Creative Biolabs offers advanced drug delivery systems specifically designed for Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer's Disease Targeting Module Development Service
Creative Biolabs delivers cutting-edge drug delivery technologies for Alzheimer's disease through the integration of Targeting Modules such as peptides, antibodies, and aptamers with drug/module delivery systems including liposomes, LNPs, and exosomes. We provide drug conjugation technologies such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and aptamer-drug conjugates (ApDCs) which target amyloid plaques and tau tangles within the brain. The method improves drug passage through the blood-brain barrier which helps to maintain proper treatment effectiveness with reduced side effects.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Overview
Alzheimer's disease develops as a neurodegenerative condition characterized by cognitive decline along with memory loss and behavioral changes. The main cause of dementia continues to be Alzheimer's disease because of brain accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles. Research teams are developing advanced drug delivery techniques by combining Targeting Modules with Drug/Module Delivery Systems to target amyloid plaques and tau tangles directly within the brain because these structures play a crucial role in Alzheimer's disease formation. Drug delivery systems like liposomes and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) protect drugs from breakdown while controlling their release and movement across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) which determines the success of medical strategies. Stable and efficient pathways allow therapeutic agents to reach the brain via these delivery systems. Targeting modules including peptides, antibodies, and aptamers enable delivery systems to focus on amyloid plaques or tau tangles which represents the main pathological targets of treatment. Drug conjugates such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and aptamer-drug conjugates (ApDCs) enable researchers to connect cytotoxic drugs with targeting modules which allows precise therapeutic delivery and reduces unintended effects. The combined treatment strategy demonstrates significant potential to enhance therapeutic success in Alzheimer's disease treatment.
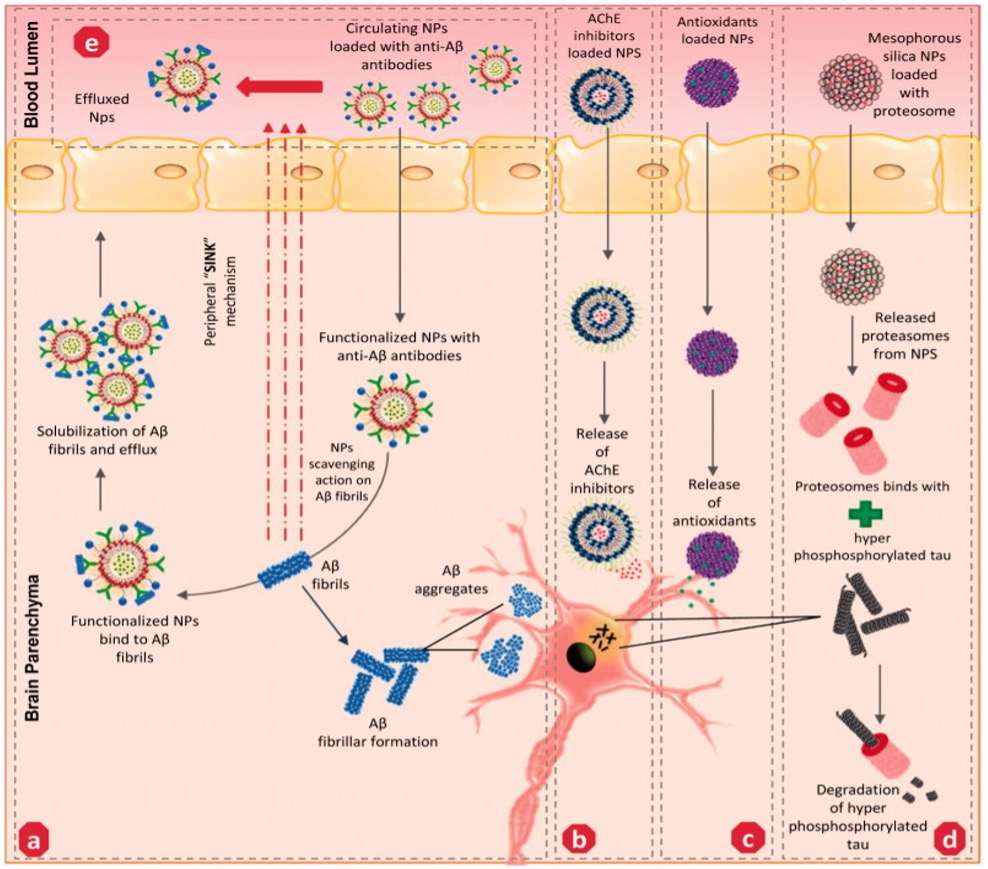 Fig. 1 Potential mechanism of action adapted by various nanoparticles-mediated drug delivery to the targeted site of action associated with AD.
Fig. 1 Potential mechanism of action adapted by various nanoparticles-mediated drug delivery to the targeted site of action associated with AD.
Alzheimer's disease Targeting Delivery Systems (TDDS)
The delivery of therapeutic agents across the blood-brain barrier combined with targeting brain-specific pathophysiology presents a substantial challenge for effective Alzheimer's disease treatment. TDDS enhance therapeutic effectiveness and minimize side effects through precise delivery of drugs directly to brain areas impacted by Alzheimer's disease (AD). Below is a list of commonly used TDDS delivery systems, illustrating their applications and unique features in different therapeutic areas.
