- Home
- Resources
- Knowledge Center
- Literatures
- Characterization of Ring-Opening Reaction of Succinimide Linker in ADCs Based on Imaging Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (iCIEF)
Characterization of Ring-Opening Reaction of Succinimide Linker in ADCs Based on Imaging Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (iCIEF)
Why Characterization of Ring-Opening Reaction of Succinimide Linker in ADCs is Needed?
The structure of an ADC comprises a mAb, a chemical linker, and a cytotoxic drug. Among the three key components of an ADC, the chemical linker plays a pivotal role in product stability and biological activity. While various chemical reactions can be applied to conjugate linker drugs to a mAb, thiol-maleimide chemistry through Michael addition is commonly used to covalently attach linker drugs to exposed sulfhydryl groups in cysteine (Cys) residues on the mAb. However, the resulting succinimide ring in the linker is susceptible to ring-opening reactions via hydrolysis, especially at high pH and elevated temperatures. Once the succinimide ring is opened, the in vivo stability of the ADCs can be altered, subsequently affecting their therapeutic activity. Theconjugation-site dependent stability of interchain-cysteine ADCs has not been extensively not reported. Therefore, there is an imperative need to develop a method to monitor ring-opening reactions in interchain-cysteine ADCs and assess the impact of conjugation sites on ADC stability.
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive one-stop ADC development services tailored to your specific requirements. We have successfully established an ADC platform of conjugation based on inter-chain cysteines. With a deep understanding of thiol conjugation chemistry, Creative Biolabs is proficient in generating highly customized ADCs efficiently and within a reasonable timeframe.
Model Antibody-Drug Conjugates (TDC and ADC)
In this study, the TDC was constructed by conjugating the maleimidocaproyl valine-citrulline para-aminobenzyl carbamate linker and monomethyl auristatin E drug onto THIOMAB™. Cysteine residues were engineered in HC (A114C) of a human IgG1 antibody. The DAR of the TDC is 2. The ADC used was created by partially reducting of interchain disulfides, followed by the same conjugation process as that of the TDC. The average DAR of the ADC is 3.41. The unconjugated antibody for the ADC is referred to as the standard mAb in this study.
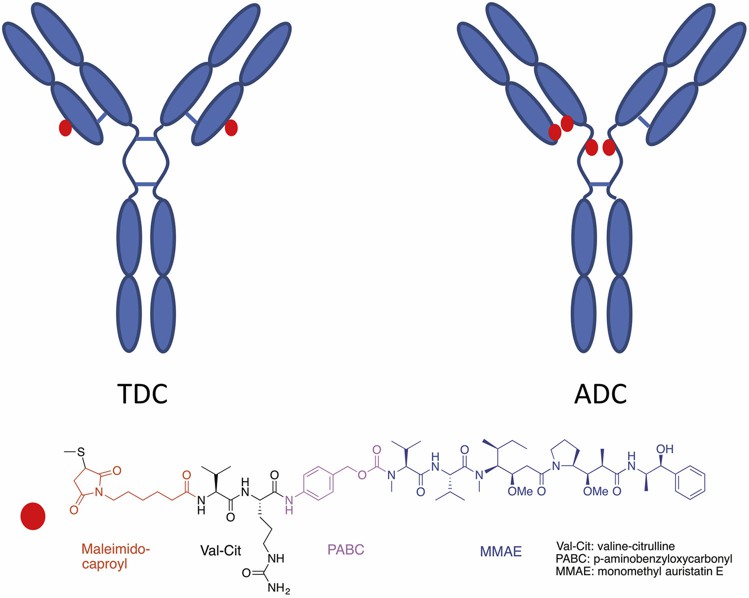 Fig. 1. Structures of TDC and interchain-cysteine ADC. Red dots represent linker drugs (Zheng K, et al., 2019)
Fig. 1. Structures of TDC and interchain-cysteine ADC. Red dots represent linker drugs (Zheng K, et al., 2019)
The study assessed the ring-opening reactions of a TDC and an interchain-cysteine ADC under stress conditions (pH 7.0-9.0 at 40°C for up to 48 hours). Their corresponding unconjugated mAbs were stored under the same conditions side by side to serve as study controls. A new methodology based on imaged capillary isoelectric focusing (iCIEF) technology was described to quantify charge increases caused by succinimide ring opening. Meanwhile, site-specific ring-opening reactions were monitored using a reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method.
