Targeted delivery systems provide an innovative and effective method for treating esophageal cancer, enhancing the efficacy of antineoplastic and chemotherapeutic agents while reducing side effects.
Esophageal Cancer Targeting Module Development Service
Creative Biolabs delivers precise treatment solutions for esophageal cancer using Targeting Modules including peptides, antibodies and aptamers combined with Drug/Module Delivery Systems like liposomes LNPs and exosomes to enhance precision and therapeutic effectiveness. Our drug conjugation techniques including ADCs, PDCs and ApDCs facilitate precise delivery of therapeutic agents to cancer cells and reduce the occurrence of unnecessary side effects.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Overview
Esophageal cancer becomes an aggressive disease that often results in poor patient outcomes because it is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage. Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma represent the two primary types of esophageal cancer which develop because of risk factors including smoking habits alcohol consumption and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Despite the availability of surgical options as well as chemotherapy regimens alongside radiation therapy and targeted treatments advanced-stage disease patients continue to experience low survival rates. The combination of Drug/Module Delivery Systems (DDS) with Targeting Modules represents a promising treatment strategy since it increases both specificity and effectiveness in treatment delivery. The combined systems enable precise drug delivery to cancer cells which reduces side effects and improves treatment effectiveness. Delivery systems such as liposomes and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) enable therapeutic agents to deliver drugs in a controlled and efficient manner. The employment of targeting modules like peptides, antibodies and aptamers enables precise cancer cell targeting because they can bind to specific cell receptors. The application of drug conjugates like antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), aptamer-drug conjugates (ApDCs), and peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs) improves the ability to selectively target therapy. By delivering toxic therapeutic agents straight to cancer cells through conjugation systems both systemic toxicity and treatment effectiveness are reduced.
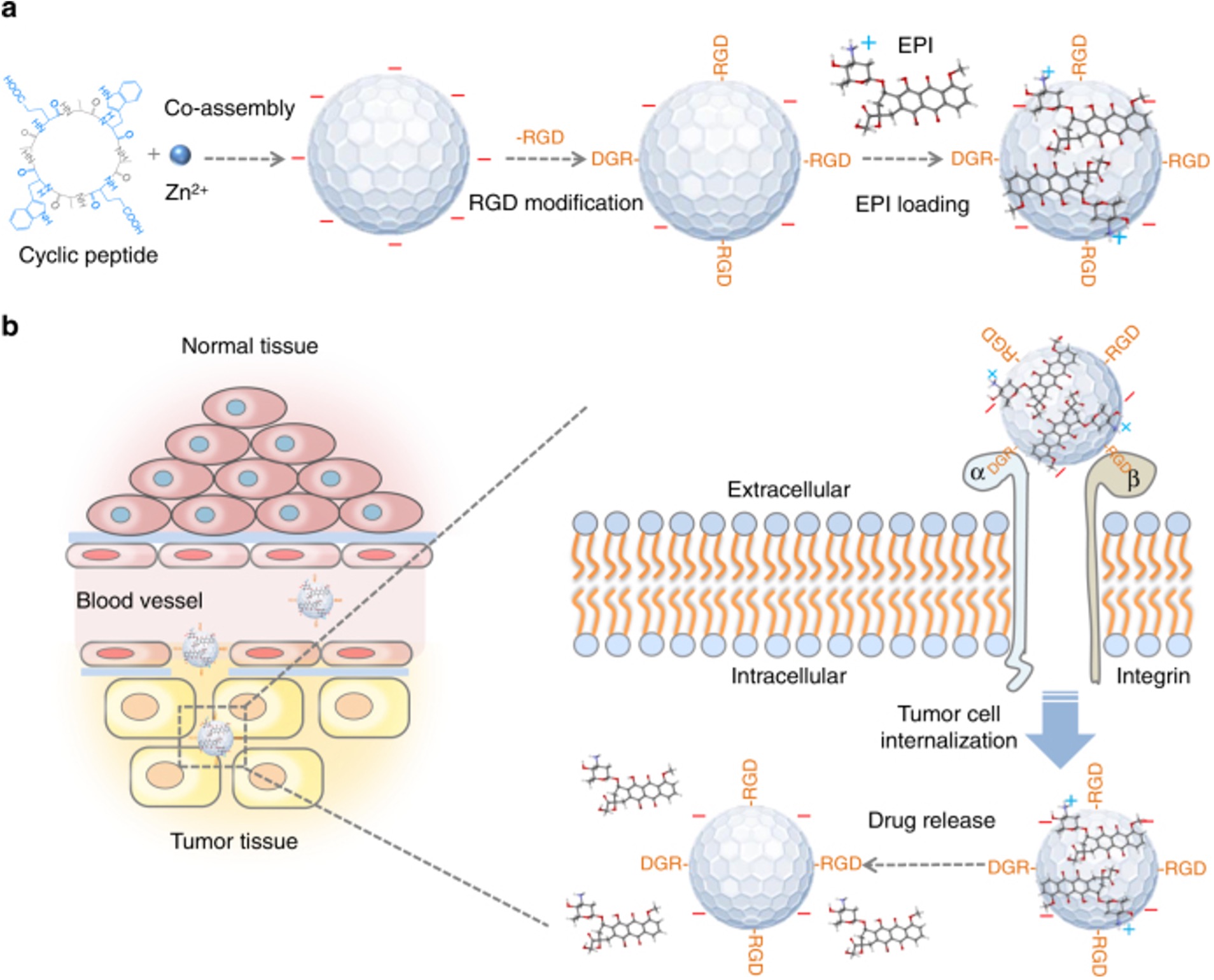 Fig. 1 A schematic illustration of the synthesis of RGD-f-PNPs/EPI and its targeted EPI delivery into EC cells.1
Fig. 1 A schematic illustration of the synthesis of RGD-f-PNPs/EPI and its targeted EPI delivery into EC cells.1
Esophageal Cancer Targeting Delivery Systems
Targeted drug delivery systems (TDDS) offer cutting-edge solutions to increase treatment precision and effectiveness in the fight against esophageal cancer. Targeted delivery systems allow therapeutic agents to directly attack tumor sites which decreases systemic toxicity and minimizes off-target effects while enhancing drug bioavailability. Below is a list of common TDDS delivery systems, each designed to optimize drug delivery for various medical applications.
