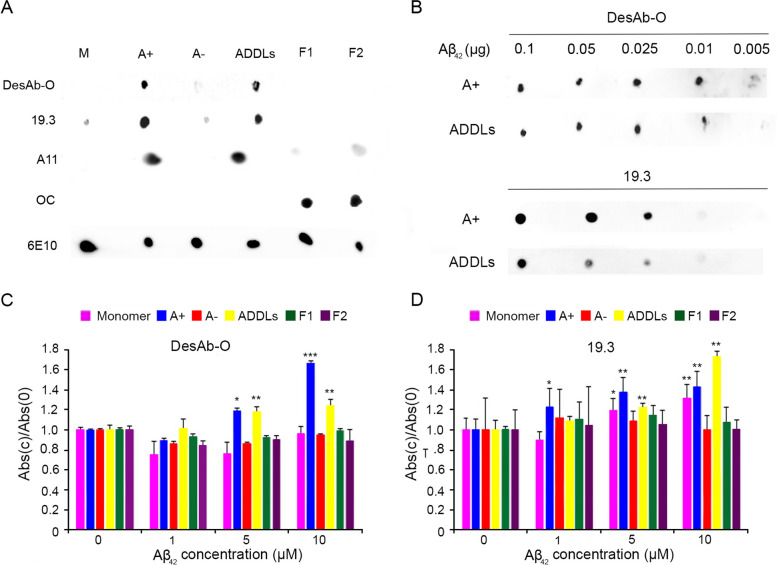 Fig. 1 DesAb-O selectively detects synthetic Aβ42 oligomers in vitro.1
Fig. 1 DesAb-O selectively detects synthetic Aβ42 oligomers in vitro.1