Module Delivery System Development Services
In the pursuit of groundbreaking therapeutics, precise delivery to the site of action is paramount. Unlocking the full potential of novel drugs—from mRNA to targeted inhibitors—requires overcoming complex biological barriers while ensuring payload stability and minimizing off-target toxicity. Module Delivery Systems represent the pinnacle of this effort, offering a new paradigm in targeted drug development. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in engineering these sophisticated, customizable delivery vehicles, empowering researchers to turn therapeutic concepts into preclinical realities with unparalleled precision.
What Are Module Delivery Systems?
Module Drug Delivery Systems are advanced nanocarriers engineered to transport a therapeutic payload to a specific location in the body. Unlike single-component systems, their design is inherently flexible, constructed from distinct, interchangeable parts. This allows for the rational design of a highly specialized vehicle tailored to the unique challenges posed by a specific drug, disease state, and biological environment.

The Core Principle: A Two-Part Solution
The power of our approach lies in its elegant simplicity. Every system combines two key components in a "plug-and-play" fashion:
- Module Delivery System (The Vehicle): This is the core carrier (e.g., LNP, liposome, exosome) responsible for encapsulating and protecting the therapeutic payload, ensuring its stability and controlling its release.
- Targeted Module (The GPS): This is a specific guiding molecule (e.g., aptamer, peptide, antibody) attached to the vehicle's surface. It acts like a biological guidance system, directing the entire complex to the desired cells or tissues.
This modular framework transforms drug delivery from a series of one-off challenges into a systematic, engineering-driven discipline. It provides the versatility to quickly adapt to new therapeutic payloads and disease targets, enhances targeting precision to improve the therapeutic index, and ultimately accelerates the research and development timeline by making delivery a solvable, predictable variable.
The Payloads We Deliver
Small molecule
Enzyme
Protein Peptide

DNA

mRNA

siRNA
MicroRNA

ASO
Virus
CRISPR-Cas9
Probe
Plasmid
A Collaborative Framework for Module Delivery Systems Development Services
We provide end-to-end services for the development of custom modular delivery systems. Our process is designed to be collaborative, transparent, and rigorously scientific, ensuring the final product meets your exact research needs.
Custom Module Delivery System Development
Our scientific team partners with you to design, synthesize, and optimize a delivery system tailored to your unique application. We meticulously consider every critical parameter to ensure success:

Liposomes
As one of the most established delivery technologies, liposomes offer exceptional versatility. These aqueous-core vesicles can carry both hydrophilic drugs in their core and hydrophobic drugs within their lipid bilayer, making them a flexible choice for a wide range of small molecules and biologics.
- Advantages: Proven clinical track record, excellent biocompatibility, and suitability for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic payloads.
- Best For: Targeted chemotherapy, antifungal/antibiotic drug delivery, and encapsulation of small molecules or peptides.

Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)
The clinical success of mRNA vaccines has made LNPs the gold standard for nucleic acid delivery. Their core structure, composed of ionizable lipids, is expertly designed to electrostatically complex with nucleic acids, providing robust protection from nuclease degradation and facilitating endosomal escape for potent cytosolic delivery.
- Advantages: Unmatched efficiency for nucleic acid encapsulation, clinically validated for potent in vivo transfection, and highly tunable lipid composition.
- Best For: mRNA vaccines and therapeutics, siRNA/miRNA gene silencing, and CRISPR-based gene editing applications.

Exosomes
Harnessing nature's own delivery system, exosomes offer unparalleled biocompatibility. As endogenous carriers, they are inherently non-immunogenic and possess a natural ability to cross biological barriers, making them an exciting frontier for delivering sensitive biologics to hard-to-reach targets.
- Advantages: Minimal immunogenicity, inherent ability to cross barriers like the BBB, and natural cell-targeting properties.
- Best For: Delivery of delicate biologics (proteins, nucleic acids), applications in regenerative medicine, and cargoes targeting the central nervous system.

Polymeric Nanoparticles
Built from biodegradable polymers (e.g., PLGA), these systems offer precise control over the therapeutic release profile. By modulating polymer molecular weight and composition, we can engineer formulations for rapid, delayed, or long-term sustained release, matching your desired pharmacokinetic profile.
- Advantages: Highly tunable drug release kinetics, excellent in vivo stability, and a wide range of available biocompatible polymers.
- Best For: Sustained-release drug formulations, oral delivery systems, and advanced vaccine adjuvants.

