
Transcriptome-wide coverage of glycoRNA species
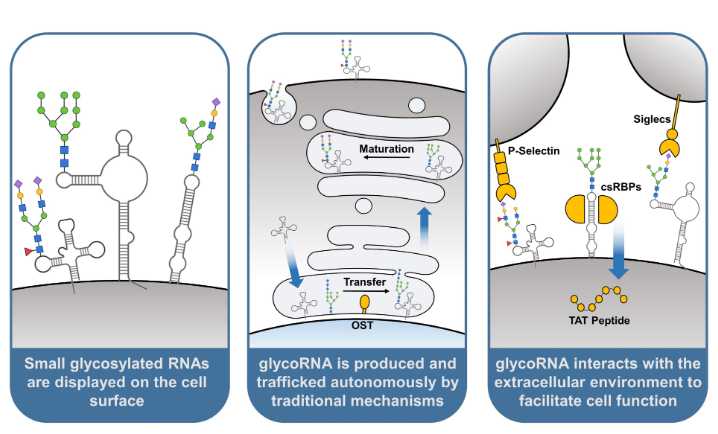 Fig.1 GlycoRNA Trafficking & Function.1,4
Fig.1 GlycoRNA Trafficking & Function.1,4
GlycoRNAs are RNA molecules covalently modified with N-linked glycans, previously thought to decorate only proteins and lipids. These RNAs—predominantly small noncoding types such as Y RNAs, tRNAs, and vault RNAs—carry sialylated and fucosylated glycans, localize to the cell surface, and participate in cell–cell signaling, immune regulation, and tumor microenvironment remodeling. They are synthesized via an atypical pathway involving RNA-specific glycosylation enzymes such as GALNTs, sialyltransferases, and DTWD2. GlycoRNAs may traverse through Golgi/ER-associated vesicular pathways or leverage RNA-binding protein (RBP)–mediated shuttling, ultimately appearing on the plasma membrane.
Currently, the known types of glycosylated non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) include small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), transfer RNAs (tRNAs), Y-RNAs, and microRNAs (miRNAs). Notably, glycosylated messenger RNAs (mRNAs) have not been identified, indicating a unique role for these modifications in non-coding RNAs rather than coding RNAs. Below, we detail the key types of GlycoRNAs:
Involved in RNA splicing, glycosylation can fine-tune their interaction with spliceosomal proteins, thereby affecting splicing efficiency.
Glycans attached to rRNAs can influence ribosome structure, stability, and the cell's response to stress.
Modifications on snoRNAs may regulate their role in rRNA maturation and ribosome biogenesis.
Glycosylation impacts tRNA folding, amino acid binding, and safeguards against degradation.
Glycans alter their stability, interaction with protein complexes, and involvement in gene silencing or DNA replication.
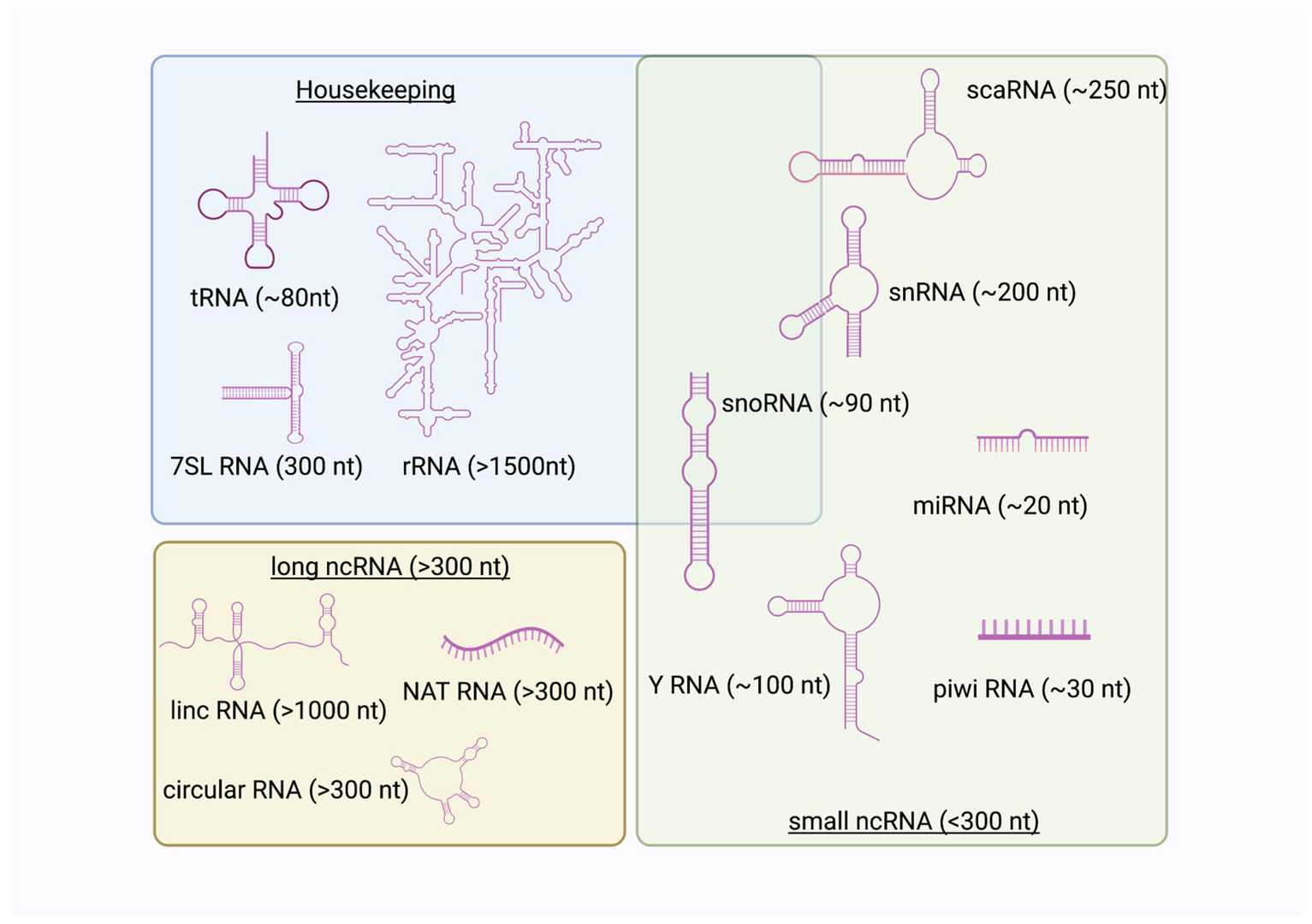 Fig.2 Three
types of non-coding RNAs.2,4
Fig.2 Three
types of non-coding RNAs.2,4
| Service Type | Description |
|---|---|
| GlycoRNA Profiling Service | High-throughput sequencing and novel subtype discovery |
| GlycoRNA Functional Analysis | Assessment of glycoRNA-mediated signaling, immune evasion, or translation impact |
| GlycoRNA Imaging Service | Spatial visualization of glycoRNAs using FRET imaging |
Whether investigating glycoRNAs in cancer biology, autoimmunity, or infection, our team delivers tailored strategies with scientific rigor and technical precision.
Creative Biolabs integrates cutting-edge transcriptomics, click chemistry, and imaging platforms to provide:

