GlycoRNA-seq: High-Throughput Sequencing of Glycosylated RNAs
The discovery that small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs) can be post-transcriptionally modified with glycans reshaped our understanding of RNA biology. GlycoRNAs (including miRNAs, tRNAs, rRNAs, YRNAs, snRNAs, and snoRNAs), first reported by Flynn, are small RNAs bearing complex N-glycans, particularly enriched in sialic acid and fucose residues. Found prominently on cell surfaces, these structures interact with Siglec receptors, implicating them in immune modulation. Traditional RNA-seq fails to capture this vital layer of information. At Creative Biolabs, we offer a dedicated glycoRNA-seq for high-throughput sequencing of glycoRNAs service, specifically optimized to enrich, sequence, and comprehensively characterize these uniquely glycosylated RNAs. Whether you're exploring surface RNA biology, immune interactions, or disease-associated glycoRNA patterns, our platform delivers unparalleled sensitivity and specificity to uncover the insights traditional RNA profiling misses. We also provide advanced glycoRNA analysis technologies—from custom enrichment workflows to glycan structure elucidation—supporting full-spectrum glycoRNA research with flexible, expert-driven solutions.
What is GlycoRNA-seq?
GlycoRNA-seq is a tailored sequencing approach for identifying, enriching, and characterizing glycosylated RNAs at a high resolution. Unlike traditional RNA-seq, which captures total RNA populations indiscriminately, glycoRNA-seq specifically enriches for RNAs conjugated to glycans, providing insights into their structure, abundance, and biological roles. GlycoRNA-seq is suitable for:
- Differential abundance and distribution of glycoRNAs across tissues and species.
- Mapping interactions with proteins (e.g., Siglecs) and investigating roles in immune modulation.
- Identification of disease-associated glycoRNAs for autoimmune conditions and cancers.
- Screening compounds that modulate glycoRNA expression or modification patterns.
Comparison Between GlycoRNA-seq and Conventional RNA-seq
| GlycoRNA-seq | Traditional RNA-seq | |
|---|---|---|
| Target Molecule | Glycosylated small noncoding RNAs | mRNAs and total noncoding RNAs |
| Enrichment Method | Metabolic labeling (Ac4ManNAz), rPAL chemical tagging | PolyA selection or total RNA extraction |
| Detection Scope | Low-abundance glycosylated RNAs, with site information | Abundant RNAs without glycosylation detail |
| Application Focus | Cell-surface interaction, immune regulation studies | Gene expression profiling, transcriptomics |
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to advancing glycoRNA research by offering a suite of specialized services tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients. To provide detailed insights into glycoRNA structures, functions, and spatial distributions, we provide comprehensive solutions that include but are not limited to:
GlycoRNA Functional Analysis Service
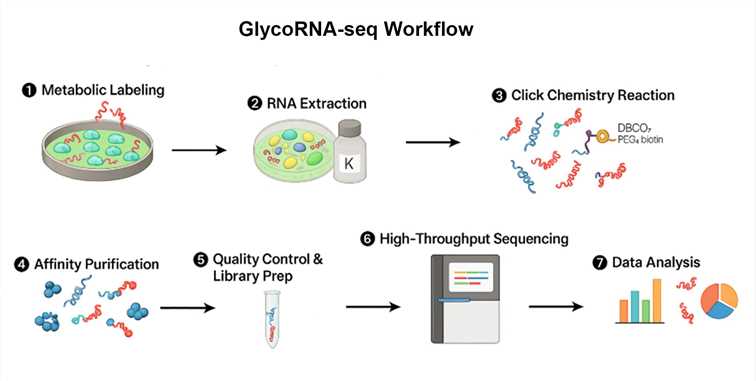
How Does GlycoRNA-seq Work?
GlycoRNA-seq integrates two distinct biochemical strategies for glycoRNA labeling and enrichment:
Ac4ManNAz Metabolic Labeling
- Cells are cultured with Ac4ManNAz (an azide-modified mannose analog), integrating azide groups into sialic acid moieties of glycoRNAs.
- After Trizol extraction, high-concentration proteinase K digestion, and RNA purification, azide-tagged RNAs undergo a click chemistry reaction with DBCO-PEG4-biotin.
- Biotinylated glycoRNAs are isolated using streptavidin magnetic beads, enriching glycoRNA for downstream high-throughput sequencing.
rPAL (RNA Periodate Oxidation and Labeling)
- Extracted RNAs undergo mild periodate oxidation, targeting sialic acid diols to generate aldehydes.
- Aldehydes react with biotinylated amines, selectively tagging glycoRNAs.
- Biotin-tagged glycoRNAs are affinity-purified using streptavidin beads for sequencing.
Glycosylation Detection and Validation Strategies
| Step | Method/Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Labeling and Enrichment | Ac4ManNAz Click Chemistry / rPAL | Selective glycoRNA enrichment |
| Sequencing | High-throughput platforms | Generating massive short-read data |
| Alignment | STAR, Bowtie | Mapping reads to reference genomes |
| Modification Site Detection | Sequence motif search and manual curation | Identifying glycosylation sites |
| Glycan Structure Elucidation | LC-MS/MS, MALDI-TOF | Confirming glycan type and structure |
Step-by-Step Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
- Cells treated with Ac4ManNAz or prepared for rPAL labeling.
2. RNA Extraction
- Trizol lysis, proteinase K digestion, silica column purification.
3. Labeling and Enrichment
- Ac4ManNAz: Click chemistry → Biotinylation → Streptavidin pull-down.
- rPAL: Periodate oxidation → Aldehyde–amine coupling → Biotin pull-down.
