IgG Fc
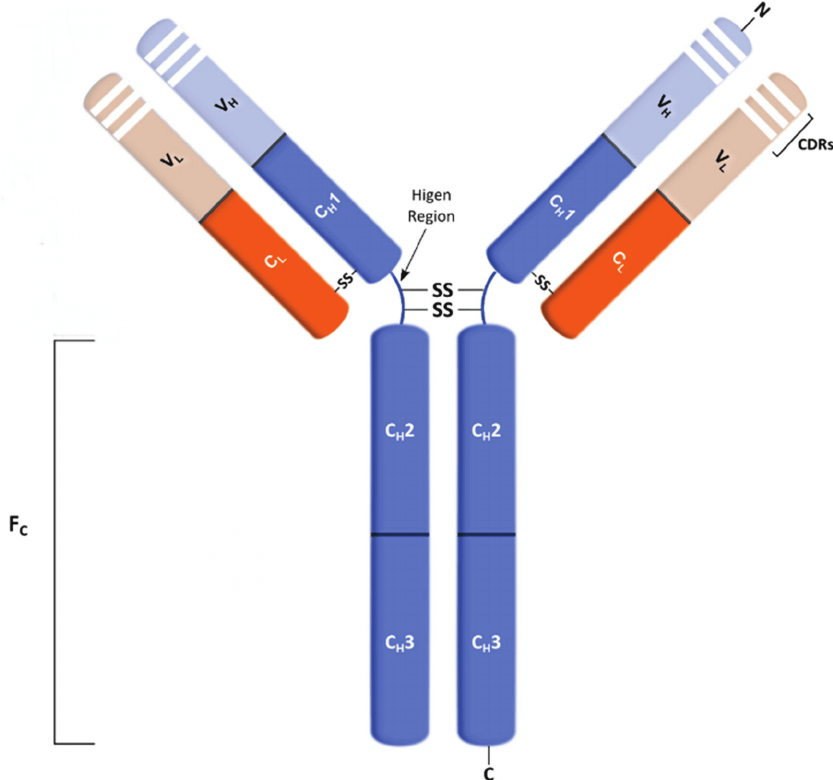 Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most abundant type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid and protects body from various bacterial and viral infections by binding those pathogens. IgG antibody is a 150 kDa tetrameric quaternary structure which contains two identical class γ heavy chains of about 50 kDa and two identical light chains of about 25 kDa. The two heavy chains are linked to each other and to a light chain each by disulfide bonds, resulting in a Y-like shape. The fragment crystallizable region (Fc region) is composed of the constant region of the two heavy chains that form the IgG molecule. The Fc region of IgG contains a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. Fc binds to various cell receptors and complement proteins thus mediating different physiological effects of antibodies, such as opsonization, antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), degranulation of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and other processes.
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most abundant type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid and protects body from various bacterial and viral infections by binding those pathogens. IgG antibody is a 150 kDa tetrameric quaternary structure which contains two identical class γ heavy chains of about 50 kDa and two identical light chains of about 25 kDa. The two heavy chains are linked to each other and to a light chain each by disulfide bonds, resulting in a Y-like shape. The fragment crystallizable region (Fc region) is composed of the constant region of the two heavy chains that form the IgG molecule. The Fc region of IgG contains a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. Fc binds to various cell receptors and complement proteins thus mediating different physiological effects of antibodies, such as opsonization, antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), degranulation of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and other processes.
If you can’t find your product on this list? Please directly send email to .
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.
Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