Micelles
These self-assembling nanostructures are the ideal solution for overcoming poor drug solubility. Composed of amphiphilic polymers, micelles form a hydrophobic core that effectively encapsulates poorly water-soluble compounds, dramatically increasing their bioavailability and allowing for intravenous administration.
- Advantages: Superior solubilization of hydrophobic drugs, small particle size for enhanced tissue penetration, and ease of large-scale manufacturing.
- Best For: Delivery of hydrophobic small molecule drugs and advanced diagnostic imaging agents.

Nanoemulsions
These kinetically stable, submicron oil-in-water dispersions are exceptional vehicles for lipophilic drugs. Their large surface area and small droplet size can significantly enhance the absorption and bioavailability of poorly soluble compounds.
- Advantages: High loading capacity for hydrophobic payloads, excellent thermodynamic stability, and enhanced bioavailability for oral and topical routes.
- Best For: Oral and topical delivery of poorly soluble drugs, parenteral nutrition, and as adjuvants in vaccine formulations.

Hydrogels
These 3D networks of crosslinked hydrophilic polymers create a biocompatible scaffold for localized and sustained drug release. Injectable formulations can form a depot in situ, releasing their therapeutic payload over days or weeks, minimizing systemic exposure.
- Advantages: High biocompatibility, tunable biodegradability, and capacity for sustained, localized drug release in response to stimuli (e.g., pH, temperature).
- Best For: Localized delivery for oncology or osteoarthritis, tissue engineering scaffolds, and advanced wound healing applications.