4. QC and Library Construction
- GlycoRNA QC followed by library construction for sequencing.
5. Sequencing
- Utilizing high-throughput sequencing platforms.
6. Bioinformatics Analysis
- sncRNA profiling, glycosylation site mapping, differential expression analysis.
Types of Data Provided
GlycoRNA-seq yields comprehensive datasets including:
- GlycoRNA Species and Quantification
- GlycoRNA Sequence Characteristics (e.g., length distributions)
- Glycosylation Patterns: Type and structure of attached glycans
- Differential Expression across different biological conditions
- Predicted Functional Interactions: Based on GO and KEGG pathway analyses
Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Quantity Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Ac4ManNAz-labeled Cells | ≥3 × 10⁶ cells | Cultured with Ac4ManNAz for 48 h |
| Total RNA | ≥25 μg | RIN ≥6, extracted from treated or untreated cells |
Samples must be stored at -80°C and transported on dry ice to preserve integrity.
Technical Advantages
- Ultra-High Sensitivity: Detects extremely low-abundance glycoRNAs.
- Multidimensional Analysis: Captures miRNAs, tRNA fragments (tsRNAs), rRNA fragments (rsRNAs), YRNAs, and snoRNAs.
- Multi-Omics Integration: Combines with mass spectrometry for glycan structure analysis.
- High Specificity: Effective removal of non-glycosylated RNAs.
- Flexible Applications: Compatible with both Ac4ManNAz and rPAL strategies.
Applications in Research
| Research Focus | Application Details |
|---|---|
| GlycoRNA Atlas | Profiling glycoRNA across species, tissues, cell types |
| Mechanistic Studies | Deciphering glycoRNA biogenesis, transport, and molecular interactions |
| Disease Biomarker Discovery | Identifying disease-specific glycoRNA signatures |
| Drug Development | Screening compounds influencing glycoRNA expression and modification |
Clier-seq: A Specialized GlycoRNA Detection Platform
Clier-seq extends glycoRNA-seq by using highly efficient click-chemistry and streamlined enrichment steps. Covering RNA sizes from 50-2000 nt, Clier-seq identifies both canonical and novel glycoRNAs including tRNA, vtRNA, and lncRNA-derived species. When combined with Clier-qPCR, Clier-seq provides orthogonal validation, ensuring low false-positive rates. It can be applied in:
- Detection of glycoRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and B lymphoma cells
- Discovery of novel glycoRNA subtypes
- Elucidation of glycoRNA roles in disease pathogenesis
GlycoRNA-seq offers an unprecedented window into the glycosylation landscape of RNA. By combining chemical biology, high-throughput sequencing, and glycomics, it enables systematic exploration of glycoRNAs across biology and disease. This powerful platform positions glycoRNA research at the interface of RNA biology, immunology, and therapeutic innovation. At Creative Biolabs, we provide expert glycoRNA detection, enrichment, sequencing, and bioinformatics analysis services. Partner with us to uncover the hidden sugar code of RNAs and unlock new opportunities for scientific discovery.
FAQs
Can RNA Be Glycosylated?
The unequivocal answer is yes. Flynn et al. demonstrated that:
- Glycans are covalently linked to conserved small noncoding RNAs.
- These glycans are composed predominantly of sialic acid and fucose residues.
- The glycosylation process depends on canonical N-glycan biosynthetic enzymes.
What labeling and enrichment strategies do you use for glycoRNA capture?
We offer two complementary labeling methods:
-
Ac4ManNAz-based metabolic labeling and click chemistry (Clier-seq compatible):
- Incorporates azide groups into sialic acid residues of glycoRNAs.
- Bioorthogonal click reaction with DBCO-biotin enables highly specific affinity purification using streptavidin beads.
-
rPAL (RNA Periodate-Assisted Labeling):
- Mild periodate oxidation of terminal sialic acid residues to generate aldehydes.
- Subsequent conjugation with aminooxy-biotin facilitates glycoRNA enrichment without prior metabolic labeling.
Both methods ensure high specificity for glycosylated RNAs, minimizing contamination from non-glycosylated species.
What sequencing platforms and data outputs are included in your glycoRNA-seq service?
Bioinformatics pipelines are fully customizable based on client project needs. We leverage high-throughput sequencing platforms for maximal depth and quality. Standard deliverables include:
- Raw data: FASTQ files with high Phred quality scores.
-
Processed data:
- Read alignment (using STAR or Bowtie) to reference genome.
- Quantitative profiling of glycoRNA species.
- Size distribution and RNA biotype classification (e.g., YRNA, snRNA, snoRNA).
-
Differential analysis: (optional)
- Comparative analysis between conditions, highlighting glycoRNA expression differences.
- Glycan modification insights: (in combination with MS data, if applicable).
How do you ensure the specificity and accuracy of glycoRNA detection?
We adopt several strategies to maximize specificity:
- Stringent washing and elution during streptavidin bead purification to eliminate non-specifically bound RNAs.
- Negative controls, including samples without Ac4ManNAz labeling or samples treated with excess free biotin.
- Clier-qPCR validation ensures that identified glycoRNAs are true positives, ruling out artifacts.
- Sialidase digestion assay to verify that detected RNA species are sialylated, confirming authentic glycosylation.
Our dual-validation system (sequencing + biochemical) delivers industry-leading confidence in glycoRNA-seq results.
Reference:
- Caldwell, Reese M., and Ryan A. Flynn. "Discovering glycoRNA: Traditional and Non‐Canonical Approaches to Studying RNA Modifications." Israel Journal of Chemistry 63.1-2 (2023): e202200059. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijch.202200059