Stability Study Protocol
THIOMAB™, TDC, standard mAb, and ADC at 2 mg/mL in buffers of 50 mM sodium phosphate at pH 7.0 and 8.0, and 50 mM sodium bicarbonate at pH 9.0 were studied to assess ring-opening reactions under various pH conditions.
iCIEF Analysis
iCIEF was used to monitor the progress of ring-opening in the TDC and ADC. The analysis by iCIEF was carried out using an ICE-280 instrument.
- All samples were buffer-exchanged into 20 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid at pH 7.0.
- The buffer-exchanged samples were diluted to a final concentration of 0.25 mg/mL in a solution containing 2.5 M urea, 3% carrier ampholytes (70% Pharmalytes [GE Healthcare] pH 8-10.5, 30% Pharmalytes pH 5-8), 0.35% methylcellulose, 0.88% 1 N HCl, and pI markers.
- The THIOMAB™ samples were treated with a 10% cysteine/cystine (10 mM/40 mM) redox pair and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours before buffer exchange.
- The sample-ampholyte mixture was introduced into the capillary under pressure and then focused at 1500 V for 1 minute followed by 8 minutes at 3000 V, during which a charge-coupled device camera captured an image of the entire capillary illuminated by a 280 nm light source. The software iCE CFR v42 was used to convert the image into an electropherogram showing absorbance as a function of the position in the capillary or of pI based on standards.
RP-HPLC Analysis With Ultraviolet and MS Detection
- RP-HPLC used to quantify the level of ring-opening reactions of succinimide linkers at different conjugation sites.
The RP-HPLC analysis was carried out using an Agilent 1200 binary pump system. Samples were diluted to approximately 1 mg/mL using a solution of 6 M guanidine hydrochloride, 360 mM Tris, and 2 mM ethylene-diamine-tetraacetic acid at pH 8.6. Subsequently, 50 μL of each diluted sample was reduced with 5 μL of 1 M dithiothreitol at 37°C for 1 hour. The reduced samples (approximately 10 μg) were then subjected to RP-HPLC analysis employing a Pursuit diphenyl column (Agilent A3041250X020, 200 Å, 250 × 2.0 mm) with a gradient elution. Mobile phase A consisted of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in water, while mobile phase B contained 0.08% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile. The gradient involved an initial 1-minute wash with 37% mobile phase B, followed by a linear gradient from 37% to 47% mobile phase B over 52 minutes, succeeded by another linear gradient from 47% to 95% mobile phase B over 7 minutes. The mobile phase was held at 95% mobile phase B for 5 minutes for column cleaning to wash the column, and then gradually returnedto 37% mobile phase B for reequilibration prior to the subsequentsample injection. The column temperature was maintained at 75°C, and the mobile phase flow rate was set at 0.2 mL/min. The eluted compounds were detectedusing ultraviolet at a wavelength of 280 nm.
- LC-MS analysis performed for peak identification and quantitation of the ring-opened species.
Each reduced sample (approximately 10 μg) was injected onto the Pursuit diphenyl column connected to an AB SCIEX Triple TOF 5600 mass spectrometer equipped with a Turbo Spray ionization source (AB SCIEX, Framingham, MA). The declustering potential was adjusted to 70 V, and the spray voltage was set at 2300 V. The source temperature was maintained at 350°C. Other parameters were optimized to maximize signal intensity and resolution. The instrument was externally calibrated over an m/z range of 800-3000 amu using cesium tridecafluoroheptanoate. Mass spectra were generated through the deconvolution of multiple charged ions using the Analyst TF 1.5.1 software package (AB SCIEX).
Experimental data confirmed the capability of iCIEFto successfully monitor the formation of succinimide ring-opening products, and it was determined that succinimide ring-opening rates in ADCs are dependent on the conjugation site. With a comprehensive understanding of the impact of the conjugation site on the final product's stability, it becomes potentially feasible to modify ring-opening rates in vitro to achieve the desired in vivo stability and biological activity.
Based on mature LC-MS, high-performance HPLC techniques, and state-of-the-art facilities, Creative Biolabs can accurately quantify and characterize the drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) of conjugated drugs, expediting the research process of candidate drugs.
Reference
- Zheng K, Chen Y, Wang J, et al. Characterization of Ring-Opening Reaction of Succinimide Linkers in ADCs. J Pharm Sci. 2019 Jan;108(1):133-141.
Related Service
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