Virus-Like Particles (VLPs)
VLPs are engineered protein shells that mimic the structure of a native virus but are non-infectious because they lack viral genetic material. Their uniform structure and viral-derived cell entry mechanisms make them highly efficient delivery vehicles.
- Advantages: Strongly immunogenic (ideal for vaccines), highly uniform structure, and can be engineered for precise cell targeting via surface modifications.
- Best For: Development of next-generation vaccines, potent immunotherapy platforms, and targeted delivery of gene therapies.
Comprehensive Quality Control (QC)
Rigorous, multi-faceted analytical testing is the cornerstone of our development process. We provide a full suite of characterization services to ensure every formulation meets stringent quality criteria for consistency, stability, and performance. To meet diverse project needs, we support the delivery of final formulations as either ready-to-use liquid suspensions or as lyophilized powders for enhanced long-term stability. Below are the standard specifications for our custom-developed delivery systems.
| Item | Method | Liposomes | LNPs | Exosomes | Polymeric Nanoparticles | Nanoemulsions | Hydrogels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Visual Inspection | Clear to Opalescent Liquid | Clear to Opalescent Liquid | Clear Liquid | Clear to Opalescent Liquid | White, Milky Emulsion | Clear to Opaque Gel |
| Particle Size | Dynamic light scattering (DLS) | 100 - 200 nm | 80 - 150 nm | 50 - 150 nm | 100 - 300 nm | 100 - 500 nm | N/A |
| Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Dynamic light scattering (DLS) | < 0.25 | < 0.2 | < 0.3 | < 0.3 | < 0.3 | N/A |
| Zeta Potential | Dynamic light scattering (DLS) | Formulation Dependent | |||||
| Encapsulation Efficiency |
UV-Vis/ HPLC/ RiboGreen |
Formulation Dependent | |||||
| Note | All items are fully customizable, and additional characterization assays (e.g., pH, TEM/Cryo-TEM, Endotoxin, RNA Integrity, Protein Content, Rheology, Viscosity, Bacteria) are available upon request to meet your specific project requirements. | ||||||
Workflow
Case Studies
Case Study 1: High-Quality Liposome Formulation for AAV Delivery
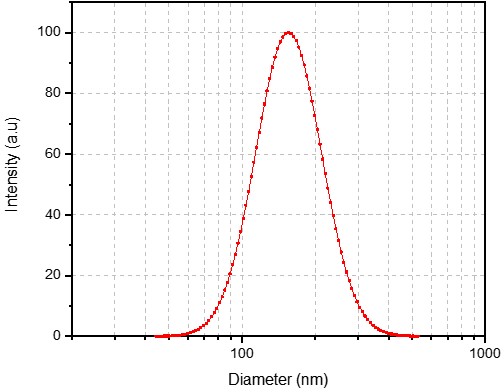
We meticulously developed a custom liposome formulation, optimizing the lipid composition and manufacturing process to be fully compatible with the client's specified buffer. The final liposome product demonstrated exceptional quality, with uniform particle size, a low PDI, and a consistent zeta potential, providing a stable and reliable vehicle for their AAV gene therapy research.
- Size: 155.23 nm
- PDI: 0.102
- Zeta Potential: 28.63 mV
Case Study 2: Spleen-Targeting mRNA-LNP Based on Published Formulation
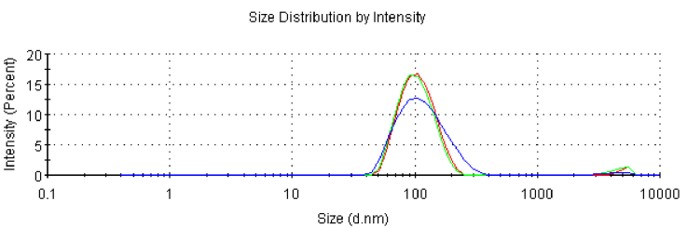
Leveraging our deep expertise in lipid nanoparticle assembly, we precisely replicated the literature-specified formulation, ensuring all lipid ratios and process parameters were matched. We successfully prepared the mRNA-LNP, which met all key analytical specifications, enabling the client to validate the published findings and advance their in vivo studies.
- Size: 105.5 nm
- PDI: 0.173
- Zeta Potential: -9.51 mV
- Encapsulation Efficiency: 91.6%
Case Study 3: Versatile NTA(Ni)-Liposome for Targeted Delivery Platforms
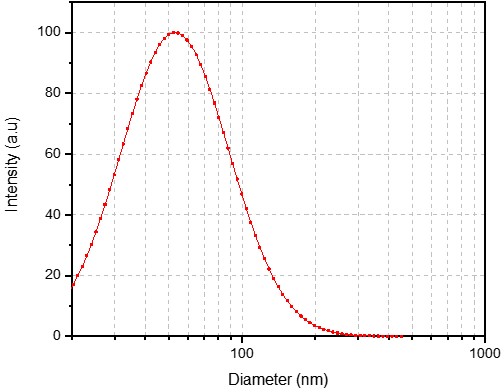
We successfully developed a stable and highly functional NTA(Ni)-Liposome formulation, which allows for the simple and efficient coupling of HIS-tagged ligands to the liposome surface. This provided the client with a versatile platform technology, significantly accelerating their research by allowing them to screen multiple targeting molecules using a single, validated liposomal carrier.
- Size: 54.54 nm
- PDI: 0.220
- Zeta Potential: -43.32 mV
Case Study 4: High-Potency Irinotecan Liposome Formulation
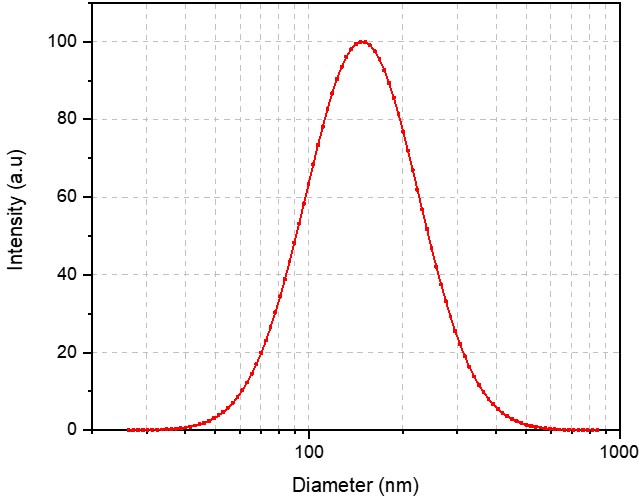
Using advanced loading techniques, we optimized the process to actively load and stably retain Irinotecan within the aqueous core of the liposomes. We successfully prepared a high-drug-load Irinotecan Liposome with excellent encapsulation efficiency, providing a potent formulation for their pre-clinical oncology pipeline.
- Size: 139.22 nm
- PDI: 0.168
- Zeta Potential: -15.3 mV
- Encapsulation Efficiency: 67.99%
Case Study 5: Liposome-in-Hydrogel System for Sustained Release
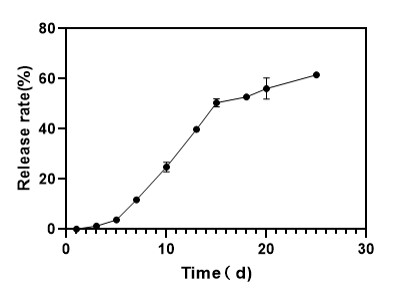
We first successfully engineered the complex protein-conjugated, drug-loaded liposomes. Subsequently, we incorporated these bespoke liposomes into an injectable hydrogel, creating an advanced dual-delivery system. The final liposome-in-hydrogel formulation acted as a depot, significantly extending the drug release rate and meeting the client's critical goal for a long-acting, localized therapeutic.
Applications in Modern Research
Our module systems are designed to unlock possibilities across a wide spectrum of biomedical research and therapeutic development.
- Oncology: Targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics, immunotherapies, or gene-silencing agents directly to tumor cells, sparing healthy tissue.
- Gene Therapy & Gene Editing: Safe and efficient delivery of nucleic acids like mRNA, siRNA, and RNA-guided gene editing systems components for treating genetic disorders.
- Vaccine Development: Advanced formulation of mRNA and protein subunit antigens for next-generation prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines.
- Immunology: Precise modulation of immune responses by targeting specific immune cell populations (e.g., T cells, macrophages).
- Neurological Disorders: Development of novel systems engineered to cross the blood-brain barrier for treating CNS diseases.
- Personalized Medicine: Creating patient-specific delivery vehicles for highly tailored treatment regimens.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?

