Development and Evaluation of Targeting-CDCP1 ADCs
CDCP1
CUB-domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1) is a cell surface glycoprotein that is elevated in a range of malignancies and mediates oncogenic processes promoting cancer cell survival, growth, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Increasing preclinical research suggests that CDCP1 could be targeted for delivering imaging and cytotoxic substances to detect and treat cancers with high levels of this receptor in a personalized manner. To support clinical research, it is necessary to further evaluate the in vivo and in vitro efficacy of targeting CDCP1 ADCs to understand their efficacy and safety in clinical applications.
Preparation of ch10D7-AMME
In the study, the antibody, the linker, and the drug are human/mouse chimeric anti-CDCP1 antibody (ch10D7), MC-vc-PAB-NH2, and monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE).
Firstly, the inter-chain disulfides of the antibodies are partially reduced using DTT to generate free thiols, which are then reacted with an excess of maleimide-activated MC-VC-PAB-MMAE in 10% DSMO at 37°C for 2 hours. Any impurities from the reaction are removed by filtering through ultra-centrifugal filters. The drug-antibody ratio (DAR) of the purified MMAE-labeled antibodies is determined to be 4.5 to 4.7 through reverse phase LC/MS analysis of the separated light and heavy chains. Finally, the ch10D7-AMME is purified and concentrated, then stored at -80 °C.
Our ready-to-use MC-VC-PAB-MMAE ADCsL
| CAT | Product name | ADC Target |
|---|---|---|
| ADC-W-2513 | Anti-SDC1 (Indatuximab)-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC | SDC1 |
| ADC-W-827 | Anti-CD38 (Daratumumab)-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC | CD38 |
| ADC-W-2592 | Anti-EGFR (Cetuximab)-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC | EGFR |
| ADC-W-2551 | Anti-CD74-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC | CD74 |
| ADC-W-2524 | Anti-CD22 (Inotuzumab)-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC | CD22 |
| ADC-W-1559 | Anti-MS4A1 (Ublituximab)-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC | MS4A1 |
| ADC-W-2477 | Anti-CD3E (Otelixizumab)-MC-Vc-PAB-MMAE ADC (ADC-W-2477) | CD3E |
ch10D7-AMME Characterization
The study indicates the characterization of ch10D7-MMAE in five aspects, including DAR analysis by RP-HPLC, antibody affinity studies by SPR spectroscopy, in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo efficacy, and ch10D7 accumulates in xenograft tumors in vivo.
Antibody Affinity Assay
ch10D7-MMAE has the same affinity for CDCP1-ECD in comparison with ch10D7 binding affinity to CDCP1-ECD, indicating that antibody affinity is unaffected by the MMAE payload.
Cytotoxicity Assay
- Nine different cell lines are chosen to test the cytotoxicity of 10D7-MMAE by assessing cellular metabolism and examining the ability of cells to form colonies after treatment (Fig. 1B, C). The results reveal that ch10D7-MMAE reduced the viability of the nine cell lines by at least 50%, indicating that it has the same potency as 10D7-MMAE. Additionally, both ch10D7-MMAE and 10D7-MMAE effectively inhibit colony formation in all nine cell lines.
- The study further analyzes the level of a protein called cell surface CDCP1 in 49 cell lines derived from various types of adenocarcinomas, including kidney, lung, colorectal, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) (Fig. 1D). The results of flow cytometry analysis reveal a wide range of cell surface CDCP1 levels across the different cancer cell lines, which indicates that higher ch10D7-MMAE efficacy correlates with higher cell surface levels of CDCP1.
- Of note, some cell lines with high levels of anti-CDCP1 antibodies bound/cell, such as kidney cancer A498, 786-O, and ACHN cells, didn't respond to ch10D7-MMAE treatment, suggesting that these cells have a mechanism to evade the cytotoxicity of the ADC.