Transcriptome-wide coverage of glycoRNA species

Single-cell resolution imaging of glycoRNA spatial distribution

Validated quantification of glycosylation sites

Functional assays to decode biological consequences
GlycoRNAs offer a unique vantage point for exploring disease-specific regulatory mechanisms. Recent studies have revealed that their surface localization and interactions with Siglec receptors, lectins, and glycan-binding proteins confer them significant roles across disease categories. Below, we categorize the relevance of glycoRNAs by pathological context:
Trusted by Scientists Worldwide


To streamline your glycoRNA project, please prepare and submit samples according to the table below. For customized protocols or uncommon sample types, contact our technical support team.
| Sample Parameter | Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Type | Cells, total RNA, tissue (frozen/fixed) | Avoid protease-based dissociation for surface glycoRNAs |
| Cell Number | ≥ 1 × 10⁷ cells | Suspension or adherent lines; growth log recommended |
| Total RNA | ≥ 5 μg; OD260/280 1.8–2.0 | TRIzol, column, or phenol-chloroform extraction |
| Tissue | ≥ 30 mg or 1 section (10 μm) | Snap-frozen or OCT-embedded; avoid paraffin |
| RNA Quality | RIN ≥ 7.0 | Required for sequencing; optional for imaging |
| Preservative-free | No RNAlater, heparin, or detergents | These inhibit click chemistry or enzymatic steps |
Using a novel glycoRNA imaging technique, researchers visualized U1, Y5, and SNORD35a glycoRNAs in:
The inverse relationship between glycoRNA abundance and tumor aggressiveness indicates potential for glycoRNA-based diagnostics.
Upon LPS stimulation, glycoRNA levels (U1, Y5) significantly increased in macrophages. Conversely, neutrophil maturation decreased glycoRNA signal. RNase treatment of immune cells impaired endothelial adhesion, supporting a functional role in immune cell–vascular interactions.
Fc/Fab glycosylation profiling, sialylation analysis
Monoclonal Antibody Glycosylation Analysis Polyclonal Antibody Glycosylation Analysis Fab Glycosylation Analysis Fc Glycosylation AnalysisGlycosphingolipid, glycoglycerolipids and more types of glycolipids characterization
Glycosphingolipids Analysis Glycoglycerolipids Analysis Lipopolysaccharide Analysis Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Anchor AnalysisAt Creative Biolabs, we use a three-tier validation strategy to ensure specificity and eliminate false positives:
This combination gives us high confidence in the biological authenticity of the glycoRNAs detected.
Yes. Our glycoRNA-seq pipeline allows transcriptome-wide discovery of both annotated and novel glycoRNA species. Common glycosylated RNA classes include:
Yes. In fact, our FRET-based glycoRNA profiling has already demonstrated potential for cancer diagnostics. With our help, you can define signature glycoRNA panels for biomarker development in oncology, immunology, or inflammation research.
References: