Status of Small Molecule-Target Interaction Detection
Over thousands of years, small-molecule drugs have been widely applied for the treatment of human diseases. It is recognized that small molecule drugs work by acting on specific targets in the body, mainly including receptors, enzymes, ion channels, transporters, nucleic acids, and other biological macromolecules. The interactions between drugs and targets not only matter on the efficacy and specificity of drugs, but also involve drug safety and potential side effects. Scientists always have been committed to exploring the mechanism-of-actions of these small molecule drugs so as to minimize the side effects, optimize treatment outcomes, and most importantly, discover and develop novel and more effective drugs. By identifying the targets of drugs, we can better understand the mechanisms of drug action, establish the relationship between drug activity and biological function, predict possible side effects and resistance mechanisms, and discover new therapeutic targets.
Two frequently-used fundamental approaches have been exploited and applied for drug discovery and development, that are phenotype-based drug discovery and target-based drug discovery. Phenotype-based drug discovery involves screening small molecules or biomolecules in cells, tissues, or organs based on pharmacological research. Target-based drug discovery involves identifying the target and then the active molecules. With the rapid development of molecular biology, the target-based drug discovery paradigm has gradually replaced traditional phenotype-based methods since it improves screening ability and benefits for reasonable and rapid drug discovery.
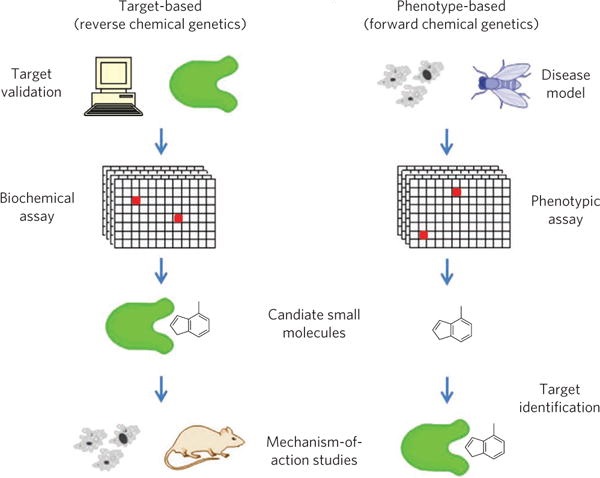 Fig. 1 Two fundamental drug discovery strategies.1
Fig. 1 Two fundamental drug discovery strategies.1
Chose Creative Biolabs for Your Drug Target Identification
Supported by our powerful technology platform, Creative Biolabs has accumulated rich experience and won a good reputation in delivering biomolecular interaction analysis services, including protein-protein interaction and protein-nucleic acid interaction. Here, we have developed a small molecule drug target identification platform and grandly launched small molecule-target interaction assay services for global customers to provide you with a full process scientific research service for unknown target identification and intermolecular interaction detection. Our qualified services primarily include:
Activity-based Protein Profiling (ABPP)
Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) combines active probes and proteomics techniques to identify small molecule protein targets and even the active sites of target proteins. The active small molecule probe (i.e., activity-based probes, ABPs) is the key factor in ABPP, which is composed of small molecules that can specifically react with the active site of targets, and reporter tags for detecting, quantifying, and/or identifying targets. In principle, small molecule compounds or their active groups directly interact with target proteins to capture targets. And further identification assays can be performed according to the reporter tags, such as fluorescent groups for rapid screening and localization of small molecules in cells or tissues and biotin tags for protein enrichment. Then captured target proteins can be identified through mass spectrometry (MS) detection. ABPP serves as a useful tool for target identification, inhibitor discovery, and target localization and visualization.