- Deep Modular Expertise: Our focus is exclusively on the rational design and engineering of modular delivery systems, giving us an unparalleled depth of knowledge.
- Payload-Agnostic Platforms: We have successfully formulated a vast array of molecules, from delicate nucleic acids and proteins to hydrophobic small molecules and complex protein degraders.
- Collaborative Project Management: Every custom project is assigned a dedicated Ph.D.-level project manager to ensure clear communication, scientific rigor, and on-time delivery.
- State-of-the-Art Characterization: We utilize a comprehensive suite of advanced analytical instruments to provide you with a complete, publication-ready data package.
- Commitment to Quality & Confidentiality: We operate under rigorous quality standards and guarantee the full confidentiality of your proprietary materials and project details.
From intricate target engagement to formidable biological barriers, we provide the advanced delivery solutions necessary to unlock the full potential of your therapeutic candidates. Contact our scientific team to discuss your project and discover how Creative Biolabs' Module Delivery Systems can drive your research forward.
Related Services
FAQs
What is the typical timeline for a custom formulation project?
A typical project, from initial consultation to delivery of the characterized formulation, ranges from 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the system and the scope of analytical work required.
What information do I need to provide to get started?
To provide an accurate proposal, we need to know about your payload (type, size, charge), the biological target (cell type, tissue), and your primary research objectives.
Can you work with a proprietary payload or targeting ligand?
Absolutely. We operate under strict confidentiality and routinely execute Confidential Disclosure Agreements (CDAs) to protect our clients' intellectual property.
What is the main difference between a liposome and an LNP?
While both are lipid-based, liposomes typically have an aqueous core suitable for hydrophilic drugs and a bilayer for hydrophobic drugs. LNPs have a dense, solid lipid core, making them exceptionally well-suited for encapsulating and protecting nucleic acids.
Do you offer GMP manufacturing?
Our services are focused on providing high-quality materials for research and pre-clinical development. For clinical advancement, we ensure a seamless and efficient technology transfer to a qualified GMP manufacturing partner, bridging the critical gap between development and commercialization.
How do I choose the right delivery system for my payload?
Our seasoned scientists will work collaboratively with you to perform a rigorous, data-driven selection process, ensuring the optimal platform is chosen to meet your specific project goals. The best choice depends on your payload's properties, the biological target, the desired release profile, and the intended route of administration.