Understanding Glycosylation: The Key to Protein Functionality
Understanding Glycosylation
Glycosylation Definition
Glycosylation is the enzymatic process by which glycans are covalently linked to proteins or lipids, modifying their biochemical and functional properties. This modification occurs through specific enzymes, known as glycosyltransferases, that mediate glycan attachment at conserved motifs on proteins. Glycosylation can occur during or after translation and is highly site- and structure-specific. Glycosylation refers to the attachment of glycans (sugar molecules) to proteins, lipids, or other molecules. This modification can affect a wide range of biological processes, from protein folding to cell recognition. For a thorough analysis of glycosylation, Creative Biolabs offers a variety of services designed to help researchers and developers gain a deeper understanding of glycosylation's impact on protein functionality.
Where Does Glycosylation Occur and Types of Protein Glycosylation
| Glycosylation Type | Primary Location | Cellular Compartment |
|---|---|---|
| N-linked | ER → Golgi apparatus | Lumen of ER and cis-, medial-, trans-Golgi |
| O-linked | Golgi apparatus | Mainly Golgi (post-translational) |
| C-linked | ER | Cytoplasmic side of the ER membrane |
| GPI-anchor | ER | ER membrane and Golgi |
| O-GlcNAc | Cytoplasm and nucleus | Nucleocytoplasmic |
What Does Glycosylation Mean for Biotherapeutics?
Glycosylation is vital in biologics:
- Glycosylation impacts immunogenicity.
- Batch-to-batch consistency depends on glycoform monitoring.
- Biosimilar approval often hinges on glycan comparability.
In biotherapeutics, glycosylation is essential for determining the stability, efficacy, and immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins, particularly monoclonal antibodies. The glycosylation patterns of antibodies can influence their interactions with Fc receptors, which is important for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), phagocytosis, and complement activation. Moreover, glycosylation impacts the half-life of therapeutic proteins. The presence of certain glycan structures can extend the circulation time of these proteins in the bloodstream, improving their therapeutic efficacy. Creative Biolabs delivers custom glycosylation services and glycosylation analysis services for antibody drugs, proteins, lipids, RNA, and more, supporting your submissions and production.
- Antibody Glycosylation Analysis
- Protein Glycosylation Analysis
- Glycolipid Analysis
- GlycoRNA Analysis
Glycosylated Biomolecules: Molecular Diversity Beyond Proteins
Glycosylation is not confined to proteins alone. In fact, the attachment of glycans occurs across a wide spectrum of biomolecules, shaping their structure, function, and biological roles. These glycosylated biomolecules—including antibodies, membrane proteins, lipids, and even RNA—form the molecular basis of cell recognition, immune modulation, and signal transduction.
Glycosylated Antibodies
Antibodies are critical players in the immune system, and their glycosylation patterns are vital to their function. The Fc region of antibodies, in particular, is heavily glycosylated, and this modification affects the antibody's interaction with Fc receptors, impacting immune effector functions like antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and phagocytosis. Variations in the glycosylation of monoclonal antibodies can be manipulated to enhance their therapeutic properties. Even subtle differences in glycan composition—such as fucosylation, sialylation, or galactosylation—can shift therapeutic potency. This makes glycosylation profiling essential in antibody drug development and comparability assessment. Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive solutions for analyzing antibody glycosylation, including:
- Monoclonal Antibody Glycosylation Analysis Service
- Polyclonal Antibody Glycosylation Analysis Service
- Fc Glycosylation Analysis Service.
- Fab Glycosylation Analysis Service
Glycosylated Proteins
Proteins are often glycosylated in both the secretory pathway and cell membranes, influencing their folding, function, and interactions. Glycosylation can alter the activity of enzymes, receptors, and structural proteins, which in turn impacts various cellular functions, including signaling, adhesion, and immune responses. Examples include:
- Erythropoietin (EPO): N-linked glycans enhance stability and serum half-life
- Mucins: Heavily O-glycosylated, contributing to mucosal barrier and hydration
- Receptors (e.g., EGFR): Glycans regulate ligand binding and endocytosis
To analyze glycosylation on proteins, Creative Biolabs provides the following services:
Glycolipids
Glycolipids are lipids with attached carbohydrate chains and are essential components of cellular membranes. Glycosphingolipids and gangliosides are glycans attached to lipid moieties, predominantly expressed on the outer leaflet of plasma membranes. They play crucial roles in:
- Cell–cell adhesion and communication
- Immune cell activation
- Pathogen recognition (e.g., influenza and HIV entry)
- Tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACAs)
Notable examples include:
- GM1, GM2, GM3: Brain-expressed gangliosides associated with neurodevelopment
- Globo H, SSEA-3/4: Cancer biomarkers and targets for CAR-T therapies
To support your glycolipid analysis, Creative Biolabs offers services such as:
- Glycosphingolipids Analysis Service
- Glycoglycerolipids Analysis Service
- Lipopolysaccharide Analysis Service
- Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Anchor Analysis Service.
GlycoRNA
Glycosylation is also found in RNA molecules, particularly in their 3' and 5' ends. Although in early stages, GlycoRNA challenges the long-held assumption that glycosylation is exclusive to proteins and lipids, suggesting RNA as a new substrate for glycobiology. For in-depth studies on glycoRNA, Creative Biolabs provides specialized glycoRNA analysis services such as:
Glycosylation is a critical modification that influences the functionality of proteins, lipids, and RNA molecules. Its role in biotherapeutics is profound, impacting the design, efficacy, and safety of protein-based drugs. As research continues to uncover the complexities of glycosylation, these insights are being harnessed to improve drug development, diagnostic tools, and personalized medicine. At Creative Biolabs, we are at the forefront of these advancements, providing cutting-edge services in glycosylation analysis for a wide range of biomolecules. For more details, explore our services or contact us for personalized assistance in your glycosylation studies.
