Creative Biolabs specializes in the development of advanced targeted drug delivery systems specifically designed for bladder cancer treatments.
Bladder Cancer Targeting Module Development Service
Creative Biolabs develops specialized drug delivery systems and targeting modules that are customized for bladder cancer treatment. We develop state-of-the-art nanoparticle systems including liposomes and LNPs while combining targeting modules like CPPs, antibodies, and aptamers to achieve accurate tumor targeting. Our team provides end-to-end support for transitioning advanced laboratory therapies into preclinical use.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Overview
Bladder cancer develops as a malignant growth originating from the urothelial cells which line the bladder's interior. The urinary system experiences one of its most frequent cancer types which shows up as blood in urine and painful urination alongside frequent urination urges. We increase bladder cancer treatment effectiveness through Targeting Modules and Drug/Module Delivery Systems which enable precise delivery of therapeutic agents directly to cancer cells while protecting healthy tissues. Our Module Delivery Systems incorporate sophisticated delivery platforms consisting of liposomes together with lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles, Exosomes, and Virus-Like Particles (VLPs). These delivery systems encapsulate medications and transport them straight to the tumor site to improve both bioavailability and drug stability. The Targeting Modules in our system incorporate various tools such as cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), homing peptides (HPs), antibodies, aptamers, and functionalized lipids. These targeting modules focus on cancer cells which allows therapeutic agents to reach bladder tumors efficiently and boosts treatment success. Our approach to more precise therapy includes the integration of drug conjugates such as Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC), Aptamer-Drug Conjugates (ApDC), and Peptide-Drug Conjugates (PDC). This treatment approach combines multiple elements to enable precise targeting of bladder cancer cells while minimizing unintended effects and enhancing treatment results.
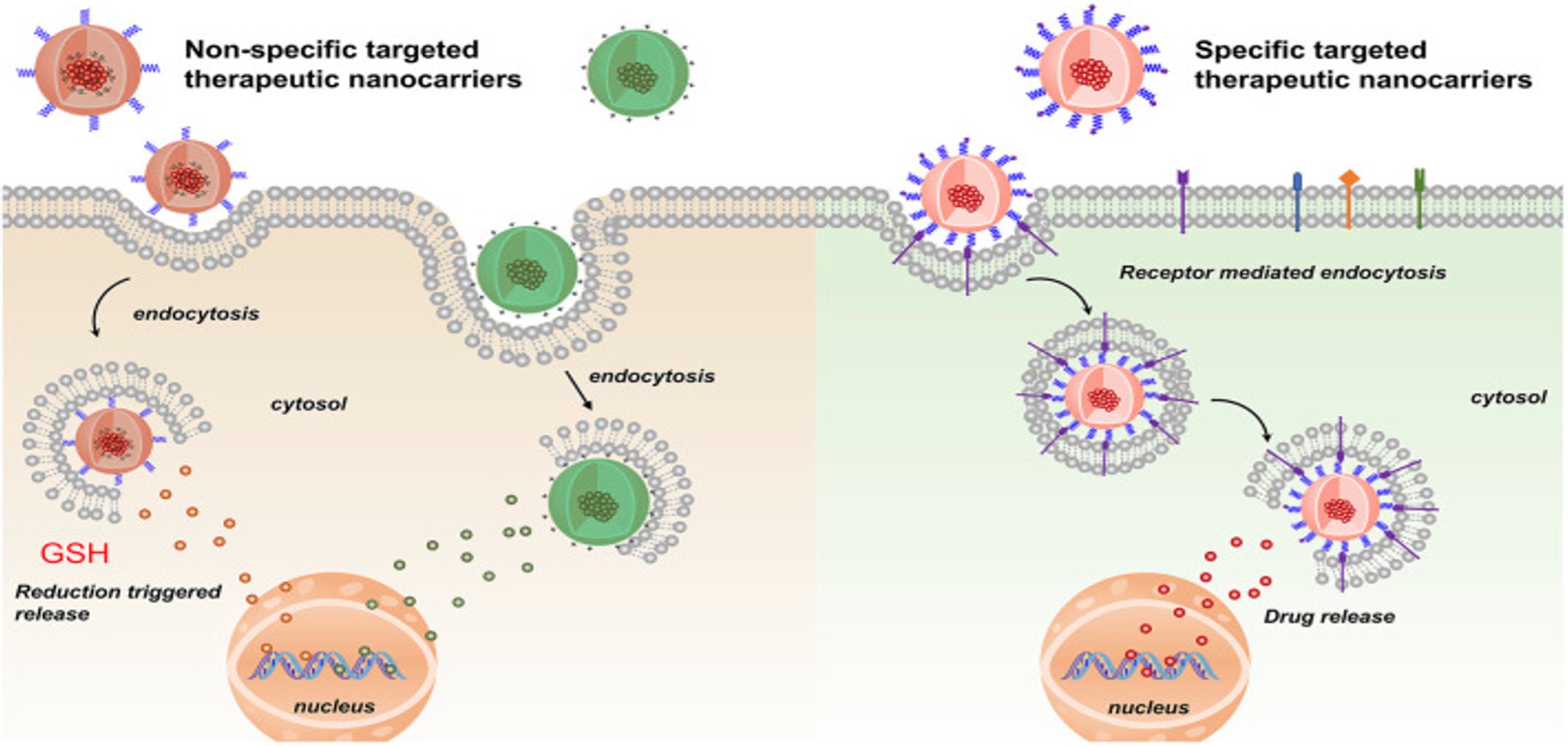 Fig.1 Non-specific and specific targeted therapeutic nano-carrier for treatment of bladder cancer.1
Fig.1 Non-specific and specific targeted therapeutic nano-carrier for treatment of bladder cancer.1
Bladder Cancer Targeting Delivery Systems (TDDS)
Urothelial carcinoma stands out as bladder cancer while representing one of the most prevalent malignancies within the urinary system. The standard treatment protocol for bladder cancer includes surgical procedures together with chemotherapy and immunotherapy as well as intravesical therapy which administers medication directly into the bladder. Standard approaches to bladder cancer therapy often encounter challenges due to harmful side effects and poor drug delivery precision. TDDS marks a significant advancement in therapy by directing drugs to tumor sites for better results and minimizing overall body toxicity. Below is a list of common TDDS, illustrating their applications and features in different therapeutic areas.