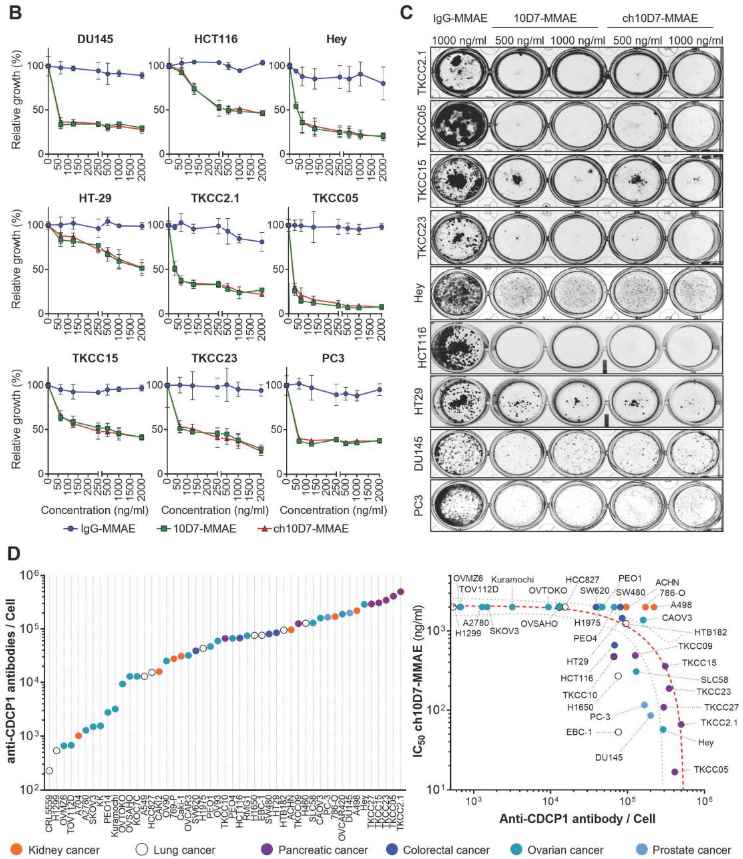 Fig. 1. In vitro cytotoxicity of anti-CDCP1 ADCs.1
Fig. 1. In vitro cytotoxicity of anti-CDCP1 ADCs.1
ch10D7 Accumulates in Xenograft Tumors In Vivo
- ch10D7 antibodies are combined with deferoxamine (DFO) and labeled with 89Zr (Fig. 2A). The labeled antibodies are then injected into mice that have been implanted with PDAC TKCC2.1 cells, which have elevated levels of CDCP1 on their cell surface. PET/CT imaging is then conducted to visualize the subcutaneous pancreatic tumors in the mice after the administration of the radiolabeled antibodies.
- PET/CT imaging performed 24, 48, 72, and 144 h later demonstrates that ch10D7-89Zr accumulated in tumors within 24 h. Quantitative biodistribution analysis of recovered organs indicates that ch10D7 can direct payloads to tumor tissues in vivo ( Fig. 2B, C).
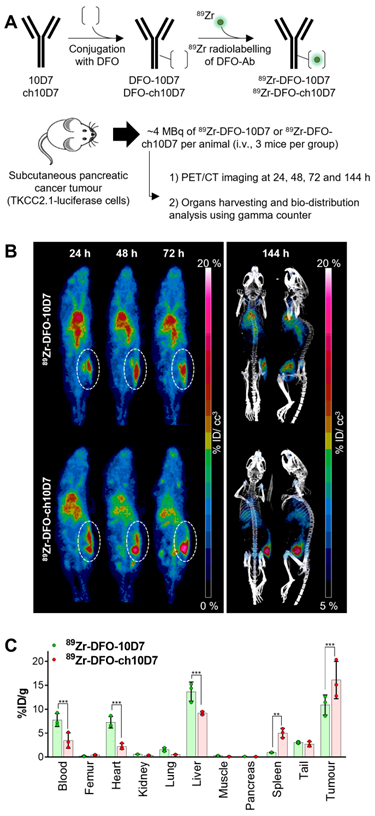 Fig. 2. Anti-CDCP1 antibody ch10D7 accumulates in CDCP1 expressing cancer tissues in vivo.1
Fig. 2. Anti-CDCP1 antibody ch10D7 accumulates in CDCP1 expressing cancer tissues in vivo.1
In Vivo Efficacy
The efficacy of ch10D7-MMAE targeting CDCP1 is evaluated in different mouse models of cancer, suggesting that the ch10D7-MMAE ADC is effective against tumors that express CDCP1 at a level above a certain threshold and show responsiveness in vitro (Fig. 3).