Published Data
A recent review on the role of glycosylation in extracellular vesicles (EVs) found that the glycosylation status of EV proteins can significantly influence their biological functions, such as immune modulation, cell-cell interactions, and disease progression. The study highlights the distribution of urinary EVs and the glycosylation patterns of proteins associated with bladder cancer, prostate cancer, and kidney diseases. Another important finding relates to the glycosylation of N-linked glycoproteins in EVs. In bladder cancer, the glycosylation profile of EVs differs significantly from those of healthy individuals, with the presence of high-mannose and complex-type glycans playing a crucial role in tumor progression and metastasis. Additionally, the overexpression of glycosyltransferases like FUT8 in prostate cancer has been shown to alter the glycosylation of EVs, affecting their release and interactions with other cells.
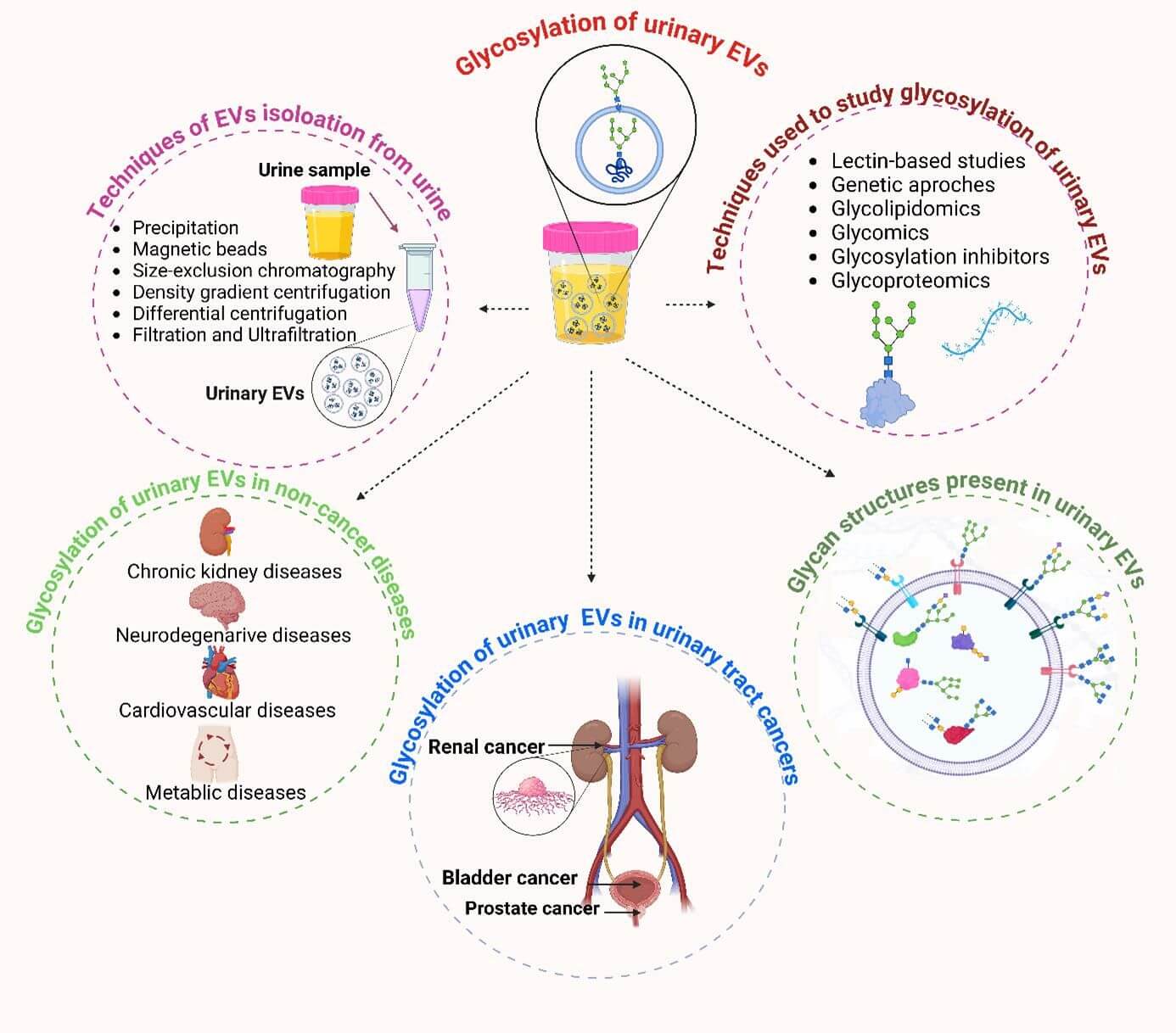 Fig.1 Glycosylation in EVs.1
Fig.1 Glycosylation in EVs.1
Reference:
- Wilczak, Magdalena, Magdalena Surman, and Małgorzata Przybyło. "Towards understanding the role of the glycosylation of proteins present in extracellular vesicles in urinary tract diseases: contributions to cancer and beyond." Molecules 29.22 (2024): 5241. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225241
Related Services
- Antibody Glycosylation Analysis
- Protein Glycosylation Analysis
- Glycolipid Analysis
- GlycoRNA Analysis