Table 1. The Primary Types of TDDS Utilized in The Treatment of Bladder Cancer
| TDDS Type | Description | Targeting Mechanism | Advantages | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | Spherical vesicles composed of lipid bilayers that encapsulate drugs. | Active or passive targeting with ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides) to tumor markers. | Improved drug stability, reduced systemic toxicity, controlled release. | Doxorubicin |
| Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles (LPHNPs) | Hybrid nanoparticles combining lipids and polymers for drug encapsulation. | Targeting via surface-modified ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides, folate). | Better drug encapsulation and controlled release profiles. | PLGA-PEG-DOX LPHNPs |
| Polymeric Nanoparticles | Nanoparticles made from biocompatible polymers (e.g., PLGA) to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs. | Functionalized with targeting ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides). | Controlled drug release, prolonged circulation time. | Paclitaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles |
| Exosomes | Nanovesicles derived from cells that can carry drugs or RNA and be engineered for targeting. | Naturally occurring targeting peptides on the exosome surface (e.g., integrins, CD44). | Biocompatibility, immune evasion, and specific targeting capabilities. | Exosome-based delivery of cisplatin |
| Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) | Nanoscale particles of gold that can be functionalized to carry drugs and imaging agents. | Targeting ligands (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, aptamers) for tumor cells. | High surface area for functionalization, ease of use, and imaging potential. | AuNPs conjugated with doxorubicin |
| Microspheres | Solid spherical particles used for local drug delivery, often in injectable form. | Targeted delivery to bladder tumors, or intravesical administration. | Prolonged drug release, minimal systemic side effects. | PLGA microspheres for intravesical therapy |
Targeting ligands are essential components in targeted drug delivery systems, enabling the selective binding of therapeutic agents to specific receptors on the surface of target cells. These ligands enhance the precision of drug delivery, ensuring that the therapeutic effect is concentrated at the site of action while minimizing systemic exposure and side effects. By choosing the right targeting ligands, treatment outcomes can be significantly improved. Below is a list of commonly used targeting ligands, with details on their applications and therapeutic potential.
Table 2. Targeting Ligands Used in Preclinical Studies for Bladder Cancer
| Targeting Ligand | Target | Mechanism of Action | Research Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2) | HER2 receptor | Antibodies or small molecules targeting overexpressed HER2 | Enhances response to targeted therapies, especially in HER2-positive tumors. |
| EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) | EGFR receptor | Antibodies, small molecules, or ADCs targeting EGFR | Prevents activation of cancer-related signaling pathways, promoting cell death. |
| FGFR (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors) | FGFR (FGFR1, FGFR2) | Small molecules or antibodies targeting FGFR family | Targeting FGFR mutations or overexpression to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. |
| PD-L1 (Programmed Death-Ligand 1) | PD-1/PD-L1 interaction | Antibodies inhibiting PD-L1 to enhance T-cell mediated immune response | Reversing immune evasion in bladder cancer via immune checkpoint inhibition. |
| Integrins (αvβ3, αvβ6) | Integrins (αvβ3, αvβ6) | Peptide-based targeting ligands or antibodies | Disrupts cancer cell adhesion, migration, and invasion. |
| Mesothelin | Mesothelin | Antibodies, CAR-Ts targeting mesothelin | Directly targets mesothelin-expressing bladder cancer cells. |
| VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) | VEGF receptor | Antibodies or small molecules inhibiting VEGF/VEGF-R interaction | Disrupts tumor angiogenesis to limit cancer growth and spread. |
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
What Can We Do for You?
Expertise in Targeted Bladder Cancer Treatments
Innovative Drug Delivery Methods
Leveraging our extensive knowledge of cutting-edge drug delivery technologies, we enhance bladder cancer treatment outcomes through precise targeting.
Integrated Solutions for Improved Efficacy
Our solutions combine nanoparticles, liposomes, and targeted delivery systems, maximizing treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Comprehensive Support for Your Project
Contact us for more information on our bladder cancer support solutions and specialized delivery systems. Our team is dedicated to helping you achieve your treatment goals with expert support.
Workflow
FAQ
Q: Can your targeting modules be integrated with drug delivery systems?
A: Yes, our targeting modules can be seamlessly integrated with various drug delivery systems, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles. These platforms help in the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents, ensuring that the drugs are released directly at the tumor site, improving the therapeutic index and reducing systemic toxicity.
Q: How is the efficacy of the targeting modules evaluated?
A: The efficacy of our targeting modules is rigorously tested using both in vitro (cell-based) and in vivo (animal model) studies. These preclinical tests help evaluate the specificity, binding affinity, and therapeutic effectiveness of the targeting modules.
Q: How long does it take to develop a bladder cancer targeting module?
A: The development time varies depending on the complexity of the project. We work closely with you throughout the process to ensure timelines align with your needs.
Reference
- Tang, Chao et al. "Functional Nanomedicines for Targeted Therapy of Bladder Cancer." Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 12 778973. 16 Nov. 2021, DOI:10.3389/fphar.2021.778973. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