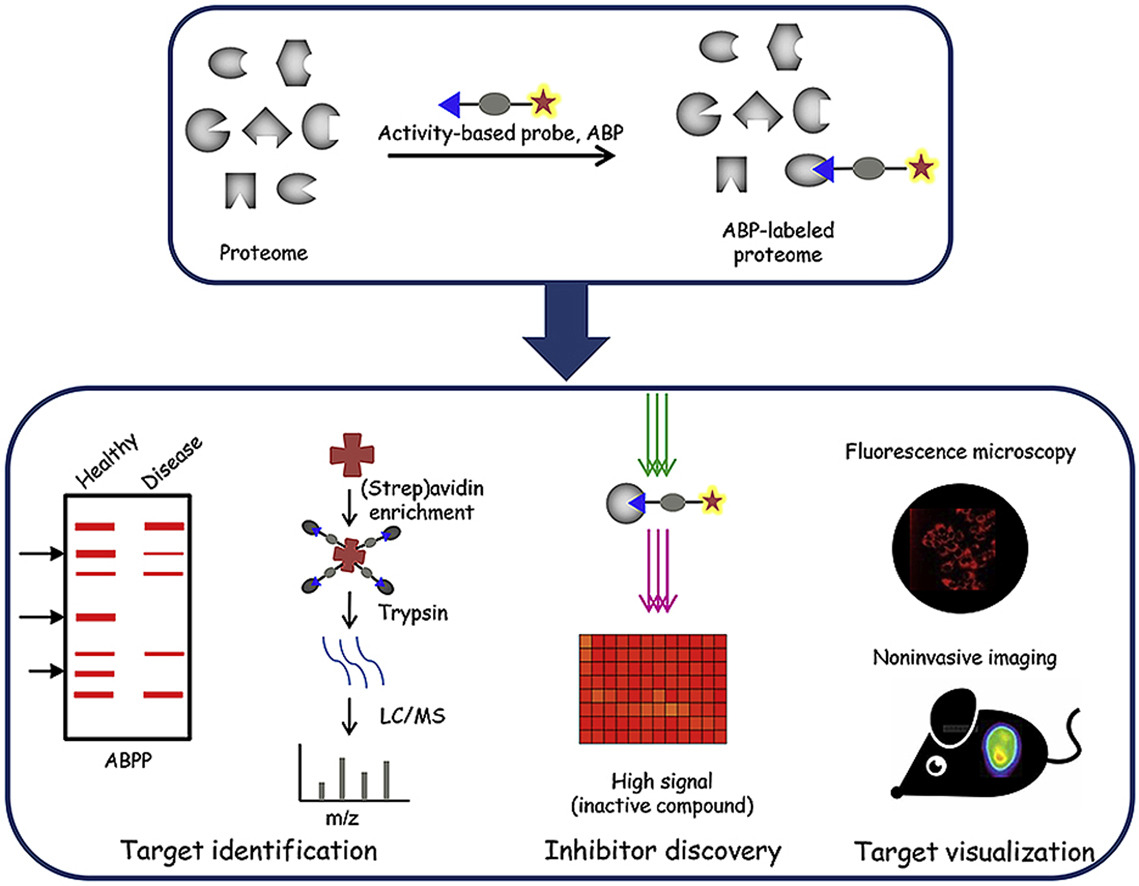 Fig. 2 Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP).2
Fig. 2 Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP).2
Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS)
Another quick and direct method for potential target identification is drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS), which relies on the protection of target proteins from protease degradation by interacting with small molecules. To identify the candidate target of a small molecule by DARTS, cell lysates are treated with a small molecule of interest and carrier controls or inactive analogues, and then digested and degraded by the proteases. Then, the samples are separated and stained using SDS-PAGE to find out the differential bands, which are protein bands stabilized by small molecules. Finally, the differential protein bands are identified by the MS. DARTS is an unbiased approach that has been successfully used to identify potential protein targets for natural products and other bioactive small molecules.
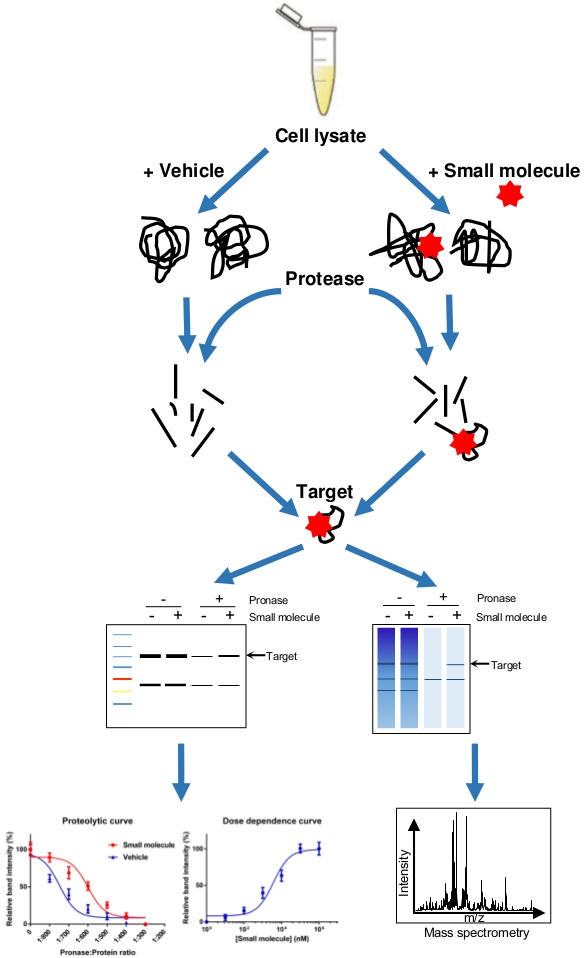 Fig.3 Drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS).3
Fig.3 Drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS).3
Limited Proteolysis-Mass Spectrometry (LiP-MS)
Similar to DARTS, limited proteolysis-mass spectrometry (LiP-MS) is a method combining protein restriction enzymolysis and MS analysis. During the LiP-MS process, small molecules are incubated with a complex sample such as a cell lysate. The binding of small molecules to proteins leads to changes in protein conformation, which affect the protease accessibility and enzymolysis mode of proteins, yielding condition-specific cleavage products. By comparing the enzymatic fragments of proteins under drug treatment and untreated conditions, the protein regions that interact with drug molecules will be identified, and the target protein can be inferred. LiP-MS is a method making more contributions to MOA exploration, especially in the targeted design of drug molecules and optimization of drug efficacy.