Table 1. The Primary Types of TDDS Utilized in The Treatment of Esophageal Cancer
| TDDS Type | Description | Targeting Mechanism | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles | Small particles (1-1000 nm) that encapsulate drugs, improving solubility and bioavailability. | Active targeting via surface modifications with ligands specific to esophageal cancer markers (e.g., EGFR, HER2). | Chemotherapy, gene therapy, immunotherapy, and drug delivery. |
| Liposomes | Biodegradable lipid-based vesicles that carry both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. | Targeting through surface modification with ligands or antibodies for specific tumor receptors. | Drug delivery, controlled release of chemotherapy, targeted gene therapy. |
| Polymeric Micelles | Amphiphilic copolymers that form micelle structures to encapsulate drugs. | Active targeting via conjugation with ligands for receptors overexpressed in esophageal cancer cells. | Targeted chemotherapy, gene delivery, and controlled drug release. |
| Dendrimers | Highly branched nanoscale polymers that offer controlled drug loading and surface modification. | Surface modification for receptor-specific targeting in esophageal cancer cells. | Gene therapy, drug delivery, RNA interference, and personalized treatments. |
| Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) | Monoclonal antibodies conjugated to cytotoxic drugs, enabling selective delivery to cancer cells. | Targeting through antibodies specific to receptors overexpressed in esophageal cancer cells (e.g., HER2, EGFR). | Targeted chemotherapy, localized drug delivery. |
| Gene Delivery Systems | Nanoparticles or viral vectors used for delivering genetic material (siRNA, mRNA) to cancer cells. | Receptor-mediated targeting or endocytosis for gene therapy in esophageal cancer. | Gene silencing, gene therapy, RNA interference to inhibit tumor growth. |
| Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs) | Peptides that facilitate direct entry of drugs or nucleic acids into cancer cells. | Facilitating drug and gene delivery into esophageal cancer cells using CPPs. | Gene therapy, protein delivery, and targeted drug delivery for esophageal cancer. |
Targeting ligands are crucial in the design of targeted drug delivery systems, as they enable the selective delivery of therapeutic agents to specific cells or tissues. By binding to receptors or biomarkers on target cells, these ligands ensure that drugs are delivered directly to the site of action, improving treatment precision, and minimizing unwanted side effects. The choice of targeting ligand is essential for the effectiveness of the drug delivery system. Below is a list of commonly used targeting ligands, highlighting their applications in various therapeutic areas.
