GlycoRNA Profiling Service
Glycosylation is a key change that happens to molecules after they are made. It affects how biomolecules act. We know a lot about it in proteins and lipids. But now, we've found something new: glycosylated RNAs, or glycoRNAs. These RNAs have sugar chains (glycans) attached. They play important roles in how cells talk to each other, how the immune system works, and even in diseases like cancer. As more scientists study glycoRNAs, the need for good glycoRNAs analysis service grows. At Creative Biolabs, our glycoRNA profiling service is here to help. We use advanced methods and work with you to fit your needs, whether you're doing research or working on preclinical projects.
What Are GlycoRNAs?
GlycoRNAs are RNA molecules with sugar (glycan) changes. Think of sialic acid, GlcNAc, or mannose attached to RNA. Enzymes add these sugars, changing how the RNA folds, how stable it is, and how it interacts with other molecules—just like how sugars affect proteins.
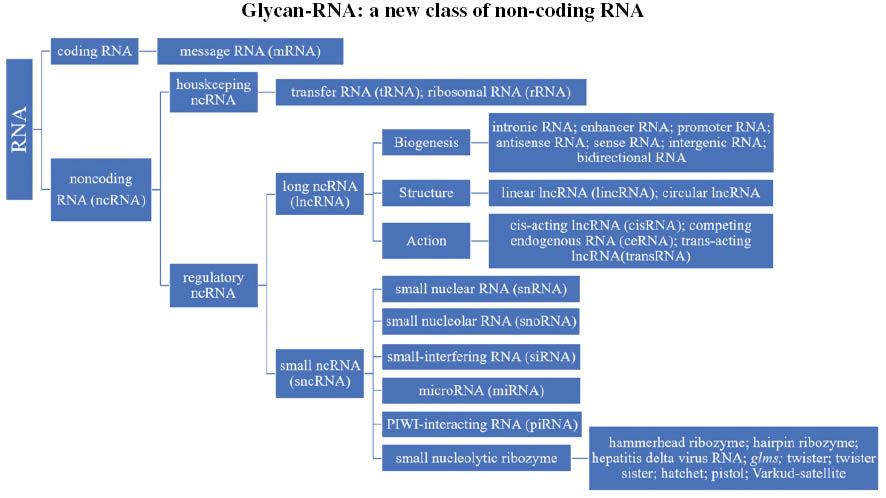 Fig.1 Classification of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).1
Fig.1 Classification of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).1
Types of GlycoRNAs
Most glycoRNAs are small non-coding RNAs:
- snRNAs: Help with RNA splicing. Sugars may change how they work with other molecules in this process.
- rRNAs: Part of ribosomes. Sugars can affect ribosome structure and how they work under stress.
- snoRNAs: Modify other RNAs. Sugars here might control how rRNAs mature.
- tRNAs: Carry amino acids. Sugars can protect them from breaking down and help them bind amino acids.
- Y-RNAs and miRNAs: Sugars change their stability and how they regulate gene expression.
These sugar changes matter in immune cell adhesion, inflammation, and disease. That's why profiling them is so important.
How We Profile GlycoRNAs: Our Workflow
Profiling glycoRNAs needs careful steps to check both the RNA and the sugars. Here's how we do it:
1. Sample Collection and Prep
We take samples from cells, tissues, or biofluids like serum or plasma. Using gentle methods (like TRIzol or column purification), we make sure the glycoRNAs stay intact and free from dirt.
2. Metabolic Labeling
We use sugars with azide tags (e.g., Ac4ManNAz). Cells take these sugars in when making glycans. This tags the sugar part of glycoRNAs, so we can find them later with click chemistry or biotin.
3. Enrichment: Focus on GlycoRNAs
Lectin beads or streptavidin beads catch the labeled glycoRNAs. This separates them from non-glycosylated RNAs, so we only look at the ones with sugar changes.
4. Detection Methods
We use several tools to study glycoRNAs:
- Northern Blotting: Separates RNAs by size and detects them with biotin probes.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): Shows sugar types, chain length, and structure. Great for small or rare samples.
