Antigen Microarray Detection Service for Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders
With advanced platforms and technologies, Creative Biolabs has developed many types of antigen microarrays that can track numerous types of proteins, enabling diagnostic and therapeutic studies on a variety of diseases. Our antigen microarray detection services for brain and central nervous system diseases can help you effectively detect autoantibodies related to neurological diseases, assisting with disease diagnosis and therapy.
Background
Overview of Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders Diagnosis
Neurodegenerative disorders (NDs) are characterized by a progressive loss of function of specific groups of neurons in different regions of the brain. The major disease groups are Alzheimer’s disease (AD), vascular dementia, Parkinson’s disease (PD), frontotemporal lobar degeneration, Lewy body dementia, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. These disorders are variably associated with dementia, personality changes, language abnormalities, or progressive muscle weakness. Because the greatest risk factor for NDs is age, these diseases are considered major health and quality of life problems in our aging society. Strategies to prevent or delay the accumulation of the protein aggregates associated with these diseases have been proposed, raising significant hope; but currently, there is no perspective cure or preventive treatment for the damage to the brain.
Neurodegenerative processes are initiated long before clinical symptoms become obvious and proceed for years in a slow and irreversible manner. Therefore, it is of paramount importance to diagnose NDs as early as possible and distinguish between different disorders, with complex and similar symptoms, which might require different treatments. Early diagnosis is also critical for enrollment in clinical trials concerning new therapeutics, before patients exhibit mild or moderate dementia, to identify and apply drugs with the best chance of preserving cognitive functions. The ability to identify subjects at high risk for incipient dementia, long before the onset of cognitive deficit, represents a major advance in the field of neurodegenerative dementia.
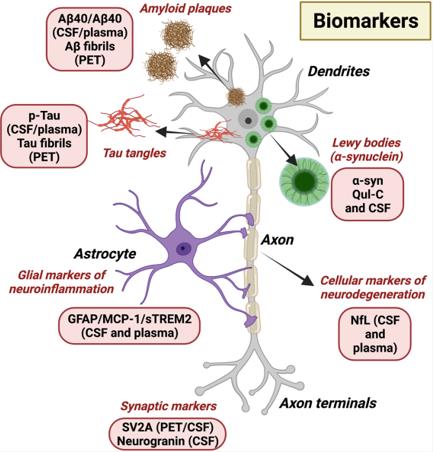 Fig.1 Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases.1
Fig.1 Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases.1
Application
Antigen Microarray in Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders Diagnosis
Previous research reported a microarray using a panel of 362 antigens (proteins of the central nervous system, lipid autoantigens, and heat-shock proteins) to characterize the patterns of antibody reactivity in 38 sera samples obtained from patients affected with multiple sclerosis (MS). Based on the results, researchers observed unique autoantibody patterns that distinguish secondary and primary progressive MS from healthy controls and other autoimmune or neurological diseases including AD. Small molecule microarrays have also been used to screen compounds that bind β-amyloid peptides to discover molecules to reduce β-amyloid peptide cytotoxicity. Novel compounds that interfere with β-amyloid aggregation represent a promising approach to the prevention and/or cure of AD. A range of intermediates along the aggregation pathway have been indicated as potential toxic species, but none of their precise structure is known, thus a structure-based design is not applicable in this context. In contrast, high-throughput screening using small molecule microarrays is a promising approach.
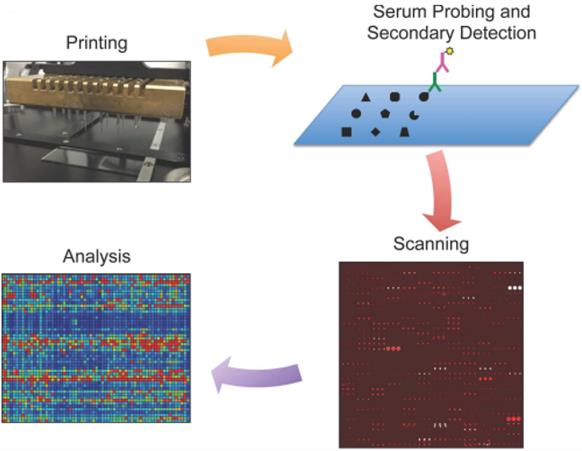 Fig.2 Schematic representation of protein microarrays used for autoantibody detection.2
Fig.2 Schematic representation of protein microarrays used for autoantibody detection.2
Sensitivity is an issue for the low concentration in the CSF of the known biomarkers β-amyloid (1-42), tau, and phosphotau. In addition, it is crucial to validate and introduce novel biomarkers in samples collected far from the brain (e.g., serum or plasma), where biomarkers will be even more diluted. Validating biomarkers in easily collectible samples (or diminishing the invasiveness of CSF collection) is therefore the only way for tests based on neurochemical biomarkers to become routinely administered. Nonetheless, the continuous advancement in microarray technology is crucial to provide clinicians with sensitive diagnostic tools as soon as biomarkers (in fluids different from CSF) for differentiate forms of dementia have been validated. Fluorescence microarrays perfectly comply with these requirements and will therefore assume increasing importance in the field.
Our Service
Services at Creative Biolabs
The roles autoantigens play in brain and central nervous system disorders have been reported in more and more studies. In the meanwhile, antigen microarray has shown great advantages in autoantigens detection. Utilize antigen microarray to help analyze brain and central nervous system disorders research is a trend with great potential. Creative Biolabs has been focusing on this field for years and has accumulated great experience. We have established a systematical technology platform with verified autoantigens related to nervous system diseases and are confident in offering customer-satisfied antigen microarray detection services to global clients.
Highlight
- Easy sample collection, collect samples away from the brain, making cerebrospinal fluid collection less invasive.
- Small volumes of fluid, making it possible to use tiny fluid volumes to analyze antibody reactivity against a wide variety of antigens.
- High sensitivity, greatly improved resolution.
FAQs
-
Q1: What is the basis for serum autoantibody signatures revealed by antigen microarray analysis of autoantibodies?
A: Rather than being based on single autoantibody reactivities, the signatures are based on collective autoantibody patterns. -
Q2: Is it personalized customer service?
A: We are focused on providing customized services to our clients. We will design detection plans according to your study requirements, including the selection of different analysis types and sample dilution ratios, etc.
Resource
If you are interested in our services or you have any other questions about antigen microarray detection, please don't hesitate to contact us for more information.
References
- Wareham, Lauren K., et al. "Solving neurodegeneration: Common mechanisms and strategies for new treatments." Molecular neurodegeneration 17.1 (2022): 23.
- Rosenberg, Jacob M., and Paul J. Utz. "Protein microarrays: a new tool for the study of autoantibodies in immunodeficiency." Frontiers in Immunology 6 (2015): 138.
Related Services:
- Autoantigens General Survey Detection
- Cancer and Neoplasms Detection
- Common Allergens Detection
- Autoimmunity, Allergy, and Infection Detection
- Coronavirus-Associated Autoimmunity Detection
- SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Detection

