- Home
- ADC Development
- ADC In Vitro Analysis
- 3D Cell Culture based In Vitro Evaluation
- ADC Solid Tumor Efficacy
ADC Solid Tumor Efficacy
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are designed to be transported to specific tumor sites and eliminate tumor cells for the treatment of cancers. Generally, the cancer killing effect of an ADC can be divided into two parts, namely the direct killing effect and the bystander killing effect. ADCs internalized by their targeted cancer cells will release the toxic payloads intracellularly, disrupting the cellular activity and hence killing the targeted cancer cells. This is known as the direct killing process. While for some ADCs, they also kill the antigen-negative cells in tumor tissues adjacent to the targeted cancer cells via the bystander killing effect. To gain a more accurate evaluation of the cancer-killing efficiency of an ADC product, both direct killing and bystander killing effects should be analyzed. The conventional cytotoxicity analysis using two-dimensional (2D) cell culture models has been widely used as the indicator of the ADC cancer-killing efficacy. Usually, ADCs are introduced to the in vitro cell culture environment and incubated with the 2D cancer cell monolayers for a certain period of time. The cell viability of cell mono-layers is then measured via diverse assay methods including a series of tetrazolium reduction assays, resazurin reduction assay, protease viability marker assay, ATP assay, and the recently developed real-time assay. Cytotoxicity analysis of ADCs using in vitro 2D models has been considering as one necessary analysis for the primary assessment of ADC efficacy. However, due to the lack of cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, cancer cells in 2D monolayers may have different growth and activity patterns compared with those growing in vivo in three dimensions. Therefore, the response of cancer monolayers to ADCs may be different from that of the cancer cells in vivo, which leads to an inaccurate evaluation of the cancer killing efficiency of ADCs. Besides, the accuracy of bystander killing evaluation is even poorer by using 2D cell culture models.
With the fast development of biotechnology, three-dimensional (3D) cell culture models are established to mimic the in vivo tumor microenvironment. With the spatial structure, as well as the cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions retained, 3D cell culture models grow cell in a much similar pattern to those in vivo. Therefore, compared to 2D culture models, cancer cells in 3D culture models respond to ADCs in a much more similar way as those in vivo. Besides the direct killing, many ADCs are also able to kill the antigen-free tumor cells adjacent to targeted cancer cells through diverse mechanisms, including the leakage of released toxins from targeted cells to their adjacent cells and the activation of specific intercellular and intracellular signaling pathways that results in cell apoptosis/death. 3D cell culture models with their ability to mimic cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions are desired approaches for the in vitro analysis of ADC bystander killing efficiency. Due to better mimicking of in vivo conditions, 3D cell culture models can provide more accurate assessment of the ADC cancer killing efficiency. Moreover, in vitro 3D models are excellent supplementations for animal models. By using human originated cancer cell lines, the established 3D models can overcome the species differences between human beings and lab animals. The well-established 3D cell viability assay protocols enable the simple and fast evaluation of the ADC cancer killing efficiency including both direct killing and bystander killing effects.
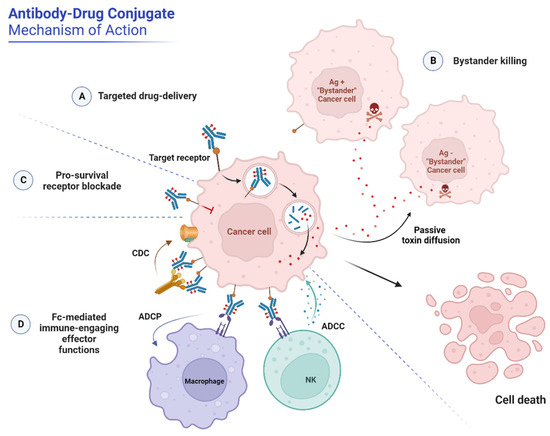 Fig.1 The mechanism of action of ADCs.1,2
Fig.1 The mechanism of action of ADCs.1,2
With diverse well-established in vitro cell culture models and our highly innovated 3D cell culture platform, Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive analysis of the ADC cancer killing efficacy using both 2D and 3D cell culture models. Our 2D targeted cell culture and mixed cell co-culture models offer primary indications of the ADC cytotoxicity induced by direct and by stander killing. While, 3D cell/tissue culture models at Creative Biolabs further assess the ADC toxicity with higher accuracy. Besides the pre-established in vitro models, our scientific team at Creative Biolabs can also help customers to establish specific tumor tissues for even more accurate evaluation of their custom ADC products. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References
- Metrangolo, Virginia, and Lars H. Engelholm. "Antibody–Drug Conjugates: The Dynamic Evolution from Conventional to Next-Generation Constructs." Cancers 16.2 (2024): 447.
- Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