Table 2. Targeting Ligands Used in Preclinical Studies for Esophageal Cancer
| Targeting Ligand | Target | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) | Overexpressed in esophageal cancer cells, especially in squamous cell carcinoma | EGFR is frequently upregulated in esophageal cancer, particularly in squamous cell carcinoma. | Targeted drug delivery, immunotherapy, and gene therapy for esophageal cancer. |
| HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2) | Esophageal cancer cells, especially adenocarcinoma | HER2 is overexpressed in some esophageal adenocarcinomas, making it a key target for therapy. | Targeted drug delivery, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and immunotherapy. |
| Folate Receptor | Esophageal cancer cells | Folate receptor is overexpressed in many esophageal cancer cells, especially in adenocarcinoma. | Targeted drug delivery, gene therapy, and nanoparticle-based therapies. |
| Integrins (αvβ3, αvβ5) | Tumor vasculature and cancer cells | Integrins are involved in tumor angiogenesis and adhesion, often overexpressed in cancer cells. | Nanoparticle-based delivery systems, anti-angiogenic therapies. |
| CD44 | Cancer stem cells in esophageal cancer | CD44 is a cell surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions and is upregulated in cancer stem cells. | Targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to cancer stem cells, gene therapy. |
| N-cadherin | Esophageal cancer cells, particularly in invasive forms | N-cadherin is involved in cell adhesion and is overexpressed in invasive and metastatic esophageal cancer. | Targeted drug delivery, cell adhesion modulation, and anti-metastatic therapies. |
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
What Can We Do for You?
Revolutionary Treatment for Esophageal Cancer (EC)
Specialized Drug Delivery and Immunotherapy Services
Creative Biolabs focuses on developing customized targeted drug delivery and immunotherapy services specifically for EC, using advanced technologies to improve treatment outcomes.
High-Quality and Affordable Services
Our expert scientists and cutting-edge platforms ensure that we deliver high-quality, affordable services that are tailored to support the success of your EC treatment projects.
Get in Touch for More Information
To learn more about our services or to request a detailed quote, please feel free to reach out to us at your convenience. We're here to help your project succeed.
Workflow
FAQ
Q: What types of targeting modules do you offer for esophageal cancer?
A: We offer a range of targeting modules, including monoclonal antibodies, peptides, aptamers, and small molecules, each specifically designed to recognize and bind to biomarkers or receptors unique to esophageal cancer cells, including those in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Q: Can the targeting modules be combined with drug delivery systems?
A: Yes, we specialize in combining targeting modules with state-of-the-art drug delivery systems such as nanoparticles, liposomes, lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles, and micelles. This allows for enhanced delivery of chemotherapeutic agents, immunotherapies, or other therapeutic molecules directly to the esophageal tumor site.
Q: How do you test the effectiveness of the targeting modules?
A: We use a variety of preclinical models, including in vitro (cell line) and in vivo (animal) studies, to assess the efficacy, specificity, and safety of the targeting modules. These studies provide valuable data on how well the modules bind to the tumor site, how effectively they deliver the therapeutic agents, and the overall therapeutic outcomes.
Reference
- Fan, Zhen et al. "Near infrared fluorescent peptide nanoparticles for enhancing esophageal cancer therapeutic efficacy." Nature communications vol. 9,1 2605. 4 Jul. 2018, DOI:10.1038/s41467-018-04763-y. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