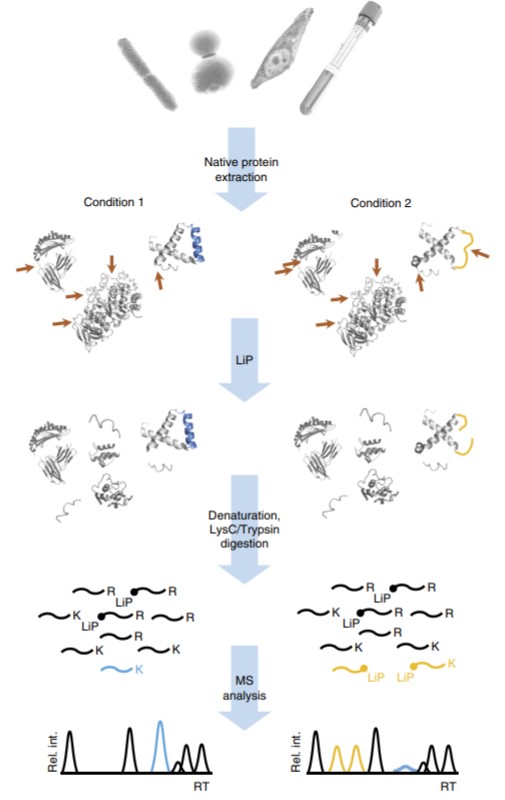 Fig. 4 Limited Proteolysis-Mass Spectrometry (LiP-MS).4
Fig. 4 Limited Proteolysis-Mass Spectrometry (LiP-MS).4
Cell-Based Thermal Shift Assay
Based on the thermo stability assay (TSA) technological platform, we developed the cell-based TSA based on the fact that proteins denature and become insoluble when heated. To perform cell-based TSA, the cell samples are incubated with small molecules and control vehicles and heated under certain temperature points. The structure of non-drug binding proteins undergoes thermal denaturation at this temperature, losing their spatial structure and function; where the structure of target protein is stabilized by molecule drugs and not easily denatured at the same temperature. Then, detect the protein bands of each group through electrophoresis or silver staining, and identify the differential protein bands using MS technology. Cell-based TSA also can be performed in vitro, in vivo, and even in situ.
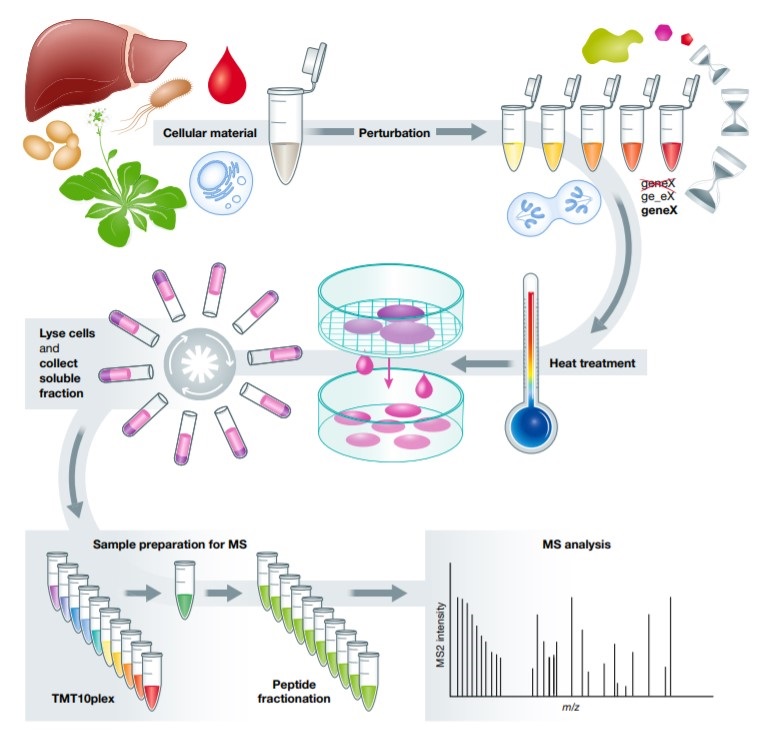 Fig. 5 Cell-Based Thermal Shift Assay.5
Fig. 5 Cell-Based Thermal Shift Assay.5
Highlights of Our Services
Creative Biolabs is devoted to the whole stage of the preclinical investigations of pharmaceutical development and provides a series of high-throughput and reliable approaches to screen and identify the target candidates of small-molecule drugs. Our Ph.D. scientist team is experienced in offering small molecule-target interaction assay services based on your specific needs.
To know more about small molecule-target interaction assay, please directly contact us to get more information or useful support.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.