- Flow Cytometry/FRET Imaging: Shows where glycoRNAs are in cells and how they interact with receptors (e.g., Siglec-5), especially on extracellular vesicles (EVs).
5. Data Analysis and Reports
We use algorithms (like PCA) to find patterns in glycoRNA expression. You'll get detailed reports with types of glycoRNAs, their modifications, and what they mean for your research—whether you're finding biomarkers or studying how they work.
Key Techniques We Use
Metabolic Labeling with Click Chemistry
This method is specific for sugars. Azide-tagged sugars mark glycoRNAs as they're made. Click reactions (e.g., with DBCO probes) let us see or purify them, so we only analyze glycosylated RNAs.
Mass Spectrometry for Sugar Details
MS is key for understanding glycan changes:
- Identify sugar types (sialic acid, GlcNAc, mannose).
- See how long and branched the sugar chains are.
- Tell the difference between glycoforms (e.g., high-mannose vs. complex glycans).
Our MS tools handle tiny samples, perfect for rare biological materials.
Imaging to See Cellular Interactions
FRET imaging and flow cytometry show glycoRNA locations and interactions in real time. For example, we can see them on EVs, which is important for studying cancer and immune responses.
Where Our Service Helps
Inflammatory Disease Research
glycoRNAs on immune cells bind to receptors like P-selectin, helping cells stick to inflamed areas. Profiling them can find new targets for treating diseases like atherosclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Cancer Diagnostics
Tumor EVs have unique glycoRNA patterns. Our service can detect these with high sensitivity:
- Breast cancer: Higher U1, U3, U35a glycoRNAs (89% accuracy).
- Pancreatic cancer: More Y5 glycoRNA (90% sensitivity).
- Lung cancer: Higher glycoRNA-L in EVs (95% specificity).
- Colorectal cancer: More U8 glycoRNA in EVs (91% accuracy).
This supports liquid biopsy development for non-invasive cancer screening.
Therapeutic Targeting
GlycoRNAs in immune modulation are great targets for drugs. Profiling can help find which ones to target for treating inflammation, autoimmune diseases, or cancer.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
Our service has key advantages:
- We have expert team who know both glycobiology and RNA biology, ensuring good experiment design and data analysis.
- We are equipped with state-of-the-art MS, FRET imaging, and metabolic labeling for precise results.
- We tailor workflows for your sample type (cells, tissues, biofluids) and goal (research, biomarkers, drugs).
- Strict checks at every step for reproducible, publishable data.
- Efficient workflows for timely results, even for urgent projects.
Challenges and Future
While glycoRNA research is exciting, there are challenges:
- Technical Difficulty: Sugar diversity and RNA instability need specialized methods—we have the expertise to handle this.
- Standardization: We work on best practices for sample prep and analysis to ensure consistency.
- Clinical Use: Our services support moving from research to real-world diagnostics and treatments.
In the future, combining glycoRNA profiling with proteomics or metabolomics will give a fuller picture of diseases. We're ready to lead in this area.
GlycoRNAs are a new frontier in understanding cell communication and disease. Analyzing them needs knowledge of both RNA and sugars—something Creative Biolabs specializes in. Our glycoRNA profiling service gives you the tools to study their roles in health and disease, from basic research to clinical use. We're here to help. With advanced tech, custom solutions, and a focus on quality, we make glycoRNA profiling accessible and effective. Contact us today to see how we can support your glycoRNA research or applications. Let's explore this new frontier together.
References:
- Li, Xiuling, et al. "Glycan-RNA: a new class of non-coding RNA." BIO Integration 3.3 (2022): 124. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.15212/bioi-2021-0032
- Ren, Tingju, et al. "FRET imaging of glycoRNA on small extracellular vesicles enabling sensitive cancer diagnostics." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 3391. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58490-2
- Li, Luoyi, et al. "Protocol for detecting glycoRNAs using metabolic labeling and northwestern blot." STAR protocols 5.4 (2024): 103321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xpro.2024.103321