- Home
- UTC Development
- Antibody-Immunostimulant Conjugate Development
- Antibody-STING Agonist Conjugate Development
Antibody-STING Agonist Conjugate Development Service
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway agonism has emerged as a potential therapeutic mechanism to stimulate an innate anti-tumor immune response. While systemic administration of a STING agonist would have many therapeutic benefits, including the delivery of STING to all tumor lesions, such an approach may be limited by toxicity. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) constitute a proven therapeutic modality that is ideally suited to enable systemic administration without associated toxicity concerns via a targeted delivery strategy. Based on the well-established ADC development platforms, Creative Biolabs offers customized antibody-STING agonist conjugate development services to achieve your goals.
The Overview of STING and STING Agonist
STING is a signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in controlling the transcription of many host defense genes, including pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and type I interferons (IFNs). STING is located on the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with its C-terminal tail residing in the cell cytosol. In early studies, STING was observed to stimulate the transcription of innate immune genes in response to some invading bacteria, DNA viruses, or transfected DNA. Further investigation revealed that STING was strongly activated by cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs), such as cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) and cyclic di-AMP (c-di-AMP). Upon binding to CDNs, STING translocates from the ER to the Golgi apparatus and further to the perinuclear microsomes or punctuate structures, which in turn recruit the downstream TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), leading to induction of type I IFNs.
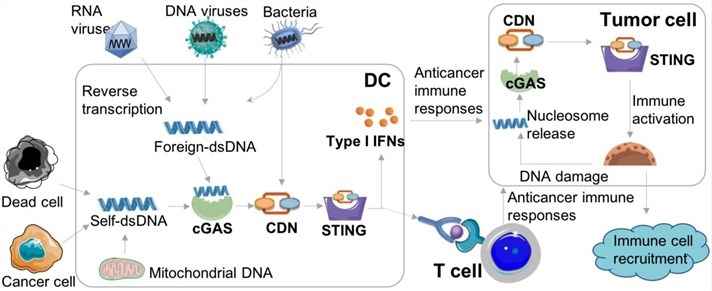 Fig.1 STING activation for cancer immunotherapy. (Su, 2019)
Fig.1 STING activation for cancer immunotherapy. (Su, 2019)
Insight into the roles of STING in immunomodulation indicated the potential of STING agonists as cancer therapeutics to activate antitumor immune responses. Small molecule STING-activating agonists have been long studied for the treatment of diseases, including cancer. For example, scientists reported the discovery of a small molecule STING agonist that is systemically efficacious to treat tumors in mice. They developed a linking strategy to synergize the effect of two symmetry-related amidobenzimidazole (ABZI)-based compounds to create linked ABZIs (diABZIs), which was empowered with enhanced STING binding affinity and strong antitumor activity. CDNs are another type of STING agonists. CDNs that are derived from bacteria might directly activate the STING signaling pathway. In mammalian cells, CDNs function as activators of the innate immune and adaptive responses.
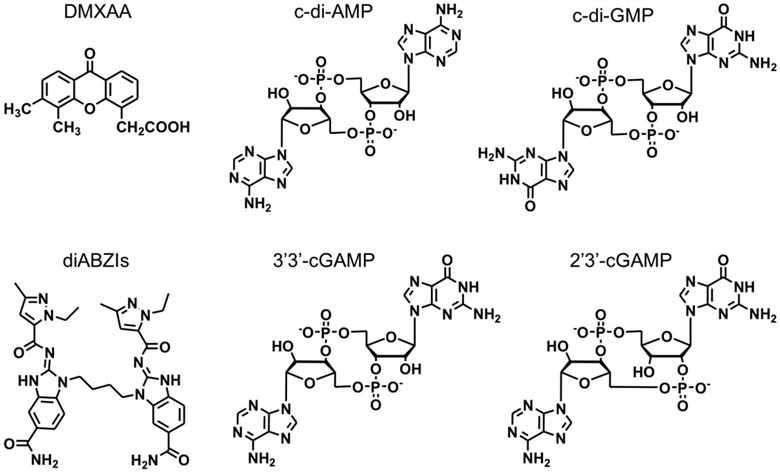 Fig.2 The chemical structures of representative STING agonists. (Su, 2019)
Fig.2 The chemical structures of representative STING agonists. (Su, 2019)
Antibody-STING Agonist Conjugates Development Service
Scientists at Creative Biolabs have explored a rational combination of STING agonists with antibodies for cancer immunotherapy. Antibody-STING agonist conjugate, in which a STING agonist is conjugated to an antibody, will overcome these limitations and exhibit several advantages, including:
- Active/Targeted-Delivery: By actively delivering STING agonists into the desired cell types in the tumor microenvironment (TME), ADCs overcome any solubility/permeability issues of the free agonist and achieve tumor specificity.
- Systemic Delivery: ADCs are administered systemically, and therefore are capable of carrying STING agonists to all tumor lesions.
- Improved Therapeutic Index: Targeted delivery increases tumor-specific immune activation and minimizes systemic inflammation.
- Enhanced Pharmacokinetic Properties: Significantly better pharmacokinetic properties of ADCs ensure increased exposure of tumors to the STING agonist.
Through the safe and efficient delivery of immunomodulatory molecules, antibody-STING agonist conjugates have the potential to address the challenges of systemic delivery and tolerability. Data from animal models show that antibody-STING agonist conjugate resulted in a greater than 100-fold increase in in vitro activity compared to a free agonist. In addition, treatment with antibody-STING agonist conjugate with a single dose resulted in complete regression of in vivo tumors. Increased immune cell infiltration and cytokine expression profile within the tumor was also observed after treatment, consistent with the activation of free STING.
As a well-recognized ADC development expert, Creative Biolabs offers a series of custom services and optimized strategies to generate high-quality antibody-STING agonist conjugates for global clients. If you’re interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Su, T.; et al. STING activation in cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics. 2019, 9(25), 7759.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