- In subcutaneous xenograft models of pancreatic cancer, ch10D7-MMAE and 10D7-MMAE treatments significantly inhibit tumor growth compared to gemcitabine chemotherapy, while vehicle and IgG-MMAE show uncontrolled growth. Kaplan-Meier analysis reveals that mice treated with ch10D7-MMAE and 10D7-MMAE have median survival times of 53 and 50 days respectively, while gemcitabine-treated, IgG-MMAE, and vehicle-treated mice have median survivals of 39, 32, and 30 days respectively.
- Similar results are observed in mouse models of ovarian and colorectal cancer. In ovarian cancer models, CDCP1-targeted ADCs effectively block tumor growth, while carboplatin chemotherapy has minimal impact on tumor growth. Median survival times are 60 and 59 days for ch10D7-MMAE and 10D7-MMAE-treated, while 35, 32, and 31 days for carboplatin-treated, IgG-MMAE-treated, and vehicle-treated, respectively.
- In colorectal cancer models, ch10D7-MMAE and 10D7-MMAE delay tumor re-growth, while 5-fluorouracil (5FU) chemotherapy marginally slows xenograft growth. Median survival is 46 days for ch10D7-MMAE and 10D7-MMAE-treated mice, and only 23 days for 5FU, IgG-MMAE, and vehicle-treated mice.
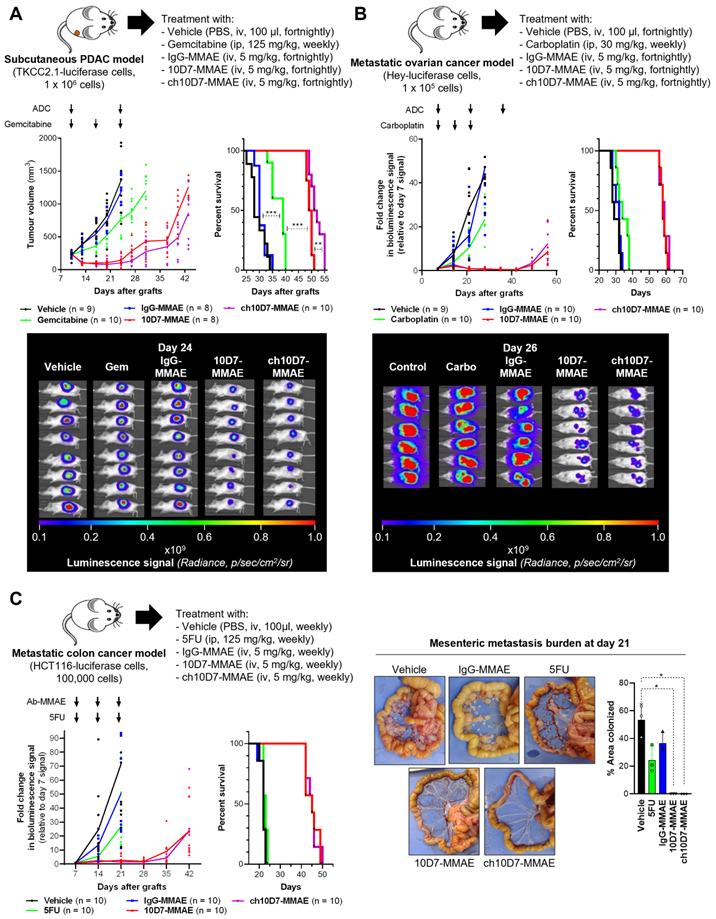 Fig. 3. Efficacy of ADC ch10D7-MMAE in in vivo cancer models.1
Fig. 3. Efficacy of ADC ch10D7-MMAE in in vivo cancer models.1
Creative Biolabs specializes in the development of ADC drugs. Our comprehensive in vivo assay and in vitro analysis help clients quickly obtain accurate drug potency data, laying the foundation for ADC candidates to enter the market.
Reference
- Khan, Tashbib, et al. "CUB Domain-Containing Protein 1 (CDCP1) is a rational target for the development of imaging tracers and antibody-drug conjugates for cancer detection and therapy." Theranostics 12.16 (2022): 6915.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Contact usUSA
Tel:
Fax:
Email:
Europe
Tel:
Email:
Germany
Tel:
Email:

