Protein-protein interaction plays an essential role in virtually every cellular process and the identification of it is a key step to understand unknown and complex protein functions. So far, Creative Biolabs has provided a bacteria-based genetic selection system, Bacterial Two-hybrid (B2H, BTH), to explore the details of protein’s interaction and achieve clients’ requirements on it.
The bacterial two-hybrid is a rapid genetic approach to detect and characterize interactions between a wide variety of bacterial, eukaryotic, or viral proteins in vivo. Similarly to the classic yeast two-hybrid (Y2H), bacterial two-hybrid is based on reconstituting the activity of a certain protein from its separate domains and a reporter gene is expressed only when the relative protein-protein interaction occurs within a test cell. It is worth noting that the phenomenon of autoactivation by baits is a less problem in bacterial systems than in the yeast. Therefore, the bacterial method provides an alternative strategy for studying proteins which cannot be assayed in Y2H because of toxicity or low expression.
The Principle of Bacterial Two-hybrid
The bacterial two-hybrid was initially devised using bacteria as a host organism in 1997. It’s a transcriptional activation-based two-hybrid approach and has become a common laboratory tool preferred in some specified circumstances.
This is a two-hybrid method in Escherichia coli where the proteins of interest are fused to two complementary fragments of the catalytic domain with Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase, T25, and T18, that are not active when physically separated. Interaction of these two proteins results in functional complementation between the two adenylate cyclase fragments, which leads to cAMP synthesis and in turn, can trigger the expression of several resident genes, such as lac and mal operons. Using this assay, scientists can select specific clones expressing a protein that interacts with a given target. And with the development of bacterial two-hybrid, proteins of bacterial origin can be analyzed for interactions under conditions that match their native environment more closely.
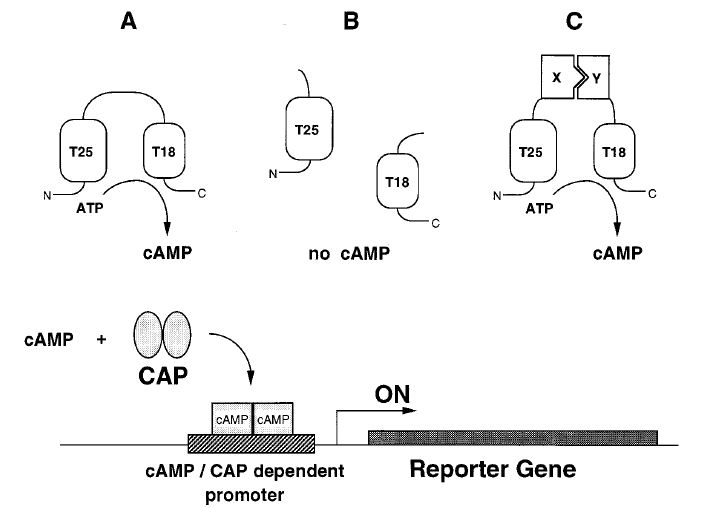 Fig.1 Principle of bacterial two-hybrid systems.
Fig.1 Principle of bacterial two-hybrid systems.
Workflow and Advantages
There are four facile steps in a bacterial two-hybrid system: construction of plasmids, transformation of microbial cells, intracellular expression of fusion proteins, and selection for reporter product. Taking E. coli as host offers potentially significant advantages over analogous two-hybrid systems:
Moreover, the bacterial two-hybrid selection system from Creative Biolabs can not only study interactions of different proteins from both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but also apply successfully in the protein-DNA analysis, and identify antigen-specific single domain antibodies.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.