Table 1. The primary types of TDDS utilized in the treatment of AD
| TDDS Type | Description | Targeting Mechanism | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | Biocompatible lipid-based vesicles that encapsulate hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, improving drug stability and solubility. | Surface-modified with antibodies, peptides, or aptamers for targeting amyloid plaques or tau proteins. | Targeted drug delivery, anti-amyloid and tau therapy, gene therapy. |
| Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) | Nanoscale lipid particles that encapsulate drugs or RNA, offering enhanced stability and brain penetration. | Functionalized with targeting ligands to cross the blood-brain barrier and target AD-specific receptors. | Gene delivery, RNA-based therapies (siRNA), and drug delivery for AD. |
| Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles | Hybrid nanoparticles combining the advantages of lipids and polymers, offering improved drug encapsulation and release. | Targeting ligands such as peptides and antibodies to deliver drugs directly to the brain. | Lipid-lowering drugs, neuroprotective agents, and AD-specific therapies. |
| Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) | Nanoscale particles that mimic viruses but lack genetic material, used to deliver drugs or genetic material. | Surface modifications for targeting amyloid-beta plaques or tau tangles. | Targeted gene delivery, RNA therapy, and protein delivery to the brain. |
| Fc Fusion Protein | Fusion proteins that combine an antibody fragment with a biologically active protein for enhanced targeting. | Targeting to amyloid plaques or tau fibrils via specific antibody domains. | Delivery of therapeutic proteins or enzymes for AD treatment. |
| Albumin-Based Nanoparticles | Biocompatible nanoparticles derived from albumin that can encapsulate drugs and cross the BBB. | Targeting the brain through albumin receptor-mediated endocytosis. | Drug delivery for neurodegenerative diseases, including AD. |
Targeting ligands are key components in targeted drug delivery systems, enabling selective binding to specific receptors or markers on the surface of target cells. By ensuring that therapeutic agents are directed precisely to the site of action, these ligands enhance treatment efficacy and reduce off-target effects. The choice of targeting ligand plays a significant role in optimizing drug delivery. Below is a list of commonly used targeting ligands, detailing their applications in various therapeutic fields.
Table 2. Targeting Ligands Used in Preclinical Studies for Alzheimer's disease
| Targeting Ligand | Target | Mechanism of Action | Research Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ-Directed Antibodies | Amyloid beta plaques (Aβ) | Antibodies such as Bapineuzumab bind to amyloid plaques, enabling targeted drug delivery or immune response. | Targeting amyloid plaques and plaque clearance. |
| Aβ-Specific Peptides | Amyloid beta plaques (Aβ) | Short peptides, such as Aβ-targeting peptides, bind to amyloid plaques to facilitate drug delivery. | Enhancing plaque targeting and drug release. |
| Anti-Tau Antibodies | Tau tangles | Antibodies like Tau5 bind to tau tangles, potentially helping in the removal of misfolded tau proteins. | Targeting tau aggregation and reducing neurofibrillary tangles. |
| Aptamers | Amyloid beta plaques, Tau tangles | Nucleic acid-based aptamers bind specifically to amyloid plaques or tau tangles, allowing for targeted drug delivery. | Targeting amyloid and tau pathology with high specificity. |
| Homing Peptides (HPs) | Amyloid plaques, Tau tangles | Short peptides (e.g., homing peptides) bind to specific receptors or misfolded proteins in AD. | Multi-targeted drug delivery for amyloid plaques and tau tangles. |
| Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs) | Neuroinflammation and cell membranes | Peptides like TAT peptides facilitate cellular entry and can be used to carry therapeutic molecules into the brain. | Overcoming the BBB and enhancing drug delivery. |
| ScFv (Single-Chain Variable Fragment) | Amyloid plaques, Tau tangles | Recombinant antibodies (e.g., scFv fragments) specifically bind to amyloid plaques or tau, serving as targeting agents. | High-affinity targeting for amyloid plaques and tau tangles. |
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
What Can We Do for You?
Specialized Drug Delivery for Alzheimer’s Disease
Innovative Delivery Technologies
We combine liposome and lipid nanoparticle platforms with targeting modules using peptides, antibodies, and aptamers to achieve precise drug delivery.
Enhancing Treatment Outcomes
Our professional team ensures efficient and accurate delivery of therapeutic agents to improve outcomes.
Contact Us for Support
Reach out to learn more about how we can support your research and therapeutic projects in Alzheimer’s disease.
Workflow
FAQ
Q: What types of targeting modules do you offer for Alzheimer's disease?
A: We offer a variety of targeting modules, including monoclonal antibodies, peptide ligands, small molecules, and aptamers, designed to bind specifically to key Alzheimer's disease-related targets such as amyloid-beta plaques, tau tangles, and neuroinflammation biomarkers.
Q: Can your targeting modules be used with drug delivery systems?
A: Yes, we integrate our targeting modules with advanced drug delivery systems such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles to deliver therapeutic agents, such as small molecules, RNA-based therapies, or biologics, directly to the brain or specific areas impacted by Alzheimer’s disease.
Q: How are the targeting modules validated for effectiveness?
A: We conduct rigorous preclinical validation using both in vitro (cell cultures) and in vivo (animal models) studies to assess the specificity, efficacy, and safety of the targeting modules. These tests ensure that the modules are effective in targeting Alzheimer's-related tissues and capable of delivering therapeutic agents to the brain.
Reference
- Karthivashan, Govindarajan et al. "Therapeutic strategies and nano-drug delivery applications in management of ageing Alzheimer's disease." Drug delivery vol. 25,1 (2018): 307-320. DOI:10.1080/10717544.2018.1428243. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



